Irodov Solutions: Nuclear Reactions- 2 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
6.271. A particle of mass m strikes a stationary nucleus of mass M and activates an endoergic reaction. Demonstrate that the threshold (minimal) kinetic energy required to initiate this reaction is defined by Eq. (6.6d).
Ans. Energy required is minimum when the reaction products all move in the direction of the incident particle with the same velocity (so that the combination is at rest in the centre of mass frame). We then have
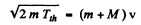
(Total mass is constant in the nonrelativistic limit).
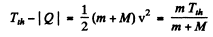
or 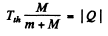
Hence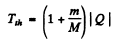
6.272. What kinetic energy must a proton possess to split a deuteron H2 whose binding energy is Eb = 2.2 MeV?
Ans. The result of the previous problem applies and we End that energy required to split a deuteron is
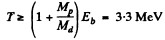
6.273. The irradiation of lithium and beryllium targets by a monoergic stream of protons reveals that the reaction Li7(p, n)Be7 -- 1.65 MeV is initiated whereas the reaction Be9(p, n)B9 — 1.85 MeV does not take place. Find the possible values of kinetic energy of the protons.
Ans. Since the reaction 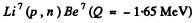 is initiated, the incident proton energy must be
is initiated, the incident proton energy must be
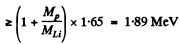
since the reaction 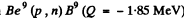 is not initiated,
is not initiated,
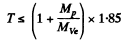 = 2.06 MeV Thus 1.89 MeV ≤ Tp ≤ 2.06 MeV
= 2.06 MeV Thus 1.89 MeV ≤ Tp ≤ 2.06 MeV
6.274. To activate the reaction (n, a) with stationary B11 nuclei, neutrons must have the threshold kinetic energy Tth = 4.0 MeV. Find the energy of this reaction.
Ans. We have 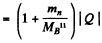
or 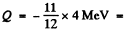 -3.67 MeV
-3.67 MeV
6.275. Calculate the threshold kinetic energies of protons required to activate the reactions (p, n) and (p, d) with Li7 nuclei.
Ans. The Q o f the reaction Li7 (p, n ) Be7 was calculated in problem 266 (a). It is - 1.64 MeV Hence, the threshold K.E. of protons for initiating this reaction is
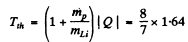
For the reaction Li7 (p, d) Li6
we find 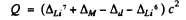
= (0.01601 + 0.00783 - 0.01410 - 0.01513) amu x c2
= - 5 02 MeV
The threshold proton energy for initiating this reaction is
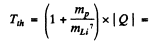 5.73 MeV
5.73 MeV
6.276. Using the tabular values of atomic masses, find the threshold kinetic energy of an alpha particle required to activate the nuclear reaction Li7 (α, n) Be9. What is the velocity of the B10 nucleus in this case?
Ans. The Q of Li7 (a, n) B10 was calculated in problem 266 (c). It is Q = 2.79 MeV Then the threshold energy of a-particle is
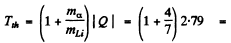 4.38MeV
4.38MeV
The velocity of B10 in this case is simply the volocity of centre of mass
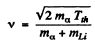
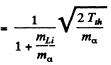
This is because both B10 and n are at rest in the CM frame at theshold. Substituting the values of various quantities
we get v = 5.27 x 106 m/s
6.277. A neutron with kinetic energy T = 10 MeV activates a nuclear reaction C12 (n, α) Be9 whose threshold is Tth = 6.17 MeV. Find the kinetic energy of the alpha-particles outgoing at right angles to the incoming neutrons' direction.
Ans. The momentum of incident neutron is 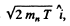 that of α particle is
that of α particle is 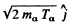 and of
and of
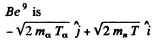
By conservation of energy
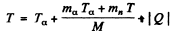
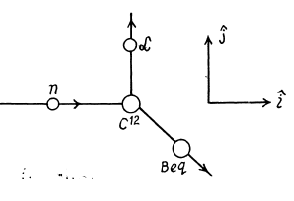
(M is the mass of Be9). Thus
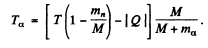
Using 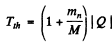
we get 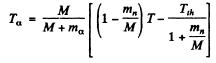
M’ is the mass of C12 nucleus.
or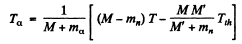 = 2.21MeV
= 2.21MeV
6.278. How much, in per cent, does the threshold energy of gamma quantum exceed the binding energy of a deuteron (Eb = 2.2 MeV) in the reaction Y + H2 → n + p?
