Irodov Solutions: Motion of Charged Particles In Electric And Magnetic Fields- 2 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q. 389. A non-relativistic proton beam passes without deviation through the region of space where there are uniform transverse mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields with E = 120 kV/m and B = 50 mT. Then the beam strikes a grounded target. Find the force with which the beam acts on the target if the beam current is equal to I = 0.80 mA.
Solution. 389. In crossed field,
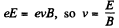
Then,F = force exerted on the plate 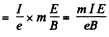
Q. 390. Non-relativistic protons move rectilinearly in the region of space where there are uniform mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields with E = 4.0 kV/m and B = 50 mT. The trajectory of the protons lies in the plane xz (Fig. 3.102) and forms an angle φ = 30° with the x axis. Find the pitch of the helical trajectory along which the protons will move after the electric field is switched off.
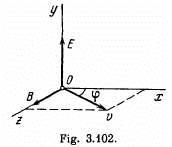
Solution. 390. When the electric field is switched off, the path followed by the particle will be helical, and pitch, 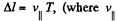 is the velocity of the particle, parallel to
is the velocity of the particle, parallel to 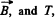 the time period of revolution.)
the time period of revolution.)
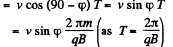 (1)
(1)
Now, when both the fields were present, 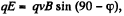 as no net force was effective
as no net force was effective
or, 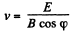 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2), 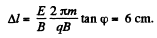
Q. 391. A beam of non-relativistic charged particles moves without deviation through the region of space A (Fig. 3.103) where there are transverse mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields with strength E and induction B. When the magnetic field is switched off, the trace of the beam on the screen S shifts by Δx. Knowing the distances a and b, find the specific charge q/m of the particles.
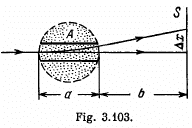
Solution. 391. When there is no deviation, 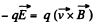
or, in scalar from,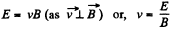 (1)
(1)
Now, when the magnetic field is switched on, let the deviation in the field be x. Then,
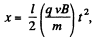
where t is the time required to pass through this region,
also, 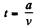
Thus 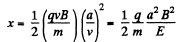 (2)
(2)
For the region where the field is absent, velocity in upward direction
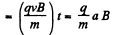 (3)
(3)
Now, 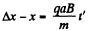
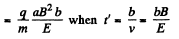 (4)
(4)
From (2) and (4),
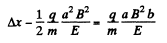
or, 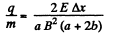
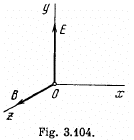
Q. 392. A particle with specific charge qim moves in the region of space where there are uniform mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields with strength E and induc- tion B (Fig. 3.104). At the moment t = 0 the particle was located at the point O and had zero velocity. For the non-relativistic case find:
(a) the law of motion x (t) and y (t) of the particle; the shape of the trajectory;
(b) the length of the segment of the trajectory between two nearest points at which the velocity of the particle turns into zero;
(c) the mean value of the particle's velocity vector projection on the x axis (the drift velocity).
Solution. 392. (a) The equation of motion is,
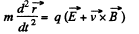
Now, 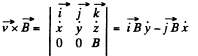
So, the equation becomes,
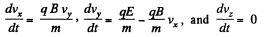
Here, 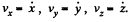 The last equation is easy to integrate;
The last equation is easy to integrate;
vz = constant = 0,
since vz is zero initially. Thus integrating again,
z = constant = 0,
and motion is confined to the x - y plane. We now multiply the second equation by i and add to the first equation.
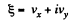
we get the equation,
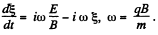
This equation after being multiplied by 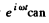 be rewritten as,
be rewritten as,
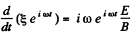
and integrated at once to give,
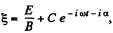
where C and α are two real constants. Taking real and imaginary parts.
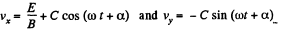
Since vy = 0, when t = 0, we can take α = 0, then vx = 0 at t = 0 gives, 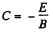 and we get,
and we get,
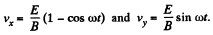
Integrating again and using x = y = 0, at t = 0, we get
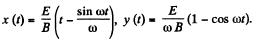
This is the equation of a cycloid.
(b) The velocity is zero, when ωt - 2nπ. We see that
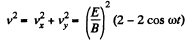
or, 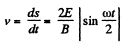
The quantity inside the modulus is positive for 0 < ωt < 2 π. Thus we can drop the modulus and write for the distance traversed between two successive zeroes of velocity.
