NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Plant Growth & Development | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Read the following statements on plant growth and development. (NEEET 2025)
A. Parthenocarpy can be induced by auxins.
B. Plant growth regulators can be involved in promotion as well as inhibition of growth
C. Dedifferentiation is a pre-requisite for re-differentiation.
D. Abscisic acid is a plant growth promoter.
E. Apical dominance promotes the growth of lateral buds.
Choose the option with all correct statements
(a) A, D, E only
(b) B, D, E only
(c) A, B, C only
(d) A, C, E only
Ans: (c)
- A. Parthenocarpy can be induced by auxins: Parthenocarpy is the development of fruit without fertilization, leading to seedless fruits. Auxins, along with gibberellins, can artificially induce parthenocarpy by mimicking the hormonal changes that occur after fertilization. This statement is correct.
- B. Plant growth regulators can be involved in promotion as well as inhibition of growth: Plant growth regulators such as auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins promote growth, while others like abscisic acid and ethylene can inhibit growth. Thus, PGRs can have dual roles depending on the physiological context. This statement is correct.
- C. Dedifferentiation is a pre-requisite for redifferentiation: Dedifferentiation refers to the process where mature cells regain the ability to divide and form callus tissue. These dedifferentiated cells can then undergo redifferentiation to develop into specific tissues or organs. This is an essential step in plant tissue culture. This statement is correct.
Incorrect Statements:
- D. Abscisic acid is a plant growth promoter: This statement is incorrect. Abscisic acid (ABA) is primarily a growth inhibitor. It plays a significant role in stress responses such as closing stomata during water stress and inducing dormancy in seeds and buds. It is not a growth promoter.
- E. Apical dominance promotes the growth of lateral buds: This statement is incorrect. Apical dominance refers to the suppression of lateral bud growth due to the activity of the apical bud, which produces auxins. This phenomenon inhibits the growth of lateral buds rather than promoting it.
Summary:
- The correct statements are A, B, and C, which are included in option 1.
- Statements D and E are incorrect because abscisic acid is a growth inhibitor, and apical dominance suppresses rather than promotes lateral bud growth.
Q2: Which one of the following phytohormones promotes nutrient mobilization which helps in the delay of leaf senescence in plants? (NEEET 2025)
(a) Gibberellin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Abscisic acid
Ans: (b)
Concept:
- Phytohormones are chemical substances produced in plants that regulate various physiological processes. Key phytohormones include auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, ethylene, and abscisic acid.
- Cytokinins are plant hormones primarily involved in promoting cell division (cytokinesis) in roots and shoots.
- Cytokinins help overcome the apical dominance. They promote nutrient mobilisation which helps in the delay of leaf senescence.
- Natural cytokinins are synthesised in regions where rapid cell division occurs, for example, root apices, developing shoot buds, young fruits etc.
- It helps to produce new leaves, chloroplasts in leaves, lateral shoot growth and adventitious shoot formation.
Other Options:
- Ethylene: Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone primarily involved in promoting fruit ripening and leaf abscission (shedding). It accelerates leaf senescence rather than delaying it.
- Abscisic Acid: Abscisic acid (ABA) is known as the "stress hormone" in plants. It plays a role in stomatal closure, seed dormancy, and stress responses. ABA generally induces senescence rather than delaying it.
- Gibberellin: Gibberellins are involved in promoting stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering.
2024
Q1: Auxin is used by gardeners to prepare weed-free lawns. But no damage is caused to grass as auxin (NEEET 2024)(a) promotes apical dominance.
(b) promotes abscission of mature leaves only.
(c) does not affect mature monocotyledonous plants.
(d) can help in cell division in grasses, to produce growth.
Ans: (c)
Auxins are plant hormones that play a crucial role in regulating growth and development in plants. When applied in high concentrations, auxins cause abnormal growth in plants, especially dicots, leading to the death of these plants. However, monocotyledonous plants, such as grasses, are less affected by auxins. This is because monocots have a different structure and metabolic response compared to dicots, making them less susceptible to the growth-disrupting effects of auxins.