Ans. The formula of problem 6.271 does not apply here because the photon is always reletivistic. At threshold, the energy o f the photon Ey implies a momentum 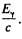 The velocity o f centre of mass with respect to the rest frame of initial H2 is
The velocity o f centre of mass with respect to the rest frame of initial H2 is
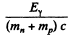
Since both n & p are at rest in CM frame at threshold, we write
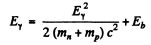
by conservation of energy. Since the first term is a small correction, we have
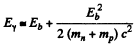
Thus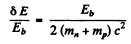
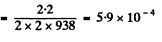
or nearly 0.06%
6.279. A proton with kinetic energy T = 1.5 MeV is captured by a deuteron H2. Find the excitation energy of the formed nucleus.
Ans. The reaction is
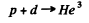
Excitation energy of He3 is just the energy available in centre of mass. The velocity of the centre of mass is
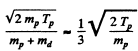
In the CM frame, the kinetic energy available is (md ≈ 2 mp)
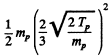
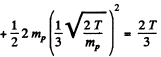
The total energy available is then 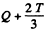
where 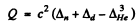
= c2 x (0.00783 + 0.01410 - 0.01603) amu
= 5.49 McV
Finally E = 6.49 MeV.
6.280. The yield of the nuclear reaction C13(d, n)N14 has maximum magnitudes at the following values of kinetic energy T1 of bombarding deuterons: 0.60, 0.90, 1.55, and 1.80 MeV. Making use of the table of atomic masses, find the corresponding energy levels of the transitional nucleus through which this reaction proceeds.
Ans. The reaction is
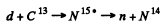
Maxima of yields deteimine the eneigy levels of N15 *. As in the previous problem the excitation eneigy is
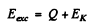
where EK = available kinetic eneigy. This is found is as in the previous problem. The velocity of the centre of mass is
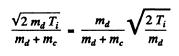
so 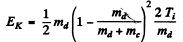
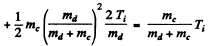
Q is the Q value for the ground state of N15 : We have
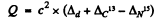
= c2 x (0.01410 + 0.00335 - 0.00011) amu
= 16.14 MeV
The excitation energies then are
16.66 MeV, 16.92 MeV
17.49 MeV and 17.70 MeV.
6.281. A narrow beam of thermal neutrons is attenuated η = 360 times after passing through a cadmium plate of thickness d = 0.50 mm. Determine the effective cross-section of interaction of these neutrons with cadmium nuclei.
Ans. We have the relation
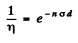
Here 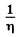 attenuation factor
attenuation factor
n = no. of Cd nuclei per unit volume
σ = effective cross section
d = thickness of the plate
Now 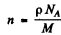
(p = density, M = Molar weight of Cd, NA = Avogadro number.)
Thus 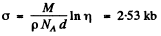
6.282. Determine how many times the intensity of a narrow beam of thermal neutrons will decrease after passing through the heavy water layer of thickness d = 5.0 cm. The effective cross-sections of interaction of deuterium and oxygen nuclei with thermal neutrons are equal to σ1 = 7.0 b and σ2 --- 4.2 b respectively.
Ans. Here
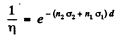
where 1 refers to O1 and 2 to D nuclei
Using n2 = 2n, n1 = n = concentration of O nuclei in heavy water we get
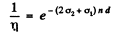
Now using the data for heavy water
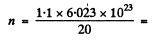 3.313 x 1022 per cc
3.313 x 1022 per cc
Thus substituting the values
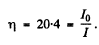
6.283. A narrow beam of thermal neutrons passes through a plate of iron whose absorption and scattering effective cross-sections are equal to σa = 2.5b and σ8 = 11b respectively. Find the fraction of neutrons quitting the beam due to scattering if the thickness of the plate is d = 0.50 cm.
Ans. In traversing a distance d the fraction which is either scattered or absorbed is clearly
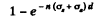
by the usual definition of the attenuation factor. Of this, the fraction scattered is (by definition of scattering and absorption cross section)
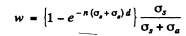
In iron 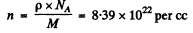
Substitution gives w = 0.352
6.284. The yield of a nuclear reaction producing radionuclides may be described in two ways: either by the ratio w of the number of nuclear reactions to the number of bombarding particles, or by the quantity k, the ratio of the activity of the formed radionuclide to the number of bombarding particles, Find: (a) the half-life of the formed radionuclide, assuming w and k to be known; (b) the yield w of the reaction Li7(p, n)Be7 if after irradiation of a lithium target by a beam of protons (over t = 2.0 hours and with beam current I = 10μA) the activity of Be7 became equal to A = = 1.35.108 dis/s and its half-life to T = 53 days.
