Ex-19.2, Geometrical Constructions, Class 6, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics PDF Download
Q.1 How many lines can be drawn which are perpendicular to a given line and pass through a given point lying (i) outside it ? (ii) on it?
Sol.1 : (i) Explanation:
Perpendicular line from a given point to a given line is the shortest distance between them.
Only one shortest distance is possible.
Thus, only one perpendicular line is possible from the given point (outside the line) to a given line.
(ii) Explanation:
At any point on the line, we can draw only one perpendicular line.
Thus, on the given line on a point, we can draw only one perpendicular line.
Q.2 Draw a line PQ. Take a point R on it. Draw a line perpendicular to PQ and passing through R.
(i) Using ruler and set square. (ii) ruler and compasses.
Sol.2 : (i) Draw a line PQ and take a point R on it.
Place a set-square, such that its one arm of the right angle is along the line PQ .
Without disturbing the position of the set-square, place a ruler along its edge.
Now, without disturbing the position of the ruler, remove the set-square and draw a line MN through point R.
MN is the required line perpendicular to line PQ passing through R.
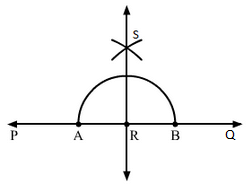
(ii) Draw a line PQ and take a point R on it.
With R as centre and taking a convenient radius, construct an arc touching the line PQ at two points A and B.
Now, with A and B as centres and radius greater than AR, construct two arcs cutting each other at S.
Join RS and extend it in both directions. This is the required line, which is perpendicular to PQ and passes through R.
Q.3 Draw a line l, take a point A not lying on l. Draw a line m such that m⊥l and passing through A.
Using (i) ruler and set square (ii) ruler and compass.
Sol.3 : (i) We draw a line L and take a point A outside it.
Place a set square PQR such that its one arm PQ of the right angle is along the line L.
Without disturbing the position of set-square, place a ruler along its edge PR.
Now, without disturbing the position of the ruler, slide the set-square along the ruler until its arm QR reaches point A.
Without disturbing the position of the set-square, draw a line m.
Line m is the required line perpendicular to line L.
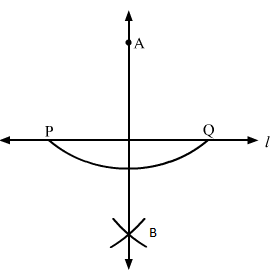
(ii) With A as centre, draw an arc PQ, which intersects line L at points P and Q.
Without disturbing the compass and taking P and Q as centres, we construct two arcs such that they intersect each other.
The point where both arcs intersect is B.
Join points A and B and extend it in both directions. This is the required line.
Q.4 Draw a line AB and take two points C and E on opposite sides of AB. Through C, draw draw CD⊥AB and through E draw EF⊥AB. Using (i) ruler and set square (ii) ruler and compass.
Sol.4 : (i) Draw a line AB and take two points C and E on the opposite sides of the line AB.
On the side of E, place a set-square PQR, such that its one arm PQ of the right angle is along the line AB. Without disturbing the position of the set-square, place a ruler along its edge PR.
Now, without disturbing the position of the ruler, slide the set square along the ruler until the arm QR reaches point C.
Without disturbing the position of the set-square, draw a line CD, where D is a point on AB.
CD is the required line and CD ⊥ AB.
We repeat the same process starting with taking set-square on the side of E, we draw a line EF ⊥ AB.
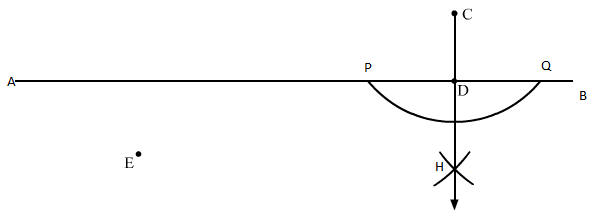
(ii) Draw a line AB and take two points C and E on its opposite sides.
With C as centre, draw an arc PQ, which intersects line AB at P and Q.
Taking P and Q as centres, construct two arcs, such that they intersect each other at H.
Join points H and C. HC crosses AB at D.
