Subjective Type Questions: The Solid State & Surface Chemistry | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
1. The density of mercury is 13.6 g/ml. Calculate approximately the diameter of an atom of mercury assuming that each atom is occupying a cube of edge length equal to the diameter of the mercury atom. (1983 - 3 Marks)
Ans : 2.91Å
Soluton:
Avogadro’s number = 6.023 × 1023
At. wt. of mercury(Hg) = 200
Q In 1 g of Hg, the total number of atom
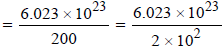
3.0115 × 1021 = 3.012 × 1021
Density of Mercury (Hg) = 13.6 g/c.c.
Q mass of 3.012 × 1021 atoms = 1g
∴ mass of 3.012 × 1021 atoms = 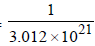
Now volume of 1 atom of mercury (Hg)
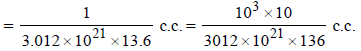
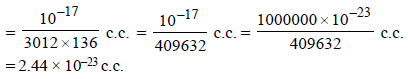
Since each mercury atom occupies a cube of edge length equal to its diameter, therefore,
diameter of one Hg atom
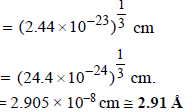
2. Sodium metal crystallizes in body centred cubic lattice with the cell edge, a = 4.29Å. What is the radius of sodium atom? (1994 - 2 Marks)
Ans: 1.86 Å
TIPS/Formulae :
For bcc lattice, (radius), 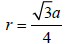
Solution:
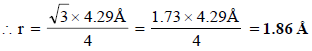
3. A metallic element crystallises into a lattice containing a sequence of layers of ABABAB..... Any packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What percentage by volume of this lattice is empty space? (1996 - 3 Marks)
Ans : 25.93%
Solution: For a hcp unit cell, there are 6 atoms per unit cell. If r is the radius of the metal atoms, volume occupied by the metallic atoms =
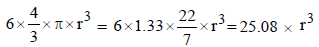 Geometrically it has been shown that the base area of hcp unit cell
Geometrically it has been shown that the base area of hcp unit cell 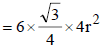 and the height
and the height 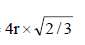
∴ Volume of the unit cell
= Area × height = 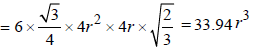
∴ Volume of the empty space of one unit cell = 33.94 r3 – 25.08 r3 = 8.86 r3
∴ Percentage void = 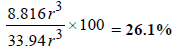
4. Chromium metal crystallizes with a body centred cubic lattice. The length of the unit cell edge is found to be 287 pm. Calculate the atomic radius. What would be the density of chromium in g/cm3? (1997 - 3 Marks)
Ans : 124.27 pm, 7.30 g/ml
Solution:
For bcc lattice ,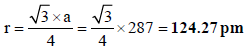
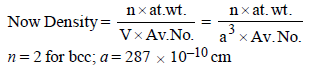
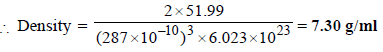
5. A metal crystallises into two cubic phases, face centered cubic (FCC) and body centred cubic (BCC), whose unit cell lengths are 3.5 and 3.0 Å, respectively, Calculate the ratio of densities of FCC and BCC. (1999 - 3 Marks)
Ans : 1.259
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae : Density in fcc = 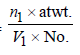
Density in bcc = 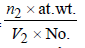
fcc unit cell length = 3.5Å; bcc unit cell length = 3.0 Å
Density in fcc = 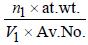
Density in bcc = 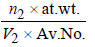
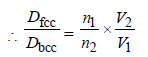
n1 for fcc = 4; Also V1 = a3 = (3.5 x 10-8)3
n2 for fcc = 2; Also V2 = a3 = (3.0 x 10-8)3
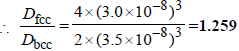
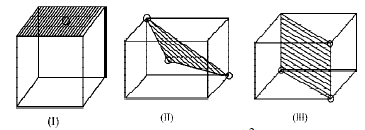
6. The figures given below show the location of atoms in three crystallographic planes in a FCC lattice. Draw the unit cell for the corresponding structure and identify these planes in your diagram. (2000 - 3 Marks)
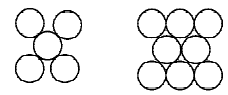
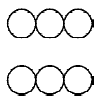
Solution :
7. You are given marbles of diameter 10 mm. They are to be placed such that their centres are lying in a square bound by four lines each of length 40 mm. What will be the arrangements of marbles in a plane so that maximum number of marbles can be placed inside the area? Sketch the diagram and derive expression for the number of molecules per unit area. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans : (a) 25
Solution:
The area of square = 4 × 4 = 16 cm2
Again to have the maximum number of spheres the packing
must be hcp.