Ans. (a) Assuming of course, that each reaction produces a radio nuclide of the same type, the decay constant α of the radionuclide is k/w . Hence
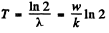
(b) number of bombarding particles is 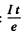
(e = charge on proton). Then the number of Be7 produced is 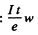
If λ = decay constant of 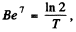 , then the activity is
, then the activity is 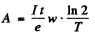
Hence 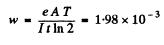
6.285. Thermal neutrons fall normally on the surface of a thin gold foil consisting of stable Au197 nuclide. The neutron flux density is J = 1.0.1010 part./(s- cm2). The mass of the foil is m = 10 mg. The neutron capture produces beta-active Au188 nuclei with half-life T = 2.7 days. The effective capture cross-section is σ = 98 b. Find: (a) the irradiation time after which the number of Au187 nuclei decreases by = 1.0%; (b) the maximum number of Au198 nuclei that can be formed during protracted irradiation.
Ans. (a) Suppose - No. of Au197 nuclei in the foil. Then the number of Au197 nuclei transformed in time t is
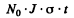
For this to equal ηN0, we must have
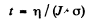 = 323 years
= 323 years
(b) Rate of formation of the Au198 nuclei is N0 • J • a per sec
and rate of decay is λn, where n is the number of Au198 at any in stant
Thus
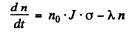
The maximum number of Au198 is clearly
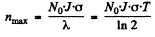
because if n is smaller, 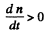 and n increase further and if n is larger
and n increase further and if n is larger
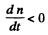 and n will decrease. (Actually nmax is approached steadily as
and n will decrease. (Actually nmax is approached steadily as 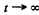 )
)
Substitution give susing 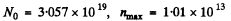
6.286. A thin foil of certain stable isotope is irradiated by thermal neutrons falling normally on its surface. Due to the capture of neutrons a radionuclide with decay constant λ appears. Find the law describing accumulation of that radionuclide N (t) per unit area of the foil's surface. The neutron flux density is J, the number of nuclei per unit area of the foil's surface is n, and the effective crosssection of formation of active nuclei is α.
Ans. Rate of formation of the radionuclide is n.J.σ per unit area per-sec. Rate of decay is λN.
Thus
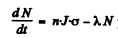 per unit area per second
per unit area per second
Then 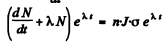 or
or 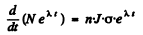
Hence 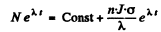
The number of radionuclide at t = 0 when the process starts is zero. So constant 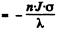
Then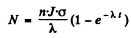
6.287. A gold foil of mass m = 0.20g was irradiated during t = 6.0 hours by a thermal neutron flux falling normally on its surface. Following ζ = 12 hours after the completion of irradiation the activity of the foil became equal to A = 1.9.107 dis/s. Find the neutron flux density if the effective cross-section of formation of a radioactive nucleus is σ = 96b, and the half-life is equal to T = 2.7 days.
Ans. We apply the formula of the previous problem except that have N = no. of radio nuclide and no. of host nuclei originally.
Here 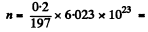 6.115 x1020
6.115 x1020
Then after time t 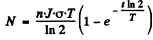
T = half life of the radionuclide.
After the source of neutrons is cut off the activity after time T will be
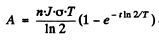
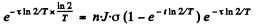
Thus 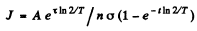
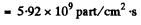
6.288. How many neutrons are there in the hundredth generation if the fission process starts with No = 1000 neutrons and takes place in a medium with multiplication constant k = 1.05?
Ans. No. of nuclei in the first generation = No .of nuclei initially = N0
N0 in the second generation = N0 x multiplication factor = N0.k
N0 in the the 3rd generation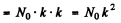
N0 in the nth generation 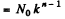
Substitution gives 1.25 x 105 neutrons
6.289. Find the number of neutrons generated per unit time in a uranium reactor whose thermal power is P = 100 MW if the average number of neutrons liberated in each nuclear splitting is v = 2.5. Each splitting is assumed to release an energy E = = 200 MeV.
Ans. No- of fissions per unit time is clearly P/E. Hence no. of neutrons produced per unit time to
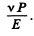 Substitution gives 7.80 x 1018 neutrons/sec
Substitution gives 7.80 x 1018 neutrons/sec
6.290. In a thermal reactor the mean lifetime of one generation of thermal neutrons is ζ = 0.10 s. Assuming the multiplication constant to be equal to k = 1.010, find: (a) how many times the number of neutrons in the reactor, and consequently its power, will increase over t = 1.0 min;
(b) the period T of the reactor, i.e. the time period over which its power increases e-fold.
Ans. (a) This number is kn - 1 where n = no. of generations in time t = t/T
Substitution gives 388.
(b) We write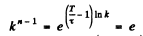
or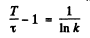 and
and 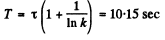
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Nuclear Reactions- 2 - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What is a nuclear reaction? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of nuclear reactions? |  |
| 3. How does a nuclear reaction produce energy? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of nuclear reactions? |  |
| 5. How do nuclear reactions contribute to radioactive decay? |  |
