Auxins are plant hormones that can promote growth in plants by enhancing cell division and elongation. They are effective in controlling weed growth but have minimal effect on mature monocots like grasses, which are more resistant to auxins compared to dicots.

Q2: Formation of interfascicular cambium from fully developed parenchyma cells is an example for (NEET 2024)
(a) Differentiation
(b) Redifferentiation
(c) Dedifferentiation
(d) Maturation
Ans: (c)
The process involved in the formation of interfascicular cambium from fully developed parenchyma cells is known as "dedifferentiation." This is because dedifferentiation refers to the phenomenon where mature, specialized cells revert to a more primitive, less specialized state. In plants, certain mature cells, such as parenchyma cells, can lose their specialized characteristics and revert to meristematic activity. This newly formed meristematic tissue can then differentiate into specialized tissues once again, in this case, forming interfascicular cambium.
In contrast, differentiation (Option A) is the process where cells develop from a less specialized form to a more specialized form. Redifferentiation (Option B) refers to the process where dedifferentiated cells become specialized again, but this is a subsequent step following dedifferentiation. Maturation (Option D) refers to the final stages of cell and tissue specialization, not the regression to a less developed state.
Therefore, the correct answer to the query is: Option C - Dedifferentiation
Q3: Spraying sugarcane crop with which of the following plant growth regulators, increases the length of stem, thus, increasing the yield? (NEET 2024)
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Abscisic acid
Ans: (b)
The correct answer to the question is Option B, Gibberellin. Gibberellins (GAs) are a group of plant hormones that play a crucial role in regulating various aspects of plant growth and development. One of the notable effects of gibberellins is their ability to promote stem elongation by stimulating cell division and elongation.
In the case of sugarcane, a crop that is valued for its stem (from which sucrose is extracted), applying gibberellin can increase the length of the stem, thereby potentially increasing the yield of the crop. This increase in stem length due to gibberellin application is primarily because gibberellins overcome the inhibitory effects of other hormones that suppress growth; they stimulate the cells in the stems to grow larger and divide more frequently.
While Auxin (Option A) and Cytokinins (Option C) also influence plant growth and have their specific uses, such as rooting and promoting cell division, respectively, they do not primarily target stem elongation to the extent gibberellins do. Abscisic acid (Option D) is generally involved in stress responses and the inhibition of growth, making it unsuitable for promoting stem elongation.
Therefore, to specifically enhance stem length and yield in sugarcane, gibberellins are the most effective plant growth regulators among the options given.
Q4: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
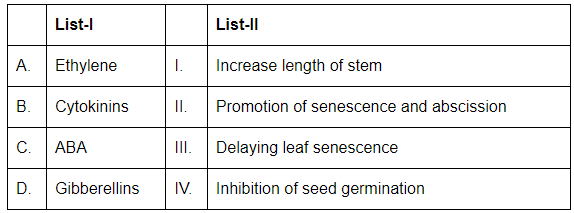
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans: (b)
- A. Ethylene: Ethylene is a plant hormone that promotes senescence (aging) and abscission (leaf drop). Thus, A corresponds to II (Promotion of senescence and abscission).
- B. Cytokinins: Cytokinins are involved in delaying leaf senescence and promoting cell division, which helps to keep the plant youthful. Thus, B corresponds to III (Delaying leaf senescence).
- C. ABA (Abscisic Acid): ABA is involved in the inhibition of seed germination and helps plants respond to stress, particularly in preventing water loss. Thus, C corresponds to IV (Inhibition of seed germination).
- D. Gibberellins: Gibberellins are plant hormones that promote growth and elongation of the stem, particularly during seed germination. Thus, D corresponds to I (Increase length of stem).
So the correct matching is:
- A-II: Ethylene promotes senescence and abscission.
- B-III: Cytokinins delay leaf senescence.
- C-IV: ABA inhibits seed germination.