Maximum number of spheres =
14 + 8 = 14 + 4 = 18.
(Full) (half)
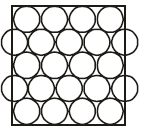
Area = 16 cm2
∴ Number of spheres per cm2 = 18/16= 1.126
8. 1 gm of charcoal adsorbs 100 ml 0.5 M CH3COOH to form a monolayer, and thereby the molarity of CH3COOH reduces to 0.49. Calculate the surface area of the charcoal adsorbed by each molecule of acetic acid. Surface area of charcoal = 3.01 × 102 m2/gm. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans : 5 × 10–19 m2
Solution :
Number of moles of acetic acid in 100 ml before adding charcoal = 0.05
Number of moles of acetic acid in 100 ml after adding charcoal = 0.049
Number of moles of acetic acid adsorbed on the surface of charcoal = 0.001
Number of molecules of acetic acid adsorbed on the surface of charcoal = 0.001 × 6.02 × 1023 = 6.02×1020
Surface area of charcoal = 3.01 × 102 m2 (given)
Area occupied by single acetic acid molecule on the surface of charcoal 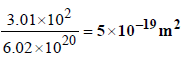
9. A compound AB has rock salt type structure. The formula weight of AB is 6.023 Y amu, and the closest A – B distance is Y1/3 nm, where Y is an arbitrary number. (2004 - 2 Marks)
(a) Find the density of lattice
(b) If the density of lattice is found to be 20 kg m–3 , then predict the type of defect.
Ans :
(a) 5.0 kg/m3,
(b) metal excess defect
Solution:
(a) TIPS/Formulae : Density of AB = 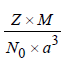
Here, Z = 4 (for fcc), M = 6.023 Y,
a = 2 Y1/3 nm = 2 Y1/3 × 10–9 m
Thus,
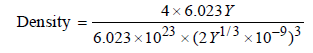
= 5.0kgm-3
(b) Since the observed density (20 kg m–3) of AB is higher than the calculated (5 kg m–3), the compound must have metal excess defect. non-stocheometric defect.
10. In face centred cubic (fcc) crystal lattice, edge length is 400 pm. Find the diameter of greatest sphere which can be fit into the interstitial void without distortion of lattice. (2005 - 2 Marks)
Ans : 117.16 pm
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae : For an octhedral void a = 2 (r + R)
In fcc lattice the largest void present is octahedral void. If the radius of void sphere is R and of lattice sphere is r. Then,
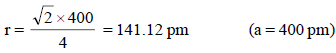
Applying condition for octahedral void, 2 (r + R) = a
∴ 2 R = a – 2r = 400 – 2 × 141. 12
∴ Diameter of greatest sphere = 117.16 pm
11. 20% of surface sites are occupied by N2 molecules. The density of surface site is 6.023 × 1014 cm–2 and total surface area is 1000 cm2. The catalyst is heated to 300 K while N2 is completely desorbed into a pressure of 0.001 atm and volume of 2.46 cm3. Find the number of active sites occupied by
each N2 molecule. (2005 - 4 Marks)
Ans: 2
Solution :
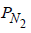 = 0.001 atm, T = 300 K, V = 2.46 cm2
= 0.001 atm, T = 300 K, V = 2.46 cm2
∴ Number of N2 molecules
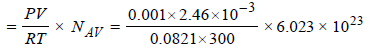
= 6.016 × 1016
Now total number of surface sites = Density × Total surface area
= 6.023 × 1014 × 1000 = 6.023 × 1017
Sites occupied by N2 molecules
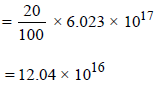
∴ No. of sites occupied by each N2 molecule 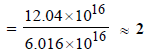
12. The edge length of unit cell of a metal having molecular weight 75 g/mol is 5Å which crystallizes in cubic lattice. If the density is 2 g/cc then find the radius of metal atom (NA = 6 × 1023). Give the answer in pm. (2006 - 6M)
Ans : 217 pm
Solution:
TIPS/Formulae : For bcc ; 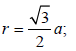
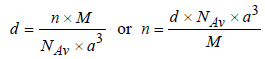
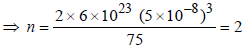
Therefore Metal crystallizes in BCC structure and for a BCC lattice 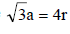
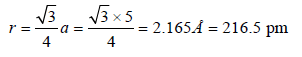
So the required answer is 217 pm
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Subjective Type Questions: The Solid State & Surface Chemistry - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What are the properties of solids in the solid state? |  |
| 2. What is surface chemistry and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between crystalline and amorphous solids? |  |
| 4. What is adsorption and how does it differ from absorption? |  |
| 5. How does the size and charge of colloidal particles affect their stability? |  |
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















