Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Refraction of Light, Solutions- 3 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Page No:246
Q1: Write the formula for a lens connecting image distance (υ), object distance (u), and the focal length (ƒ). How does the lens formula differ from the mirror formula?
Sol: Formula for a lens connecting image distance (v). object distance (u) and the focal length (f) is:

This is the lens formula.
The lens formula has a minus sign (-) between 1/v and 1/u whereas the mirror formula has a plus sign (+) between 1/v and 1/u.
Mirror formula:-

Q2: Write down the magnification formula for a lens in terms of object distance and image
distance. How does this magnification formula for a lens differ from the corresponding formula for a mirror?
Sol: Magnification (m) fomula for a lens is:

The magnification formula for a mirror has a minus sign (-) but the magnification formula for a lens has no minus sign.
The magnification formula for a mirror is:

Q3: What is the nature of the image formed by a convex lens if the magnification produced by the lens is +3?
Sol: The image will be virtual and erect since the magnification has a positive value.
Q4: What is the nature of the image formed by a convex lens if the magnification produced by the lens is, – 0.5?
Sol: The image will be real and inverted since the magnification has a negative value.
Q5: What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm ?
Sol: u = -10 cm, f = 10 cm
we have

Q6: Describe the nature of the image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
Sol: Since the object is placed at a distance greater than the focal length of the convex lens, so the image formed is real and inverted.
Q7: At what distance from a converging lens of focal length 12 cm must an object be placed so that an image of magnification 1 will be produced?
Sol:

 The object should be placed at a distance of 24 cm from the lens (on the left side).
The object should be placed at a distance of 24 cm from the lens (on the left side).
Q8: State and explain the New Cartesian Sign Convention for spherical lenses.
Sol: New Cartesian Sign Convention for spherical lenses:
(i) All the distances are measured from the optical center of the lens.
(ii) The distances measured in the same direction as that of incident light are taken as positive.
(iii) The distances measured against the direction of incident light are taken as negative.
(iv) The distances measured upward and perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as positive.
(v) The distances measured downward and perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as negative.
Q9: An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature, and size of the image.
Sol:

v = - 20 cm (Image is 20 cm in front of the convex lens)

The image is 8 cm in size and is real and inverted.
Q10: A small object is so placed in front of a convex lens of 5 cm focal length that a virtual image is formed at a distance of 25 cm. Find the magnification.
Sol:


Q11: Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
Sol:


The image is formed 15cm behind the convex lens and it is real and inverted.
Q12: Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
Sol:

Q13: An object is placed at a distance of 100 cm from a converging lens of focal length 40 cm.
(i) What is the nature of image?
(ii) What is the position of image?
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
Sol: (i) Since the object Is placed at a distance greater than the focal length of the lens, so the Image formed Is real and inverted.
(ii) u = - 100cm. f = 40cm

The image is formed 66.6cm behind the convex lens.
Q14: A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
Sol:


Page No:247
Q15: A converging lens of focal length 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a screen. How far from the lens should an object be placed so as to form its real image on the screen?
Sol:

Q16: An object 5 cm high is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Find the position, size, and nature of the image formed. Also draw the ray diagram.
Sol:

The image is 16.6cm behind the convex lens.

The image is 3.33 cm in size and Is real and inverted.

Q17: At what distance should an object be placed from a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to obtain an image at 24 cm from it on the other side? What will be the magnification produced in this case?
Sol:

Q18: An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical center of the lens. Find the nature, position, and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Sol:

The image is formed 5.02cmbehind a die convex lens and is real and inverted

Since the object distance is much greater than the focal length, this example illustrates the case when the object is placed.
Q19: The filament of a lamp is 80 cm from a screen and a converging lens forms an image of it on a screen, magnified three times. Find the distance of the lens from the filament and the focal length of the lens.
Sol : -u + v = 80cm------(1)
m = -3 (The image is real since it firms on a screen)
m = v/u = -3
v = -3u
Put in eq (1),
u = -3u = 80
-4u = 80
u = -20cm
Distance of lens from filament is 20cm.
v = -3u = 60cm

Q20: An erect image 2.0 cm high is formed 12 cm from a lens, the object being 0.5 cm high. Find the focal length of the lens.
Sol:


Q21: A convex lens of focal length 0.10 m is used to form a magnified image of an object of height 5 mm placed at a distance of 0.08 m from the lens. Calculate the position, nature and size of the image.
Sol:
 The image is formed 0.40 m in front of the convex lens.
The image is formed 0.40 m in front of the convex lens.
 ⇒ h2 = 0.025m = 25mm
⇒ h2 = 0.025m = 25mm
The size of the image is 25 mm and the image is virtual and erect
Q22: A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
Sol:

 The image is 1.5 cm high, virtual, erect, and magnified.
The image is 1.5 cm high, virtual, erect, and magnified.
Q23: Determine how far an object must be placed in front of a converging lens of focal length 10 cm in order to produce an erect (upright) image of linear magnification 4.
Sol:

 The object must be placed 7.5 cm in front of the converging lens.
The object must be placed 7.5 cm in front of the converging lens.
Q24: A lens of focal length 20 cm is used to produce a ten times magnified image of a film slide on a screen. How far must the slide be placed from the lens ?
Sol:


Q25: An object placed 4 cm in front of a converging lens produces a real image 12 cm from the lens.
(a) What is the magnification of the image?
(b) What is the focal length of the lens?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of an image. Mark clearly F and 2F in the diagram.
Sol:



Q26: (a) An object 2 cm tall stands on the principal axis of a converging lens of focal length 8 cm. Find the position, nature, and size of the image formed if the object is :
(i) 12 cm from the lens
(ii) 6 cm from the lens
(b) State one practical application for each of the use of such a lens with the object in position (i) and (ii).
Sol:

 The image is 24 cm behind the lens.
The image is 24 cm behind the lens. Image is 4 an high, real, and inverted,
Image is 4 an high, real, and inverted, The image is 24 cm in front of the lens
The image is 24 cm in front of the lens
The image is 8 cm high, virtual, and erect.
(b) (i) Used in film projector.
(ii) Used as a magnifying glass.
Q27: (a) An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
(b) If the object is moved to a point only 3 cm away from the lens, what is the new position, height and nature of the image ?
(c) Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass ?
Sol :
 The image is formed 12 cm behind the lens.
The image is formed 12 cm behind the lens. The image is 1.5cm high, real and inverted image is framed 4.8cm In front of the lens.
The image is 1.5cm high, real and inverted image is framed 4.8cm In front of the lens. The image is 4.8cm high, virtual, and erect
The image is 4.8cm high, virtual, and erect
(c) Case (b)
Q28: (a) Find the nature, position, and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of :
(i) 0.50 m
(ii) 0.25 m
(iii) 0.15 m
(b) Which of the above cases represents the use of a convex lens in a film projector, in a camera, and as a magnifying glass?
Sol:
 The image is formed 0.33 m behind the lens image is formed 1 m behind the lens image is formed 0.60 m in front of the die lens.
The image is formed 0.33 m behind the lens image is formed 1 m behind the lens image is formed 0.60 m in front of the die lens.
The image is virtual and erect
(b) Film projector Case (ii)
Camera: Case (i)
Magnifying glass: Case (iii)
Page No:248
Q41: A student experimented with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm, and 120 cm from the lens. In each case, he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm, and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately, his results are written in the wrong order.
(a) Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
(b) What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
(c) Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
(d) What is the focal length of this lens?
Sol: (a) 100 cm; 60 cm; 40 cm; 30 cm; 24 cm
(b) When u = -25cm, v = 100cm


(c) 25 cm
(d) 20 cm (As calculated in part (b))
Q42: A magnifying lens has a focal length of 100 mm. An object whose size is 16 mm is placed at some distance from the lens so that an image is formed at a distance of 25 cm in front of the lens.
(a) What is the distance between the object and the lens ?
(b) Where should the object be placed if the image is to form at infinity ?
Sol:

The distance between the object and the lens Is 7.14 cm.
(b)The object should be placed at the focus so that the image is formed at infinity.
So, u = -100 mm = -10cm
The object should be placed 10 cm In front of the lens.
Q43: A lens forms a real image 3 cm high of an object 1 cm high. If the separation of object and image is 15 cm, find the focal length of the lens.
Sol:


Page No:249
Q44: An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
Sol:


Page No:251
Q1: If the image formed by a lens is always diminished and erect, what is the nature of the lens ?Sol: Concave lens.
Q2: Copy and complete the diagram below to show what happens to the rays of light when they pass through the concave lens :