- D-I: Gibberellins increase the length of the stem.
Q5: F. Skoog observed that callus proliferated from the internodal segments of tobacco stem when auxin was supplied with one of the following, except: (NEET 2024)
(a) Extract of vascular tissues
(b) Coconut milk
(c) Abscisic acid
(d) Yeast extract
Ans: (c)
F. Skoog's experiments on callus formation in tobacco stem segments revealed that the presence of auxin (a plant hormone) in combination with certain substances promotes callus growth. The substances that helped in the proliferation of callus included:
- Extract of vascular tissues
- Coconut milk
- Yeast extract
However, abscisic acid is not involved in promoting callus formation. In fact, abscisic acid generally acts as an inhibitor of growth and can prevent the formation of callus, making it the exception in Skoog's experiment. Thus, abscisic acid is not effective in promoting callus formation when used with auxin.
Q6: Given below are some statements about plant growth regulators: (NEET 2024)
A. All GAs are acidic in nature.
B. Auxins are antagonists to GAs.
C. Zeatin was isolated from coconut milk.
D. Ethylene induces flowering in Mango.
E. Abscisic acid induces parthenocarpy.
Choose the correct set of statements from the ones given below:
(a) A, C, D
(b) B, E
(c) A, B, C
(d) B, D, E
Ans: (a)
- A. All GAs are acidic in nature: This is correct. Gibberellins (GAs) are indeed acidic in nature, as they are derived from gibberellic acid.
- B. Auxins are antagonists to GAs: This is incorrect. While auxins and gibberellins (GAs) can have opposing effects in some processes, they are not strictly antagonistic. In fact, they often work together in promoting growth and development in plants.
- C. Zeatin was isolated from coconut milk: This is correct. Zeatin is a type of cytokinin, and it was first isolated from coconut milk.
- D. Ethylene induces flowering in Mango: This is correct. Ethylene is a plant hormone that can induce flowering in some plants, including mango.
- E. Abscisic acid induces parthenocarpy: This is incorrect. Abscisic acid (ABA) generally inhibits fruit development and promotes fruit drop, rather than inducing parthenocarpy (development of fruit without fertilization). Auxins and gibberellins (GAs) are more commonly involved in inducing parthenocarpy.
Thus, the correct set of statements is (a): A, C, D.
Q7: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)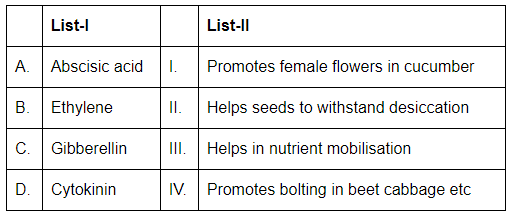 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-III, C- IV, D- I
(b) A-III, B-II, C- I, D- IV
(c) A-II, B-I, C- IV, D- III
(d) A-II, B-I, C- III, D- IV
Ans: (c)
- A. Abscisic acid (ABA): ABA helps seeds to withstand desiccation (drying out), which is essential for seed dormancy and survival under dry conditions. Thus, A corresponds to II (Helps seeds to withstand desiccation).
- B. Ethylene: Ethylene is involved in regulating the formation of female flowers in certain plants, such as cucumbers. It also plays a role in fruit ripening and the abscission of plant parts. Thus, B corresponds to I (Promotes female flowers in cucumber).
- C. Gibberellin: Gibberellin promotes bolting (flowering and rapid growth) in plants such as beet, cabbage, etc., often leading to early flowering. Thus, C corresponds to IV (Promotes bolting in beet, cabbage, etc.).
- D. Cytokinin: Cytokinins are involved in nutrient mobilization and are important for promoting cell division and growth, as well as delaying leaf senescence. Thus, D corresponds to III (Helps in nutrient mobilisation).
Thus, the correct match is:
- A-II: Abscisic acid helps seeds to withstand desiccation.
- B-I: Ethylene promotes female flowers in cucumber.
