Subsidiary books - Class 11 PDF Download
Name any three subsidairy books and also mention the transaction that are recorded in each of them?
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/632020/Name-any-three-subsidairy-books-and-also-mention-the-transaction-that-are-recorded-in-each-of-them-
Subsidiary book is the sub division of Journal. These are known as books of prime entry or books of original entry as all the transactions are recorded in their original form. In these books the details of the transactions are recorded as they take place from day to day in a classified manner.
The important subsidiary books used are as following:-
-Cash Book : Used to record all the cash receipts and payments.
-Purchase Book : Used to record all the credit purchases.
-Sales Book : Used to record all the credit sales
-Purchase Return Book : Used to record all goods returned by business to the supplier
-Sales Return Book : Used to record all good returned by the customer to the business.
-Bills Receivable Book : Used to record all accepted bills received by business.
-Bills Payable Book : Used to record all bill accepted by us to our creditors.
-Journal Proper : Used to record those transactions for which there is no separate book.
These subsidiary books are maintained because it may be impossible to record each transaction into the ledger as it occurs. And these books record the details of the transactions and therefore help the ledger to become brief. Future reference and any desired analysis becomes easy as transactions of similar nature are recorded together.
THREE BOOKS EXPLAIN HERE:
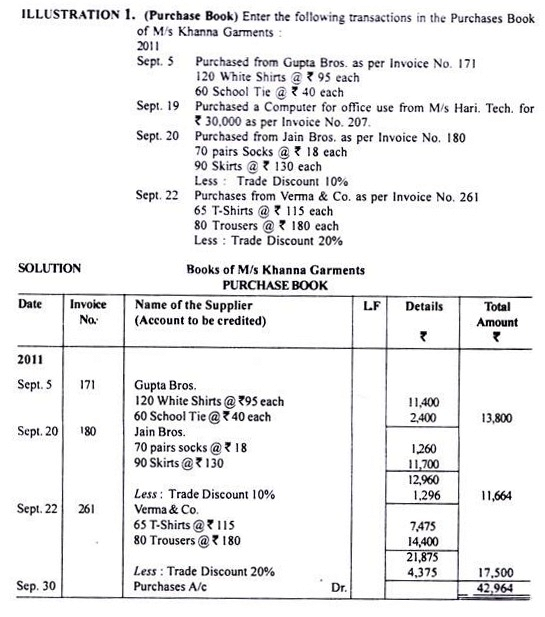
1. Purchase Book or Purchase Journal:
Purchase book is a book of original entry in which only credit purchases of goods are recorded. Cash purchases of goods are recorded in the cash book. Credit purchases of other assets are also not recorded in the purchase book; they are recorded in the journal proper.
Goods here mean the items or articles in which business enterprise is dealing with or we can say that goods are the items which are used by the business enterprise for regular sale. For example, purchase of computer by a business enterprise which is dealing in cloth shall not be treated as its goods and items related to computers shall be regarded as its assets. Similarly, purchase of cloth by a business enterprise which is dealing in computers shall not be treated as its goods since items relating to only computers are its goods.
Instead of recording transactions in the journal, the transactions relating to credit purchases of goods are directly recorded in the purchases book. However, the total of the purchases book shall be recorded on the debit side of the ‘Purchases Account’. The main intention for preparing the purchases book is to know the credit purchases at any particular period of time.
The format of purchases book is as under:
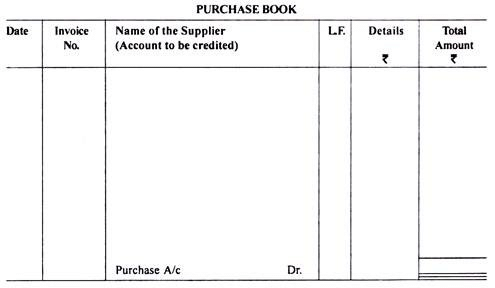
Explanations to Various Columns of Purchase Book:
(a) Date:
In this column, the date of the transaction, on which goods were purchased on credit, shall be recorded.
(b) Invoice Number:
The number of invoice (i.e., source document) showing the purchase of goods shall be recorded in this column.
(c) Name of the Suppliers:
In this column, name of the person/supplier, from whom the goods were purchased, shall be written along with detailed description of goods viz., quantity, quality, rate, gross amount, trade discount and sales tax etc.
(d) Ledger Folio (L.F.):
Page number of the ledger of the supplier on which the transaction is recorded shall be recorded in this column.
(e) Details:
The individual total amount of various items, if purchased from the same supplier, shall be recorded in this column. Total trade discount by the supplier and sales tax paid (if any) shall also be adjusted in this column.