We have CD ⊥ AB.
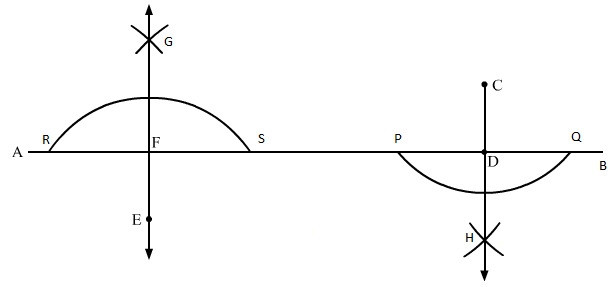
Similarly, take E as centre and draw an arc RS.
Taking R and S as centres, draw two arcs which intersect each other at G.
Join points G and E. GE crosses AB at F.
We have EF ⊥ AB.
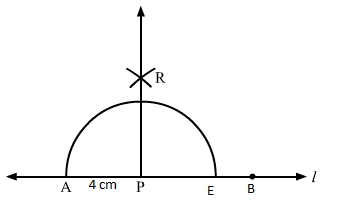
Q.5 Draw a line segment AB of length 10 cm.Mark a point P on AB such that AP = 4 cm. Mark a point P on AB such that AP = 4 cm. Draw a line through P perpendicular to AB.
Sol.5 : We draw line L and take a point A on it.
Using a ruler and a compass, we mark a point B, 10 cm from A, on the line L.
AB is the required line segment of 10 cm.
Again, we mark a point P, which is 4 cm from A, in the direction of B.
With P as centre, take a radius of 4 cm and construct an arc intersecting the line L at two points A and E.
With A and E as centres, take a radius of 6 cm and construct two arcs intersecting each other at R.
We join PR and extend it. PR is the required line, which is perpendicular to AB.
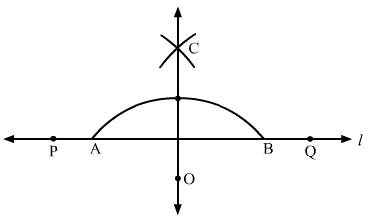
Q.6 Draw a line segment PQ of length of length 12 cm. Mark a point O outside this segment. Draw a line through O perpendicular to PQ.
Sol. 6 : Draw a line L and take a point P on it.
Using a ruler and a compass, mark a point Q on the line L, where PQ = 12 cm.
Mark a point Q outside PQ.
Now, with O as centre, draw an arc of appropriate radius such that the arc cuts the line at points A and B.
Taking A and B as centres, construct two arcs such that they intersect each other at C.
Join OC. OC is the required line, which is perpendicular to PQ.
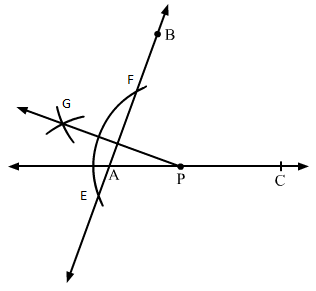
Q.7 Using a protractor, draw ∠BAC of measure 700. On side AC, take a point P, such that AP = 2cm. From P draw a line perpendicular to AB.
Sol.7 : Draw a line segment AC on a line L
(i) Take a protractor and place it on the segment AC such that segment AC coincides with the line of diameter of protractor and middle of this line coincides with point A.
(ii) Counting from the right side, mark the point as B at the point of 70° of the protractor and draw AB. (iii) Now, measuring 2 cm from A on AC, mark a point P.
(iv) With P as centre, draw an arc intersecting line 1 at points E and F.
(v) Using the same radius and E and F as centres, construct two arcs that intersect at point G on the other side.
(vi) Join PG.
Q.8 Draw a line segment AB of length 8 cm. At each end of this line segment, draw a line perpendicular to AB. Are these two lines parallel?
Sol.8 : (i) Take a convenient radius with A as centre and draw an arc intersecting the line at points W and X.
(ii) With W and X as centres and radius greater than AW, construct two arcs intersecting each other at M.
(iii) Join AM and extend it in both directions to P and Q.
(iv) Take a convenient radius with B as centre and draw an arc intersecting the line at points Y and Z.