- C-IV: Gibberellin promotes bolting in beet, cabbage, etc.
- D-III: Cytokinin helps in nutrient mobilization.
2023
Q1: Spraying of which of the following phytohormone on juvenile conifers helps hastening the maturity period, that leads early seed production? (NEET 2023)
(a) Indole-3-butyric Acid
(b) Gibberellic Acid
(c) Zeatin
(d) Abscisic Acid
Ans: (b)
Gibberellic acid (GA) is a plant hormone that stimulates cell elongation, germination, and influences a variety of developmental processes, including maturation and seed production. In the forestry industry, it is often used to hasten the maturity period and stimulate early seed production in juvenile conifers.
Q2: Which hormone promotes internode/petiole elongation in deep water rice? (NEET 2023)
(a) GA3
(b) Kinetin
(c) Ethylene
(d) 2, 4-D
Ans: (c)
The hormone that promotes internode/petiole elongation in deep water rice is Ethylene.
Ethylene is a plant hormone that plays a critical role in growth and development, including responses to environmental stimuli. In the case of deep water rice, when the plants are submerged, the ethylene concentration increases and promotes rapid internodal elongation, which allows the plant to keep its leaves above the water surface.
So, the correct answer is Option C - Ethylene.
Q3: In tissue culture experiments, leaf mesophyll cells are put in a culture medium to form callus. This phenomenon may be called as:
(a) Senescence
(b) Differentiation
(c) Dedifferentiation
(d) Development (NEET 2023)
Ans: (c)
In tissue culture, when leaf mesophyll cells are placed in a culture medium, they can undergo dedifferentiation, which means that specialized cells revert to a more meristematic (undifferentiated) state. This allows the cells to proliferate and form a callus, a mass of undifferentiated cells. Dedifferentiation is the key process here, as it enables the formation of callus tissue.
Q4: The phenomenon which is influenced by auxin and also played a major role in its discovery is: (NEET 2023)
(a) Phototropism
(b) Root initiation
(c) Gravitropism
(d) Apical Dominance
Ans: (a)
Phototropism is the growth of a plant in response to light. Auxins play a significant role in this process by accumulating on the shaded side of the plant, promoting cell elongation and causing the plant to bend toward the light. This phenomenon was crucial in the discovery of auxins, as researchers observed how light influences plant growth through the action of auxins. Therefore, phototropism is not only influenced by auxin but was also instrumental in the identification and study of this important plant growth regulator.
Q5: Match List - I with List - II (NEET 2023)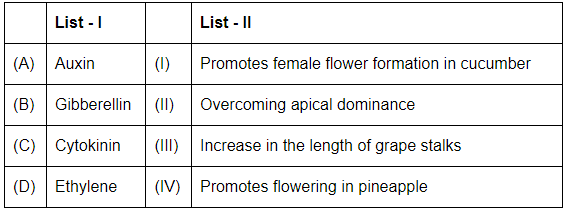 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)II (B)I (C)IV (D)III
(b) (A)IV (B)III (C)II (D)I
(c) (A)I (B)III (C)IV (D)II
(d) (A)III (B)II (C)I (D)IV
Ans: (b)
- (A) Auxin: Auxin is responsible for promoting female flower formation in cucumber. Thus, A corresponds to IV (Promotes female flower formation in cucumber).
- (B) Gibberellin: Gibberellin plays a role in increasing the length of grape stalks by promoting stem elongation. Thus, B corresponds to III (Increase in the length of grape stalks).
- (C) Cytokinin: Cytokinins help in overcoming apical dominance and encourage the growth of lateral buds. Thus, C corresponds to II (Overcoming apical dominance).
- (D) Ethylene: Ethylene induces flowering in pineapple by triggering the flowering process. Thus, D corresponds to I (Promotes flowering in pineapple).
Thus, the correct match is:
- A-IV: Auxin promotes female flower formation in cucumber.
- B-III: Gibberellin increases the length of grape stalks.
