Irodov Solutions: Radioactivity- 1 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.214. Knowing the decay constant λ of a nucleus, find: (a) the probability of decay of the nucleus during the time from 0 to t; (b) the mean lifetime ζ of the nucleus.
Ans. (a) The probability of survival (i.e. not decaying) in time t is e-λt. Hence the probability of decay is 1 - e-λt
(b) The probability that the particle decays in time dt around time t is the difference
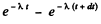
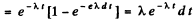
Therefore the mean life time is
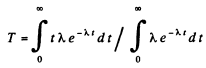
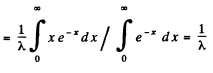
Q.215. What fraction of the radioactive cobalt nuclei whose halflife is 71.3 days decays during a month?
Ans. We calculate λ first
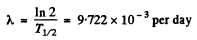
Hence
fraction decaying in a month 
Q.216. How many beta-particles are emitted during one hour by 1.0μg of Na24 radionuclide whose half-life is 15 hours?
Ans. Here
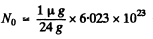 = 2.51 x 1016
= 2.51 x 1016
Also 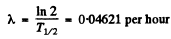
So the number of β rays emitted in one hour is
No (1 - e-λt) = 1.13 x1015
Q.217. To investigate the beta-decay of Mg23 radionuclide, a counter was activated at the moment t = 0. It registered N1 beta-particles by a moment t1 = 2.0s, and by a moment t2 = 3t1 the number of registered beta-particles was 2.66 times greater. Find the mean lifetime of the given nuclei.
Ans. If N0 is the number of radionuclei present initially, then
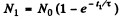
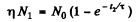
where 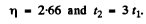 Then
Then
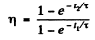
or 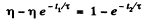
Substituting the values
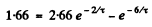
Put 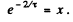 Then
Then
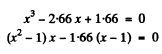
or 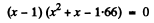
Now 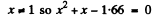
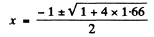
Negative sign has to be rejected as x >0.
Thus x = 0.882
This gives 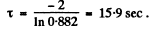
Q.218. The activity of a certain preparation decreases 2.5 times after 7.0 days. Find its half-life.
Ans. If the half-life is T days
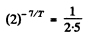
Hence 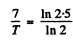
or 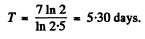
Q.219. At the initial moment the activity of a certain radionuclide totalled 650 particles per minute. What will be the activity of the preparation after half its half-life period?
Ans. The activity is proportional to the number of parent nuclei (assuming that the daughter is not radioactive). In half its half-life period, the number of parent nucli decreases by a factor
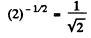
So activity decreases to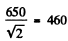 articles per minute.
articles per minute.
Q.220. Find the decay constant and the mean lifetime of Co55 radionuclide if its activity is known to decrease 4.0% per hour. The decay product is nonradioactive.
Ans. If the decay constant (in (hour)-1 ) is λ., then the activity after one hour will decrease by a factor e~λ Hence
0.96 = e~λ
or 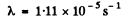 = 0.0408 per hour
= 0.0408 per hour
he mean life time is 24.5 hour
Q.221. A U238 preparation of mass 1.0 g emits 1.24.104 alphaparticles per second. Find the half-life of this nuclide and the activity of the preparation.
Ans. Here
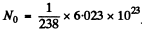
= 2.531 X 1021
The activity is A = 1.24 x 104 dis/sec .
Then 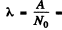 4.90 x 1018 per sec .
4.90 x 1018 per sec .
Hence the half life is
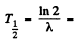 4.49 x109 years
4.49 x109 years
Q.222. Determine the age of ancient wooden items if it is known that the specific activity of C14 nuclide in them amounts to 3/5 of that in lately felled trees. The half-life of C14 nuclei is 5570 years.
Ans. in old wooden atoms the number of C14 nuclei steadily decreases because of radioactive decay. (In live trees biological processes keep replenishing C14 nuclei maintaining a balance. This balance starts getting disrupted as soon as the tree is felled.)
If T1/2 is the half life of C14 then 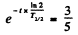
Hence 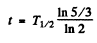 = 4105 years ≈ 4.1x103 years
= 4105 years ≈ 4.1x103 years
Q.223. In a uranium ore the ratio of U238 nuclei to Pb206 nuclei is η = 2.8. Evaluate the age of the ore, assuming all the lead Pb206 to be a final decay product of the uranium series. The half-life of U238 nuclei is 4.5.109 years.
Ans. What this implies is that in the time since the ore was formed 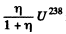 nuclei have remained undecayed. Thus
nuclei have remained undecayed. Thus
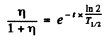
or

Substituting 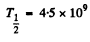 years, η = 2.8
years, η = 2.8
we get t = 1.98 x 109 years.
Q.224. Calculate the specific activities of Na24 and U235 nuclides whose half-lifes are 15 hours and 7.1.108 years respectively.
Ans. The specific activity of Na24 is
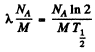 = 3.22 x 1017 dis/(gm.sec)
= 3.22 x 1017 dis/(gm.sec)
Here M = molar w eight of 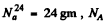 is Avogadro num ber &
is Avogadro num ber & 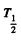 is the half-life of Na24
is the half-life of Na24
Sim ilarly the specific activity of U235 is
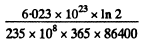
= 0.793 x 105 dis/(gm-s)
Q.225. A small amount of solution containing Na24 radionuclide with activity A = 2.0.103 disintegrations per second was injected in the bloodstream of a man. The activity of 1 cm3 of blood sample taken t = 5.0 hours later turned out to be A' = 16 disintegrations per minute per cm3. The half-life of the radionuclide is T = 15 hours. Find the volume of the man's blood.