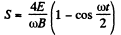
Putting 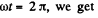
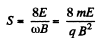
(c) The drift velocity is in the x-direction and has the magnitude,
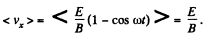
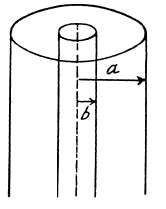
Q. 393. A system consists of a long cylindrical anode of radius a and a coaxial cylindrical cathode of radius b (b < a). A filament located along the axis of the system carries a heating current I producing a magnetic field in the surrounding space. Find the least potential difference between the cathode and anode at which the thermal electrons leaving the cathode without initial velocity start reaching the anode.
Solution. 393. When a current I flows along the a x is, a magnetic field 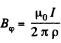 is set up where
is set up where 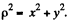 In terms of components,
In terms of components,
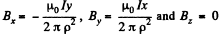
Suppose a p.d. V is set up between the inner cathode and the outer anode. This means a potential function of the form
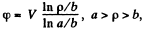
as one can check by solving Laplace equation. The electric field corresponding to this is,
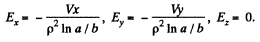
The equations of motion are,
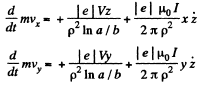
and 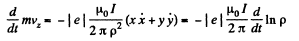
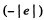 is the charge on the electron,
is the charge on the electron,
Integrating the last equation,
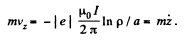
since vz = 0 where p = a. We now substitute this 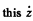 in the other two equations to get
in the other two equations to get
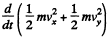
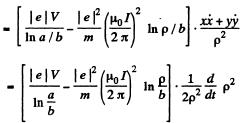
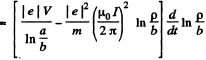
Integrating and using v2 = 0, at p = b, we get,
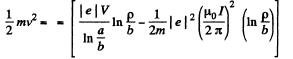
The RHS must be positive, for all a > p > b. The condition for this is,
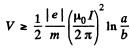
Q. 394. Magnetron is a device consisting of a filament of radius a and a coaxial cylindrical anode of radius b which are located in a uniform magnetic field parallel to the filament. An accelerating potential difference V is applied between the filament and the anode. Find the value of magnetic induction at which the electrons leaving the filament with zero velocity reach the anode.
Solution. 394. This differs from the previous problem in 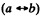 and the magnetic field is along the z-direction. Thus Bx = By = 0, Bz = B
and the magnetic field is along the z-direction. Thus Bx = By = 0, Bz = B
Assuming as usual the charge of the electron to be - | e |, w e write the equation of motion
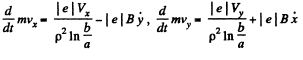
and 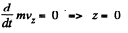
The motion is confined to the plane z = 0. Eliminating B from the first two equations,
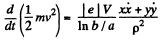
or, 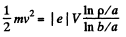
so, as expected, since magnetic forces do not work,
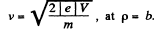
On the other hand, eliminating V, we also get,
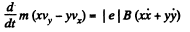
i.e. 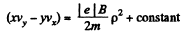
The constant is easily evaluated, since v is zero at p = a. Thus,
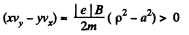
At 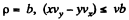
Thus, 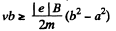
or, 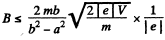
or, 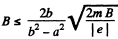
Q. 395. A charged particle with specific charge qim starts moving in the region of space where there are uniform mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. The magnetic field is constant and has an induction B while the strength of the electric field varies with time as E = Em cos ωt, where ω = qB/m. For the non-relativistic case find the law of motion x (t) and y (t) of the particle if at the moment t = 0 it was located at the point O (see Fig. 3.104). What is the approximate shape of the trajectory of the particle?

Solution. 395. The equations are as in Q.392.
with 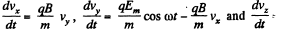
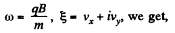
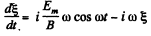
or multiplying by 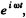
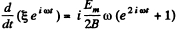
or integrating, 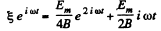
or, 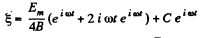
since 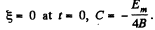
Thus, 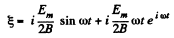
or, 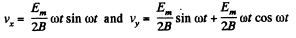
Integrating again,
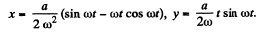
where 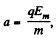 and we have used x = y = 0, at t = 0.
and we have used x = y = 0, at t = 0.