- C-II: Cytokinin overcomes apical dominance.
- D-I: Ethylene promotes flowering in pineapple.
Q6: Which of the following statements is not correct? (NEET 2023)
(a) Phase of cell elongation of plant cells is characterized by increased vacuolation.
(b) Cells in the meristematic phase of growth exhibit abundant plasmodesmatal connections
(c) Plant growth is generally determinate
(d)Plant growth is measurable
Ans: (c)
- (a) Phase of cell elongation of plant cells is characterized by increased vacuolation: This statement is correct. During cell elongation, the vacuole of the plant cell increases in size, which helps in the expansion of the cell.
- (b) Cells in the meristematic phase of growth exhibit abundant plasmodesmatal connections: This statement is correct. Meristematic cells, which are actively dividing and growing, have many plasmodesmata (cytoplasmic channels) that connect adjacent cells, allowing communication and transport of materials.
- (c) Plant growth is generally determinate: This statement is incorrect. Plant growth is generally indeterminate, meaning that plants can grow continuously throughout their life, especially in areas such as the tips of roots and shoots (apical meristems). Some parts of the plant, such as flowers and fruits, may exhibit determinate growth, but overall, plant growth is indeterminate.
- (d) Plant growth is measurable: This statement is correct. Plant growth can be measured in various ways, such as by measuring the increase in size, weight, or volume of a plant.
Thus, the statement that is not correct is (c): "Plant growth is generally determinate."
2022
Q1: Which one of the following plants does not show plasticity? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Coriander
(b) Buttercup
(c) Maize
(d) Cotton
Ans: (c)
Plants follow different pathways in response to environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called plasticity e.g. heterophylly in cotton, coriander and larkspur. In such plants, leaves of juvenile plant are different in a shape from those in mature plants.
Maize does not show plasticity.
Q2: The gaseous plant growth regulator is used in plants to: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) promote root growth and root hair formation to increase the absorption surface
(b) help overcome apical dominance
(c) kill dicotyledonous weeds in the fields
(d) speed up the malting process
Ans: (a)
Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone. It induces development of adventitious roots on various types of cutting. It promotes the development of lateral roots and growth of root hairs. Cytokinin helps to overcome the apical dominance.
Auxin is used to kill dicot weeds. Gibberellin speeds up the malting process.
Q3: Production of Cucumber has increased manifold in recent years. Application of which of the following phytohormones has resulted in this increased yield as the hormone is known to produce female flowers in the plants: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) ABA
(b) Gibberellin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Cytokinin
Ans: (c)
Ethylene increases the number of female flowers and fruits in certain plants such as cucumber. Gibberellins are used to increase the size of fruits in some plants.
Q4: The ability of plants to follow different pathways in response to environment leading to formation of different kinds of structures is called (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Differentiation
(b) Redifferentiation
(c) Development
(d) Plasticity
Ans: (d)
- The ability of plant to follow different pathways and produce different structures in response to environment is called plasticity.
- During differentiation, cells lose their ability to divide and form permanent cell.
- The process where the differentiated cells again lose the ability to divide and form permanent cells is called redifferentiation.
Q5: Which of the following growth regulators is an adenine derivative? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Abscisic acid
(b) Auxin
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Ethylene
Ans: (c)
- Cytokinins are derived from adenine.
- Auxins are derivatives of indole compounds.
- Abscisic acid is derived from carotenoids.
- Ethylene is derived from methionine.
2021
Q1: The plant hormone used to destroy weeds in a field is: (NEET 2021)
(a) 2, 4-D
(b) IBA
(c) IAA
(d) NAA
Ans: (a)
- Some synthetic auxins are used as weedicides. 2, 4-D is widely used to remove broad leaved weeds or dicotyledonous weeds in cereal crops or monocotyledonous plants.
- Auxins like IAA and IBA are used to induce parthenocarpy. IAA also stimulate nodule formation.
- Auxin like NAA is used to increase dwarf shoots.
