Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Class 10 Electricity numerical questions
Class 10 Electricity numerical questions PDF Download
Given below are the Class 10 Science Numerical Questions for electricity
a) Concepts questions
b) Calculation problems
c) Multiple choice questions
d) Long answer questions
e) Fill in the blank's
1) A wire of length 3 m and area of cross-section 1.7X10-6 m2 has a resistance 3X10-2ohm.
a) What is the formula for resistivity of the wire and what is the unit of it
b) Calculate the resistivity of the wire
Ans)
a) Resistivity of the wire is given by
ρ=RAL
And It unit is Ohm-m
b) In this case
L=3 m
A=1.7X10-6 m2
R=3X10-2 ohm
So
ρ=1.7X10-8 Ohm-m
2) The table given below shows the resistivity of three Material X, Y and Z?
a) Arrange the samples in increasing order of conductivity
b) Which of these is best conductor?
c) Which are these is best insulator?
Ans)
a) Conductivity is inversely proportional to resistivity
So
Y< X< Z
b) Z is the best conductor as it has least resistivity
c) Y is the best insulator as it has highest resistivity
3) There are m resistor each of resistance R. First they all are connected in series and equivalent resistance is X. Now they are connected in parallel and equivalent resistance is Y. What is the ratio of X and Y?
Ans)
Series combination
X=R R R …….= mR
Parallel combination
1Y=1R 1R 1R ...=mR
Or Y=R/m
So X : Y=m2 : 1
4) We have four resistors A ,B ,C and D of resistance 4ohm,8ohm ,12 ohm and 24 ohm respectively?
Ans)
Lowest resistance is obtained in parallel combination
1R=14 18 112 124
Or R=2Ω
Highest resistance is obtained in series combination
R=4 8 12 24=48Ω
5) Three resistors 5Ω, 10Ω and 30Ω are connected in parallel with the battery of Voltage 6V?
Ans)
Potential difference remains same across parallel combination
So current in each resistor is calculated as
I1=V/R1=6/5=1.2 A
I2=V/R2=6/10=.6 A
I3=V/R3=6/30=.2 A
Total current in the circuit
I=I1 I2 I3=1.2 .6 .2=2 A
Effective resistance
1R=15 110 130
a) Find the power consumed by the bulb
b) If the electric distribution company changes Rs 5 for 6 KWH, what is the monthly bill for 60 days
Ans) Power of the electrical bulb is given by
P=V X I=.8 A X 250 V= 200 W =.2 KW
Total energy consumption by the bulb in 60 days
E=P X t= .2 X8 X60=96 KWH
So cost will be =5X96/6=80 Rs
7)
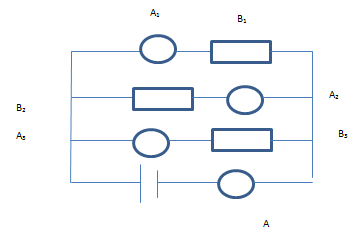
A1 ,A2 ,A3 and A are ammeters connected in the circuit
B1 ,B2 and B3 are three identical bulbs
They all are connected to Voltage source as shown in Figure
When the three bulb are working good and glowing ,the current recorded in Ammeter A is 6 A
Answer Following questions
a) Same amount of current will go through each Bulb. And the value is 2 A .True or False
b) If the Bulb B3 is blown away, the bulb B1and B2 will start glowing more. True or False
c) What will happen to all the ammeter reading if Bulb B1 is blown away
d) The current shown in Ammeter A remains even any bulb goes down. True or False
Ans)
a) Since Bulb are identical and connected in parallel with Voltage. Same current will flow through each bulb. Since the total current is 6 A.Individual current will be 2 A
b) If the Bulb B3 is blown away, The potential difference across other bulb still remains same, So same current will flow and they will glow as it is. No change
c) when Bulb B1 goes down, the current in that part become zero.
So reading of Ammeter A1 becomes zero
Reading of Ammeter A2 will remain same i.e. 2 A
Reading of Ammeter A3 will remain same i.e. 2 A
Reading of Ammeter A will be = 2 2=4 A
d) As shown above, the reading of Ammeter A will change
8) Gave the formula for each
Solutions
a) Concepts questions
b) Calculation problems
c) Multiple choice questions
d) Long answer questions
e) Fill in the blank's
1) A wire of length 3 m and area of cross-section 1.7X10-6 m2 has a resistance 3X10-2ohm.
a) What is the formula for resistivity of the wire and what is the unit of it
b) Calculate the resistivity of the wire
Ans)
a) Resistivity of the wire is given by
And It unit is Ohm-m
b) In this case
L=3 m
A=1.7X10-6 m2
R=3X10-2 ohm
So
ρ=1.7X10-8 Ohm-m
2) The table given below shows the resistivity of three Material X, Y and Z?
| Samples | X | Y | Z |
| Resistivity | 3 X10-9 | 11.1 X10-6 | 18X10-17 |
b) Which of these is best conductor?
c) Which are these is best insulator?
Ans)
a) Conductivity is inversely proportional to resistivity
So
Y< X< Z
b) Z is the best conductor as it has least resistivity
c) Y is the best insulator as it has highest resistivity
3) There are m resistor each of resistance R. First they all are connected in series and equivalent resistance is X. Now they are connected in parallel and equivalent resistance is Y. What is the ratio of X and Y?