The trajectory is an unwinding spiral.
Q. 396. The cyclotron's oscillator frequency is equal to v = 10 MHz. Find the effective accelerating voltage applied across the dees of that cyclotron if the distance between the neighbouring trajectories of protons is not less than Δr = 1.0 cm, with the trajectory radius being equal to r = 0.5 m.
Solution. 396. We know that for a charged particle (proton) in a magnetic field,

But, 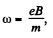
Thus 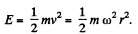
So, 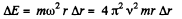
On the other hand ΔE = 2 eV, where V is the effective acceleration voltage, across the Dees, there being two crossings per revolution. So,
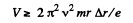
Q. 397. Protons are accelerated in a cyclotron so that the maximum curvature radius of their trajectory is equal to r = 50 cm. Find:
(a) the kinetic energy of the protons when the acceleration is completed if the magnetic induction in the cyclotron is B = 1.0 T;
(b) the minimum frequency of the cyclotron's oscillator at which the kinetic energy of the protons amounts to T = 20 MeV by the end of acceleration.
Solution. 397. 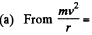 Bev, or, mv = Ber
Bev, or, mv = Ber
and 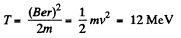
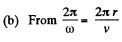
we get, 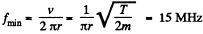
Q. 398. Singly charged ions He+ are accelerated in a cyclotron so that their maximum orbital radius is r = 60 cm. The frequency of a cyclotron's oscillator is equal to v = 10.0 MHz, the effective accelerating voltage across the dees is V = 50 kV. Neglecting the gap between the dees, find:
(a) the total time of acceleration of the ion;
(b) the approximate distance covered by the ion in the process of its acceleration.
Solution. 398. (a) The total time of acceleration is,
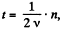
where n is the number of passages of the Dees.
But, 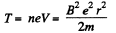
or, 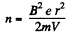
So, 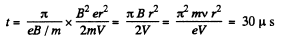
(b) The distance covered is, 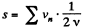
But, 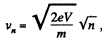
So, 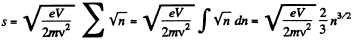
But, 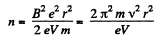
Thus, 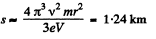
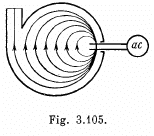
Q. 399. Since the period of revolution of electrons in a uniform magnetic field rapidly increases with the growth of energy, a cyclotron is unsuitable for their acceleration. This drawback is rectified in a microtron (Fig. 3.105) in which a change ΔT in the period of revolution of an electron is made multiple with the period of accelerating field T0. How many times has an electron to cross the accelerating gap of a microtron to acquire an energy W = 4.6 MeV if ΔT = T0, the magnetic induction is equal to B = 107 mT, and the frequency of accelerating field to v = 3000 MHz?
Solution. 399. In the nth orbit, 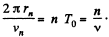 We ignore the rest mass of the electron and write
We ignore the rest mass of the electron and write
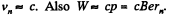
Thus, 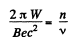
or, 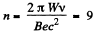
Q. 400. The ill effects associated with the variation of the period of revolution of the particle in a cyclotron due to the increase of its energy are eliminated by slow monitoring (modulating) the frequency of accelerating field. According to what law ω (t) should this frequency be monitored if the magnetic induction is equal to B and the particle acquires an energy ΔW per revolution? The charge of the particle is q and its mass is m.
Solution. 400. The basic condition is the relativistic equation,
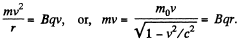
Or calling, 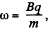
we get, 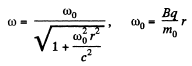
is the radius of the instantaneous orbit.
The time of acceleration is,
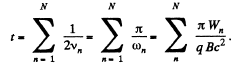
N is the number of crossing of either Dee.
But, 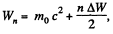 there being two crossings of the Dees per revolution.
there being two crossings of the Dees per revolution.