(v) With Y and Z as centres and a radius greater than YB, construct two arcs intersecting each other at N.
(vi) Join BN and extend it in both directions to S and R.
Let the lines perpendicular at A and B be PQ and RS, respectively.
Since, ∠QAB = 90° and ∠ABR = 90°
Therefore, ∠QAB = ∠ABR.
When two parallel lines are intersected by a third line, the two alternate interior angles are equal.
Since, ∠QAB = ∠ABR
Therefore, PQ and RS are parallel.
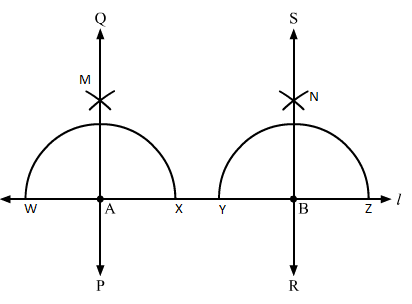
Q.9 Using a protractor, draw ∠BAC of measure 450. Take a point P in the interior of ∠BAC. From P draw line segments PM and PN such that PM⊥AB and PN⊥AC. Measure ∠MPN.
Sol.9 : (i) Draw a line segment A on the line L .
(ii) Take a protractor and place it on the segment AC such that AC coincides with the line of the diameter of the protractor and the middle point of the line coincides with point A.
(iii) Counting from the right side, mark a point as B at the point of 45° of protractor and draw a line segment AB.
(iv) Take a convenient radius with P as centre, construct an arc intersecting the line segments AB at T and Q and AC at R and S.
(v) Using the same radius and with T and Q as centres, construct two arcs intersecting at G on the other side.
(vi) Using the same radius and with R and S as centres, construct two arcs intersecting at H on the other side.
(vii) Join PG and PH which intersects AB and AC at M and N, respectively.
On measuring ∠MPN using a protractor, we get it equal to 135°.
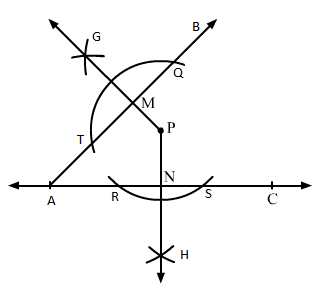
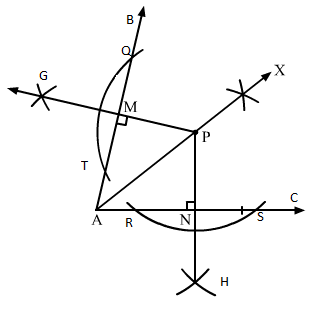
Q.10 Draw an angle and label it as ∠BAC. Draw a bisector ray AX and take point P on it. From P draw line segments PM and PN, such that PM⊥AB and PN⊥AC, where M and N are respectively, points on rays AB ansd AC. Measure PM and PN. Are the two lengths equal.?
Sol.10 : (i) Draw ∠BAC on the line segment AC.
With a convenient radius and A as centre, draw an arc from AB and AC.
(ii) The points where arc cuts AB and AC, take both points as centres and draw two small arcs intersecting at X. Now, draw AX.
(iii) Take a point P on the ray AX.
(iv) Take a convenient radius with P as centre and construct an arc intersecting the line segments AB at T and Q and AC at R and S, respectively.
(v) Using the same radius and with T and Q as centres, construct two arcs intersecting at G on the other side.
(vi) Using the same radius and with R and S as centres, construct two arcs intersecting at H on the other side.
(vii) Join PG and PH, which intersects AB and AC at M and N, respectively.
On measuring PM and PN using a ruler, we find that both are equal.
FAQs on Ex-19.2, Geometrical Constructions, Class 6, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 6 Mathematics
| 1. What are RD Sharma Solutions? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of geometrical constructions in mathematics? |  |
| 3. How can I use RD Sharma Solutions for geometrical constructions? |  |
| 4. Are RD Sharma Solutions for geometrical constructions suitable for Class 6 students? |  |
| 5. Can RD Sharma Solutions for geometrical constructions be accessed online? |  |





