Q2: Plants follow different pathways in response to environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called: (NEET 2021)
(a) Plasticity
(b) Maturity
(c) Elasticity
(d) Flexibility
Ans: (a)
Plant plasticity refers to the ability to modify itself by forming different kind of structures to adapt and cope with changes in its environment. It can be intrinsic plasticity or extrinsic plasticity. In both the cases plants shows heterophylly along with other morphological features, e.g. in the leaves Larkspur and buttercup.
Examples:
- Cotton, coriander and larkspur show heterophylly in which the leaves of a juvenile plant are different in shape from those in mature plants.
- Buttercup produces leaves of different shapes in air and water, which is also an example of heterophylly.
Q3: The site of perception of light in plants during photoperiodism is: (NEET 2021)
(a) Axillary bud
(b) Leaf
(c) Shoot apex
(d) Stem
Ans: (b)
- The site of perception of light in plants during photoperiodism is leaf.
- The site of perception of low temperature stimulus during vernalisation is shoot apex and embryo.
- Axillary bud are not sites of perception of photoperiod.
2020
Q1: Name the plant growth regulators which upon spraying on sugarcane crop, increases the length of stem, thus increasing the yield of sugarcane crop. (NEET 2020)
(a) Ethylene
(b) Abscisic acid
(c) Cytokinin
(d) Gibberellin
Ans: (d)
Spraying sugarcane crop with gibberellins increases the length of the stem, thus increasing the yield by as much as 20 tonnes per acre.
Q2: Which of the following is not an inhibitory substance governing seed dormancy? (NEET 2020)
(a) Para-ascorbic acid
(b) Abscisic acid
(c) Gibberellic acid
(d) Phenolic acid
Ans: (c)
Gibberellic acid breaks seed dormancy. It activate synthesis of alpha-amylase which breakdown starch into simple sugar.
2019
Q1: What is the site of perception of photoperiod necessary for induction of flowering in plants? (NEET 2019)
(a) Leaves
(b) Lateral buds
(c) Pulvinus
(d) Shoot apex
Ans: (a)
The site of perception of light / dark duration are leaves. It is hypothesized that there is a hormonal substance migrates from leaves to shoot apices for inducing flowering when plants are exposed to the necessary inductive photoperiod.
2017
Q1: Fruit and leaf drop at early stages can be prevented by the application of (NEET 2017)
(a) Ethylene
(b) Auxins
(c) Gibberellic-acid
(d) Cytokinins
Ans: (b)
In low concentrations, auxins such as 2, 4- D(2,4- Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid) is useful in preventing pre-harvest fruit drop and leaf drop.
2016
Q1: You are given a tissue with its potential for differentiation in an artificial culture. Which of the following pairs of hormones would you add to the medium to secure shoots as well as roots? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) IAA and gibberellin
(b) Auxin and cytokinin
(c) Auxin and abscisic acid
(d) Gibberellin and abscisic acid
Ans: (b)
Cytokinin and auxin are two plant hormones that are supplied to the tissue culture medium in definite proportions. They bring about cell division and differentiation of callus. A low auxin to cytokinin ratio promotes shoot formation whereas a high auxin to cytokinin ratio promotes rooting of callus.
Q2: Phytochrome is a (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Flavoprotein
(b) Glycoprotein
(c) Lipoprotein
(d) Chromoprotein
Ans: (d)
Phytochrome is a chromoprotein, plant pigment that can detect the presence or absence of light and is involved in regulating many processes that are linked to day length (photoperiod), such as seed germination and initiation of flowering. It consists of a light detecting portion, called a chromophore, linked to a small protein and exists in two inter-convertible forms with different physical properties.
Q3: The Avena curvature is used for bioassay of (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) IAA
(b) ethylene
(c) ABA
(d) GA3
Ans: (a)
Auxin has been clearly demonstrated in the leaf sheath or coleoptile of oat plant (Avena sativa). This plant coleoptile has been used for the test of hormone Auxin (IAA) participating in the growth of the plant.