(f) Total Amount:
In this, the net amount payable to the supplier shall be recorded. The total of this column shall be transferred to the debit side of purchases account.
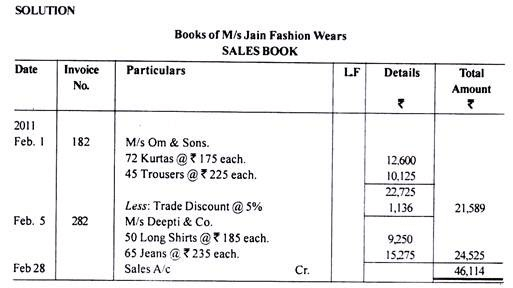
2. Sales Book or Sales Journal:
Sales book is a book of original entry in which only credit sales of goods are recorded. Cash sales of goods are recorded in the cash book. Credit sales of other assets are also not recorded in the sales book; they are recorded in the journal proper.
Goods here mean the items or articles in which business enterprise is dealing or we can say that goods are the items which are used by the business enterprise for regular sale. For example, sale of furniture by a business enterprise which is dealing in stationery shall not be treated as its goods and items related to stationery alone shall be regarded as its goods.
Instead of recording transactions in the journal, the transactions relating to credit sales of goods are directly recorded in the sales book. However, the total of the sales book shall be recorded on the credit side of the ‘Sales Account’ The main intention for preparing the sales book is to know the credit sales at any particular period of time.
The format of sales book is as under:
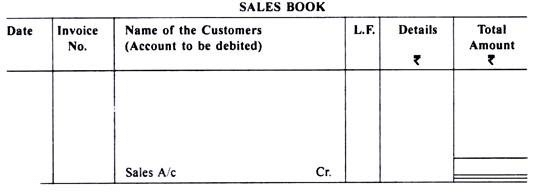
Explanations to Various Columns of Sales Book:
(a) Date:
In this column, the date of the transaction, on which goods were sold on credit, shall be recorded.
(b) Invoice Number:
The number of invoice (i.e., the source document) showing the sales of goods shall be recorded in this column.
(c) Name of the Customers:
In this column, name of the person/customers, to whom the goods were sold on credit, is written along with all details and description of goods viz., quantity, quality, rate, gross amount and trade discount etc.
(d) Ledger Folio (L.F.):
Page number of the ledger of the customer, on which the transaction is recorded, shall be recorded in this column.
(e) Details:
The individual total amount of various items, if sold to the same customer, shall be recorded in this column. Total trade discount allowed to the customer (if any) shall also be adjusted in this column.
(f) Amount:
In this the net amount receivable from the customer shall be recorded. The total of this column shall be transferred to the credit side of sales account.

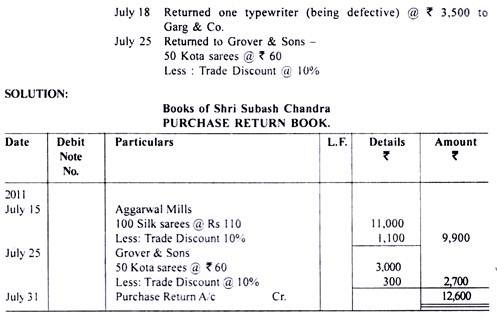
3. Purchases Return Book or Purchases Return Journal:
Purchases return book is a book of original entry in which transactions related to the return of purchases of goods are recorded.
There may be several reasons for returning the goods to the supplier; some of them are as under:
(a) On finding some defects in the goods.
(b) When goods sent are not as per the samples or specifications.
(c) If the quantity of goods supplied is more than the requirements.
(d) When there is a breach of agreement between the seller and the purchaser.
When the business enterprise returns the goods to the supplier, a debit note is sent to the party to whom this document is sent. Business enterprise may make a debit note against the supplier for an amount which is to be recovered from him when the business enterprise returns some goods which are defective in nature or not as per specifications.
In this document, all details about the date and amount of transaction, the name of the party whose account is debited along with reason for debiting his account shall be mentioned.It should be noted that the trade discount availed at the time of purchase shall also be adjusted at the time of returning the goods.
The format of purchases return book is as under:


FAQs on Subsidiary books - Class 11
| 1. What are subsidiary books in accounting? |  |
| 2. Why are subsidiary books important in accounting? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of the cash book in subsidiary books? |  |
| 4. How does the purchases book function in subsidiary books? |  |
| 5. Why is the sales book important in subsidiary books? |  |




