Sol:

Page No:252
Q3: Which type of lenses are :
(a) thinner in the middle than at the edges?
(b) thicker in the middle than at the edges?
Sol: (a) Concave lenses.
(b) Convex lenses.
Q4: A ray of light is going towards the focus of a concave lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of this ray of light after refraction through the lens.
Solution :
 Ray of light going towards the focus of a concave lens.
Ray of light going towards the focus of a concave lens.
Q5: (a) What type of images can a convex lens make ?
(b) What type of image is always made by a concave lens ?
Solution : (a) Real and virtual.
(b) Virtual.
Q6: Take down this figure into your answer book and complete the path of the ray.
 Sol:
Sol:

Q7: Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) A convex lens……. rays of light, whereas a concave lens……….. rays of light.
(b) Lenses refract light to form images: a……… lens can form both real and virtual images, but a diverging
lens forms only……….. images.
Sol: (a) converges; diverges
(b) converging; virtual
Q8: Things always look small on viewing through a lens. What is the nature of the lens ?
Sol: Concave lens.
Q9: An object lies at a distance of 2ƒ from a concave lens of focal length ƒ. Draw a ray-diagram to illustrate the image formation.
Sol:

Q10: Show by drawing a ray diagram that the image of an object formed by a concave lens is virtual, erect, and diminished.
Sol:

Q11: Give the position, size and nature of the image formed by a concave lens when the object is placed: (a) anywhere between the optical center and infinity.
(b) at infinity.
Sol: (a) When the object is placed anywhere between the optical center and infinity, the image is formed between the optical center and focus. It is diminished, virtual, and erect.
(b) When the object is placed at infinity, the image is formed at focus. It is highly diminished, virtual and erect.
Q12: Which type of lens is : (a) a converging lens, and which is (b) a diverging lens? Explain your answer with diagrams.
Sol: (a) A convex lens is a converging lens because it converges a parallel beam of light rays passing through it at its focus.

Figure — A convex lens converges (brings closer) a parallel beam of light rays to a point F on its other side (right side).
(b) A concave lens is a diverging lens because it diverges the parallel beam of rays passing through it.

Figure — A concave lens diverges (spreads out) a parallel beam of light rays.
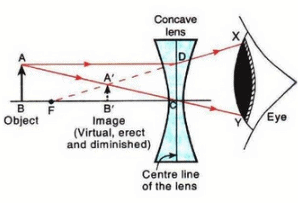
Q13: With the help of a diagram, explain why the image of an object viewed through a concave lens appears smaller and closer than the object.
Sol: (a) Smaller.
(b) Bigger.
The image is virtual in both cases.

As shown by the diagram, the image of an object viewed through a concave lens appears smaller and
closer than the object.
Q14: How would a pencil look like if you saw it through (a) a concave lens, and (b) a convex lens? (Assume the pencil is close to the lens). Is the image real or virtual?
Sol:


(b) Use of convex mirror: As rear-view mirror in vehicles
Use of concave mirror: As shaving mirrors
Use of convex lens: For making a simple camera
Use of concave lens: As eye-lens in Galilean telescope
Q15: (a) An object is placed 10 cm from a lens of focal length 5 cm. Draw the ray diagrams to show the formation of the image if the lens is (i) converging, and (ii) diverging.
(b) State one practical use for each convex mirror, concave mirror, convex lens and concave lens.
Sol :


(b) Use of convex mirror: As rear view mirror in vehicles
Use of concave mirror: As shaving mirrors
Use of convex lens: For making a simple camera
Use of concave lens: As eye-lens in Galilean telescope
Q16: (a) Construct ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using (i) a converging lens, and
(ii) a diverging lens.
(b) What is the difference between the two images formed above?
Sol: (a)
(i) Formation of virtual image using a converging lens:

(ii) Formation of virtual image using a diverging lens;
(b) The virtual image formed by a converging lens is magnified whereas that formed by a diverging lens is diminished.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Refraction of Light, Solutions- 3 - Science Class 10
| 1. What is refraction of light? |  |
| 2. How does refraction of light occur? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of refraction of light? |  |
| 4. What is the refractive index of a medium? |  |
| 5. How is the angle of refraction related to the angle of incidence? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|


