Ans. Let V = volume of blood in the body of the human being. Then the total activity of the blood is A' V. Assuming all this activity is due to the injected Na24 and taking account of the decay of this radionuclide, we get
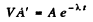
Now 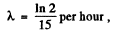 t = 5 hour
t = 5 hour
Thus 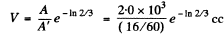 = 5.99 litre
= 5.99 litre
Q.226. The specific activity of a preparation consisting of radioactive Co58 and nonradioactive Co59 is equal to 2.2.1012 dis/(s•g). The half-life of Co58 is 71.3 days. Find the ratio of the mass of radioactive cobalt in that preparation to the total mass of the preparation (in per cent).
Ans. We see that
Specific activity of the sample
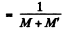 {A ctivity of M gm of Co58 in the sample}
{A ctivity of M gm of Co58 in the sample}
Here M and At are the masses of Co58 and Co59 in the sample. Now activity of M gm of Co58
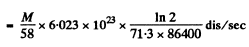
= 1.168 x l015M
Thus from the problem
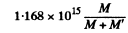 = 2.2 x 1012
= 2.2 x 1012
or 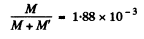
Q.227. A certain preparation includes two beta-active components with different half-lifes. The measurements resulted in the following dependence of the natural logarithm of preparation activity on time t expressed in hours:
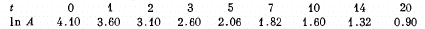
Find the half-lifes of both components and the ratio of radioactive nuclei of these components at the moment t = 0.
Ans. Suppose N1 N2 are the initial number of component nuclei whose decay constants are λ1 , λ2 ( in (hour)-1 Then the activity at any instant is
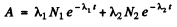
The activity so defined is in units dis/hour. We assume that data In A given is of its natural logarithm. The daughter nuclei are assumed nonradioactive.
We see from the data that at large t the change in In A per hour of elapsed time is constant and equal to - 0.07. Thus
λ2 = 0.07 per hour
We can then see that the best fit to data is obtained by
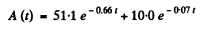
[To get the fit we calculate 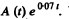 We see that it reaches the constant value 10.0 at t = 7, 10, 14, 20 very nearly. This fixes the second term. The first term is then obtained by subtracting out the constant value 10.0 from each value of
We see that it reaches the constant value 10.0 at t = 7, 10, 14, 20 very nearly. This fixes the second term. The first term is then obtained by subtracting out the constant value 10.0 from each value of 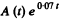 in the data for small t ]
in the data for small t ]
Thus we get λ1 = 0.66 per hour
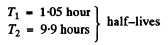
Ratio 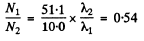
The answer given in the book is misleading.
Q.228. A P32 radionuclide with half-life T = 14.3 days is produced in a reactor at a constant rate q = 2.7.109 nuclei per second. How soon after the beginning of production of that radionuclide will its activity be equal to A = 1.0.109 dis/s?
Ans. Production of the nucleus is governed by the equation
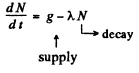
We see that N will approach a constant value 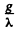 This can also be proved directly. Multiply by
This can also be proved directly. Multiply by 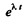 and write
and write
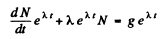
Then
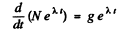
or 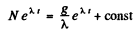
At t = 0 when the production is starteed, N = 0
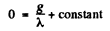
Hence
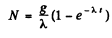
Now the activity is
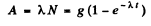
From the problem
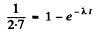
This gives λt = 0.463
so 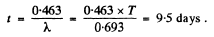
Algebraically 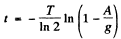
Q.229. A radionuclide A1 with decay constant λ1 transforms into a radionuclide A2 with decay constant λ2. Assuming that at the initial moment the preparation contained only the radionuclide A1, find:
(a) the equation describing accumulation of the radionuclide A2 With time;
(b) the time interval after which the activity of radionuclide A2 reaches the maximum value.
Ans. (a) Suppose N1 and N2 are the number of two radionuclides A1, A2 at time t. Then
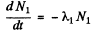 (1)
(1)
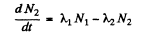 (2)
(2)
From (1)
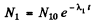
where N10 is the initial number of nuclides Al at time t = 0
From (2)
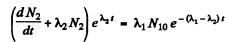
or 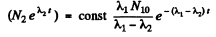
since N2 = 0 at t = 0
Constant 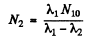
Thus 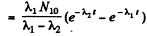
(b) The activity of nuclide A2 is λ2 N2. This is maximum when N2 is maximum. That happens when
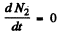
This requires
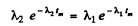
or
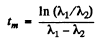
Q.230. Solve the foregoing problem if λ1 = X2 = X.
Ans. a) This case can be obtained from the previous one on putting
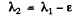
where ε is very small and letting ε → 0 at the end. Then
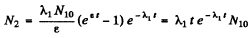
or dropping the subscript 1 as the two values are equal
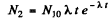
(b) This is maximum when
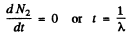
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Radioactivity- 1 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is radioactivity? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of radiation emitted during radioactivity? |  |
| 3. How does radioactivity affect living organisms? |  |
| 4. How is radioactivity measured? |  |
| 5. What are some real-life applications of radioactivity? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