Ans)
Series combination
X=R R R …….= mR
Parallel combination
Or Y=R/m
So X : Y=m2 : 1
4) We have four resistors A ,B ,C and D of resistance 4ohm,8ohm ,12 ohm and 24 ohm respectively?
| 1 | Lowest resistance which can be obtained by combining these four resistors | |
| 2 | highest resistance which can be obtained by combining these four resistors |
Lowest resistance is obtained in parallel combination
Or R=2Ω
Highest resistance is obtained in series combination
5) Three resistors 5Ω, 10Ω and 30Ω are connected in parallel with the battery of Voltage 6V?
| S.no | Questions | |
| 1 | The value of current across each resistor | |
| 2 | The value of Potential difference across each resistor | |
| 3 | Total current in the circuit | |
| 4 | Effective resistance of the circuit |
Potential difference remains same across parallel combination
So current in each resistor is calculated as
I1=V/R1=6/5=1.2 A
I2=V/R2=6/10=.6 A
I3=V/R3=6/30=.2 A
Total current in the circuit
I=I1 I2 I3=1.2 .6 .2=2 A
Effective resistance
- R= 3Ω
a) Find the power consumed by the bulb
b) If the electric distribution company changes Rs 5 for 6 KWH, what is the monthly bill for 60 days
Ans) Power of the electrical bulb is given by
P=V X I=.8 A X 250 V= 200 W =.2 KW
Total energy consumption by the bulb in 60 days
E=P X t= .2 X8 X60=96 KWH
So cost will be =5X96/6=80 Rs
7)
A1 ,A2 ,A3 and A are ammeters connected in the circuit
B1 ,B2 and B3 are three identical bulbs
They all are connected to Voltage source as shown in Figure
When the three bulb are working good and glowing ,the current recorded in Ammeter A is 6 A
Answer Following questions
a) Same amount of current will go through each Bulb. And the value is 2 A .True or False
b) If the Bulb B3 is blown away, the bulb B1and B2 will start glowing more. True or False
c) What will happen to all the ammeter reading if Bulb B1 is blown away
d) The current shown in Ammeter A remains even any bulb goes down. True or False
Ans)
a) Since Bulb are identical and connected in parallel with Voltage. Same current will flow through each bulb. Since the total current is 6 A.Individual current will be 2 A
b) If the Bulb B3 is blown away, The potential difference across other bulb still remains same, So same current will flow and they will glow as it is. No change
c) when Bulb B1 goes down, the current in that part become zero.
So reading of Ammeter A1 becomes zero
Reading of Ammeter A2 will remain same i.e. 2 A
Reading of Ammeter A3 will remain same i.e. 2 A
Reading of Ammeter A will be = 2 2=4 A
d) As shown above, the reading of Ammeter A will change
8) Gave the formula for each
| 1 | Ohm’s Law | |
| 2 | Resistance in terms of Length,Area,resistivity | |
| 3 | Current in terms of Resistance and Voltage | |
| 4 | Equivalent Resistance for Resistors in Series | |
| 5 | Equivalent Resistance for Resistors in Parallel | |
| 6 | Power produced in the resistance |
| 1 | Ohm’s Law | V=IR |
| 2 | Resistance in terms of Length,Area,resistivity | |
| 3 | Current in terms of Resistance and Voltage | |
| 4 | Equivalent Resistance for Resistors in Series | R=R1 R2 R3….. |
| 5 | Equivalent Resistance for Resistors in Parallel | |
| 6 | Power produced in the resistance | P=I2R |
FAQs on Class 10 Electricity numerical questions
| 1. What is electricity and how does it work? |  |
Ans. Electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It is caused by the movement of electrons from one atom to another. When a source of energy, such as a battery or a power plant, is connected to a circuit, it creates a potential difference or voltage. This voltage then causes the electrons to move, creating an electric current.
| 2. What are the different units used to measure electricity? |  |
Ans. The basic units used to measure electricity are voltage (measured in volts), current (measured in amperes), and resistance (measured in ohms). These units are interconnected through Ohm's law, which states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied and inversely proportional to the resistance.
| 3. How does a circuit work? |  |
Ans. A circuit is a closed loop through which electricity can flow. It typically consists of a power source, such as a battery, wires to carry the electric current, and different components, such as resistors, capacitors, and switches. When the circuit is complete, meaning all components are connected in a continuous path, the electric current can flow, allowing the circuit to work.
| 4. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits? |  |
Ans. In a series circuit, the components are connected one after another, forming a single path for the electric current. In this type of circuit, the same current flows through each component, and the voltage is divided among them. In contrast, a parallel circuit has multiple branches, with each component connected to the power source independently. Here, the voltage across each component is the same, but the current is divided among the branches.
| 5. How does resistance affect the flow of electricity in a circuit? |  |
Ans. Resistance is a property of a material that opposes the flow of electric current. It can be affected by factors such as the length, cross-sectional area, and temperature of the conductor. The higher the resistance, the more difficult it is for the current to flow. According to Ohm's law, the current in a circuit is inversely proportional to the resistance. Therefore, an increase in resistance leads to a decrease in current flow.
Related Searches




