So, 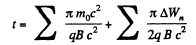
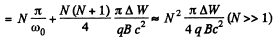
Also, 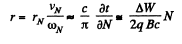
Hence finally,
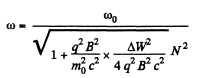
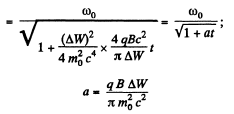
Q. 401. A particle with specific charge q/m is located inside a round solenoid at a distance r from its axis. With the current switched into the winding, the magnetic induction of the field generated by the solenoid amounts to B. Find the velocity of the particle and the curvature radius of its trajectory, assuming that during the increase of current flowing in the solenoid the particle shifts by a negligible distance.
Solution. 401. When the magnetic field is being set up in the solenoid, and electric field will be induced in it, this will accelerate the charged particle. If B is the rate, at which the magnetic field is increasing, then.
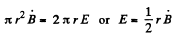
Thus, 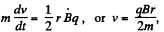
After the field is set up, the particle will execute a circular motion of radius p, where
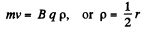
Q. 402. In a betatron the magnetic flux across an equilibrium orbit of radius r = 25 cm grows during the acceleration time at practically constant rate 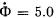 Wb/s. In the process, the electrons acquire an energy W = 25 MeV. Find the number of revolutions made by the electron during the acceleration time and the corresponding distance covered by it.
Wb/s. In the process, the electrons acquire an energy W = 25 MeV. Find the number of revolutions made by the electron during the acceleration time and the corresponding distance covered by it.
Solution. 402. The increment in energy per revolution is 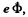 so the number of revolutions is,
so the number of revolutions is,
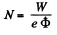
The distance traversed is, 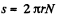
Q. 403. Demonstrate that electrons move in a betatron along a round orbit of constant radius provided the magnetic induction on the orbit is equal to half the mean value of that inside the orbit (the betatron condition).
Solution. 403. On the one hand,
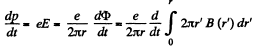
On the other
p = B (r) er, r = constant.
so, 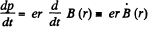
Hence, 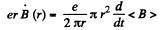
So, 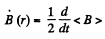
This equations is most easily satisfied by taking 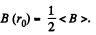
Q. 404. Using the betatron condition, find the radius of a round orbit of an electron if the magnetic induction is known as a function of distance r from the axis of the field. Examine this problem for the specific case B = B0 — ar2, where B0 and a are positive constants.
Solution. 404. The condition 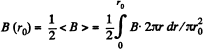
or, 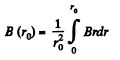
This gives r0.
In the present case,
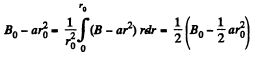
or, 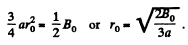
Q. 405. Using the betatron condition, demonstrate that the strength of the eddy-current field has the extremum magnitude on an equilibrium orbit.
Solution. 405. The induced electric field (or eddy current field) is given by,
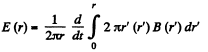
Hence,
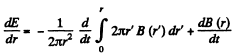
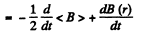
This vanishes for r = r0 by the betatron condition, where r0 is the radius of the equilibrium orbit
Q. 406. In a betatron the magnetic induction on an equilibrium orbit with radius r = 20 cm varies during a time interval Δt = 1.0 ms at practically constant rate from zero to B = 0.40 T. Find the energy acquired by the electron per revolution.
Solution. 406. From the betatron condition,
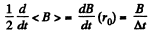
Thus, 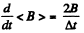
and 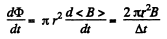
So, energy increment per revolution is,
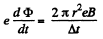
Q. 407. The magnetic induction in a betatron on an equilibrium orbit of radius r varies during the acceleration time at practically constant rate from zero to B. Assuming the initial velocity of the electron to be equal to zero, find:
(a) the energy acquired by the electron during the acceleration time;
(b) the corresponding distance covered by the electron if the acceleration time is equal to Δt.
Solution. 407. (a) Even in the relativistic case, we know that : p = Her
Thus, 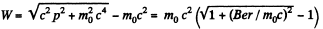
(b) The distance traversed is,
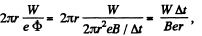
on using the result of the previous problem.
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Motion of Charged Particles In Electric And Magnetic Fields- 2 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is the motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields? |  |
| 2. How does the motion of a charged particle differ in electric and magnetic fields? |  |
| 3. What is the effect of the velocity of a charged particle on its motion in electric and magnetic fields? |  |
| 4. How does the strength of the electric and magnetic fields affect the motion of charged particles? |  |
| 5. Can a charged particle experience simultaneous motion in both electric and magnetic fields? |  |



















