Ex-16.1, Understanding Three Dimensional Shapes, Class 6, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics PDF Download
Q.1 Name any four objects from your environment, which have the form of
(i) A cuboid (ii) A cube
Sol.1: (i) A lunch box, a compass box, a book, and a duster.
(ii) A disc, a chalk box,a cubical cabin, and a tissue box.
Q.2 Draw a diagram to represent a cuboid. Label its vertices as P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W. Now write the names of its faces and edges.
Sol.2 : The diagram of a cuboid is shown below :
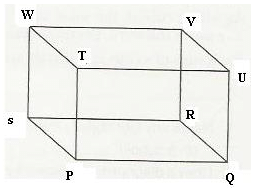
Faces -
PQRS (bottom)
TUVW (top)
TPQU (front)
WSRV (back)
TPSW (left)
UVRQ (right)
Edges –
PQ, QR, RS, SP
TU, UV, VW, WT
WS, SR, RV, VW
UV, VR, RQ, QU
Q.3 Draw a diagram to represent a cube. Label its vertices as A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H.
Now write the names of its faces and edges.
Sol.3 : The cube given below :
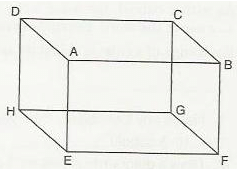
A cube has 6 faces and 12 edges.
Faces –
ABCD, EFGH, BVGF, ADHE, ABFE and CDHG.
Edges –
AB, BC, CD, DA, EF, FG, GH, HE, BF, CG, AE and HD.
Q.4 Figure represents a cuboid. The lengths of the edges AE, EF and FG are indicated as l, b and h respec. Indicated the lengths of all other edges.
Sol. 4 : AE = DH = BF = CG = L
EF = AB = CD = GH = B
FG = EH = AD = BC = H
Q5. In figure, if the face EFGH is taken as the base, the name the lateral faces. Also, name the line segment represent the height of the cuboid. (fig. from book)
Sol.5 : Following are the lateral faces for the base EFGH.
AEHD, AEFB, BFGC, DHGC.
AE or DH or BF or CG are the line segments representing the height of the cuboid.
Q.6 In fig. name the four diagonals of the cuboid. (fig. from book)
Sol.6 : The four diagonals of the cuboid CE, BH, AG and DF.
Q.7 In fig., name the(fig. from book)
(i) face parallel to BFGC
(ii) faces adjacent to BFGC
(iii) three edges which meet in the vertex G.
Sol.7 : (i) The faces parallel to BFGC is AEHD.
(ii) The faces adjacent to BFGC are BCDA, DCGH, ABFE, and EFGH.
(iii) GF, GH, CG.
Q.8 Fill in the blanks to make the following statements true :
(i) A cuboid has .................. vertices.
(ii) A cuboid has .................. edges.
(iii) A cuboid has .................. faces.
(iv) The number of lateral faces of a cuboid is ..................
(v) A cuboid all of whose edges are equal is called a ..................
(vi) Two adjacent faces of a cuboid meet in a line segment called its ..................
(vii)Each edge of a cuboid can be obtained as a line segment called in which two .................. meet.
(viii) .................. edges of a cube (or cuboid) meet at each of its vertices.
(ix) A .................. is a cuboid in which all the six faces are squares.
(x) The three concurrent edges of a cuboid meet at a point called the .................. of the cuboid.
Sol.8 : (i) eight
(ii) twelve
(iii) six
(iv) four
(v) cube
(vi) edge
(vii) adjacent faces
(viii) three
(ix) cube
(x) vertex or corner.
Q.9 In each of the following , state if the statement is true (T) or false (f) :
(i) Number of faces in a cuboid and the number of faces in a cube are equal.
(ii) A cube has twelve vertices.
Sol.9 : (i) True
(ii) False
Q.10 For the cuboid shown : (fig. from book)
(i) What is the base of this cuboid?
(ii) What are the lateral faces of this cuboid?
(iii) Name one pair of opposite faces. How many pairs of opposite faces are there. Name them.
(iv)Name all the faces of this cuboid which have X as a vertex. Also, name those which have VW as a side.
(v) Name the edges of this cuboid which meet at the vertex P. Also name those faces which meet at this vertex.
Sol.10 : (i) UVWX is the base of a cuboid.
(ii) The lateral faces for the base UVWX are UXSP, QVWR, PQVU and SXWR.
(iii) Any one pair of opposite faces among the lateral faces of the base are PQVU and SXWR or UXSP and QVWR.
There are two pairs of opposite faces among the lateral faces of the base of the cuboid.
(iv) The faces, which have one of the vertex as X, are UVWX, UXSP and SXWR.
The faces, which have VW as side, are QVWR and UVWX.
(v) Edges which meet at P are UP, SP, and PQ.
Faces which meet at vertex P are PQRS, UPSX,and PQVU.
Q.11 The dimensions of a cuboid with vertices A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H are as shown
(i) Which edges are of length 4 cm? Which edges are of length 5 cm?
(ii) Which faces have area equal to 20cm2?
(iii) Which faces have the largest area? What is this largest area?
(iv) Which faces have a diagonal equal to 5 cm?
(v)What is the area of the base of this cuboid?
(vi) Do all the lateral faces have the same area?
Sol.11 : (i) The edges of 4 cm length are AD, EH, BC, and FG.
The edges of 5 cm length are AB, EF, CD and GH.
(ii) The faces having dimensions of 5 cm x 4 cm would have an area of 20 cm2. And such faces are ABCD and EFGH.
(iii) ABCD and EFGH have the largest area of 20 cm2.
(There are three pairs of opposite faces of equal area. The area of opposite faces are: 3 x 4 cm2, 4 x 5 cm2, and 3 x 5 cm2. And among these, 4 x 5 cm2 is the largest.
(iv) The faces having sides of 3 cm and 4 cm respectively would have the diagonal of 5 cm. (As hypotenuse of a right- angles triangle is: 32 + 42 = 52).
Therefore, the faces ADHE and BCGF have the diagonal of 5 cm.
(v) The base has q dimension of 4 cm x 5 cm, so area of abase is: 4 x 5 = 20 cm2.
(vi) No, all lateral faces do not have the same area. The two lateral faces have an area of 3 x 5 = 15 cm2and rest of the two lateral faces have an area of 3 x 4 = 12 cm2.
FAQs on Ex-16.1, Understanding Three Dimensional Shapes, Class 6, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics
| 1. What are three-dimensional shapes? |  |
| 2. How do you define the volume of a three-dimensional shape? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a two-dimensional shape and a three-dimensional shape? |  |
| 4. How can understanding three-dimensional shapes be useful in real life? |  |
| 5. Can you provide some examples of three-dimensional shapes commonly found in our surroundings? |  |
