2015
Q1: Typical growth curve in plants is: (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Linear
(b) Stair-steps shaped
(c) Parabolic
(d) Sigmoid
Ans: (d)
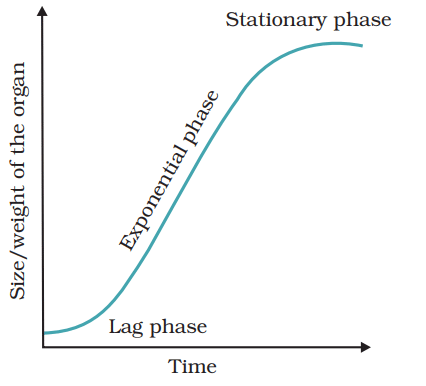
Geometric growth cannot be sustained for long in natural condition. Limited nutrient availability slows down the growth. It leads to a stationary phase or even a decline. Plotting the growth against time, gives a typical sigmoid or S-curve. Sigmoid curve of growth is typical of most organisms in their natural environment including plants.
An idealised sigmoid growth curve is drawn below:
Q2: What causes a green plant exposed to the light on only one side, to bend toward the source of light as it grows?
(a) Green plants seek light because they are phototropic
(b) Light stimulates plant cells on the lighted side to grow faster
(c) Auxin accumulates on the shaded side, stimulating greater cell elongation there.
(d) Green plants need light to perform photosynthesis (AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
Ans: (c)
Auxin stimulates cell elongation. It accumulates on shaded side which results in more elongation of cells towards shaded side of the plant. This causes bending of the plant towards source of light.
Q3: Auxin can be bioassayed by: (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015)
(a) Hydroponics
(b) Potometer
(c) Lettuce hypocotyl elongation
(d) Avena coleoptile curvature
Ans: (d)}
Avena coleoptile curvature is used for the bioassay of auxin.
2014
Q1: Dr. F. Went noted that if coleoptile tips were removed and placed on agar for one hour, the agar would produce a bending when placed on one side of freshly-cut coleoptile stumps. Of what significance is this experiment? (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014)
(a) It made possible the isolation and exact identification of auxin.
(b) It is the basis for quantitative determination of small amounts of growth-promoting substances.
(c) It supports the hypothesis that IAA is auxin.
(d) It demonstrated polar movement of auxins.
Ans: (b)
Charles Darwin and his son Francis Darwin observed that the coleoptiles of Oat (Avena sativa) and canary grass (Phalaris canariensis) responded to unilateral illumination by growing towards the light source (phototropic curvature or phototropism). After a series of experiments, it was concluded that the tip of the coleoptile was the site of production of a substance, that caused the bending of coleoptile.
Q2: A few normal seedlings of tomato were kept in a dark room. After a few days they were found to have become white-coloured like albinos. Which of the following terms will you use to describe them? (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014)
(a) Mutated
(b) Embolized
(c) Etiolated
(d) Defoliated
Ans: (c)
Etiolation is the abnormal form of growth observed when plants grow in darkness or severely reduced light. Such plant characteristically have branched leaves and shoots, excessively long shoots and reduced leaves and root systems.
Q3: Which one of the following growth regulators is known as 'stress hormone'? (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014)
(a) Abscissic acid
(b) Ethylene
(c) GA3
(d) Indole acetic acid
Ans: (a)
Abscisic Acid (ABA) is called stress hormone which works in adverse environmental condition when there is low water content in atmosphere or in drought conditions. ABA causes the stomatal closure of leaves due to which the water loss by the plant is minimized.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Plant Growth & Development - Biology Class 11
| 1. What are the key factors influencing plant growth and development? |  |
| 2. How do plant hormones affect growth and development? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of photosynthesis in plant development? |  |
| 4. How do environmental stresses affect plant growth? |  |
| 5. What role does soil quality play in plant growth and development? |  |






















