Subjective Type Questions: Chemical Kinetics & Nuclear Chemistry- 2 | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
11. The nucleidic ratio, 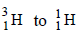 in a sample of water is 8.0 × 10–18 : 1. Tritium undergoes decay with a half life period of 12.3 years. How many tritium atoms would 10.0 g of such a sample contain 40 years after the original sample is collected? (1992 - 4 Marks)
in a sample of water is 8.0 × 10–18 : 1. Tritium undergoes decay with a half life period of 12.3 years. How many tritium atoms would 10.0 g of such a sample contain 40 years after the original sample is collected? (1992 - 4 Marks)
Solution:
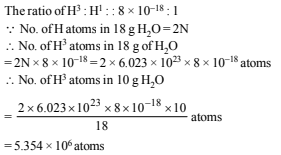
No. of atoms left after 40 years are derived as follows using the relation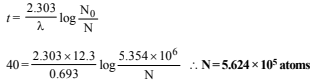
12. A first order reaction A→ B , requires activation energy of 70kJ mol–1. When a 20% solution of A was kept at 25°C for 20 minutes, 25% decomposition took place. What will be the percent decomposition in the same time in a 30% solution maintained at 40°C? Assume that activation energy remains constant in this range of temperature. (1993 - 4 Marks)
Solution:


13. The gas phase decomposition of dimethyl ether follows first order kinetics.
CH3 -O- CH3(g) → CH4(g) + H2(g) + CO(g)
The reaction is carried out in a constant volume container at 500°C and has a half life of 14.5 minutes. Initially, only dimethyl ether is present at a pressure of 0.40 atmosphere.
What is the total pressure of the system after 12 minutes? Assume ideal gas behaviour. (1993 - 4 Marks)
Solution: 
Since volume and temp. are constant, final pressure :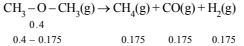
Hence total pressure = 0.4 – 0.175 + 3 × 0.175 = 0.749 atm
14. The progress of the reaction, A  nB with time, is presented in figure given below. Determine
nB with time, is presented in figure given below. Determine
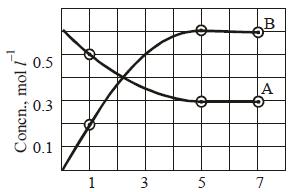
(i) the value of n
(ii) the equilibrium constant, K and
(iii) the initial rate of conversion of A. (1994 - 3 Marks)
Solution:
(i) According to Fig. in the given time of 4 hours (1 to 5) concentration of A falls from 0.5 to 0.3 M, while in the same time concentration of B increases from 0.2 M to
0.6 M.
Decrease in concentration of A in 4 hours
= 0.5 – 0.3 = 0.2 M
Increase in concentration of B in 4 hours
= 0.6 – 0.2 = 0.4 M
Thus increase in concentration of B in a given time is twice the decrease in concentration of A. Thus n = 2.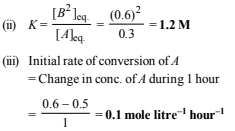
15. From the following data for the reaction between A and B. (1994 - 5 Marks)
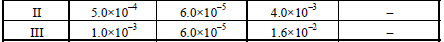
Calculate
(i) the order of the reaction with respect to A and with
respect to B,
(ii) the rate constant at 300K
(iii) the energy of activation, and
(iv) the pre-exponential factor
Solution:
Let the order with respect to A is x and the order with respect to B is y
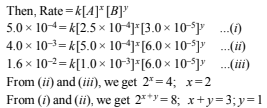
∴ The rate equation for the reaction is
Rate = k [A]2[B]
(i) Thus order of reaction with respect to A = 2 and order of reaction with respect to B = 1.
(ii) Rate constant (k1) at 300 K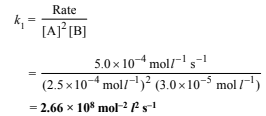
(iii) Determination of energy of activation :Rate constant (k2) at 320 K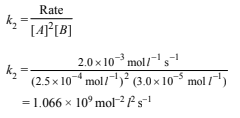
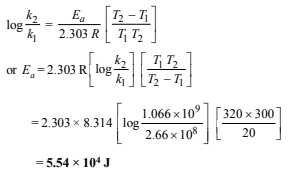
(iv) Determination of the pre-exponential factor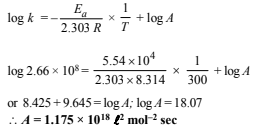
16. One of the hazards of nuclear explosion is the generation of 90Sr and its subsequent incorporation in bones. This nuclide has a half-life of 28.1 years. Suppose one microgram was absorbed by a new-born child, how much 90Sr will remain in his bones after 20 years? (1995 - 2 Marks)
Solution:
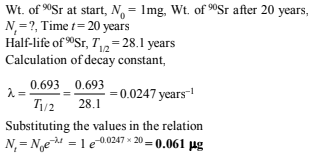
17. At 380°C, the half-life period for the first order decomposition of H2O2 is 360 min. The energy of activation of the reaction is 200 kJ mol-1 . Calculate the time required for 75% decomposition at 450°C. (1995 - 4 Marks)
Solution:

On usual calculations, k723 K =6.81 ×10–2 min–1
Calculation of time for 75% decomposition at 723 K
Let the initial amount of H2O2, a = 1
∴ Amount at the required time, (a – x) = 0.25
Substituting the values in the given relation,
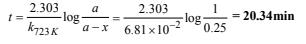
18. 227Ac has a half-life of 21.8 years with respect to radioactive decay. The decay follows two parallel paths. one leading to 227Th and the other to 223Fr. The percentage yields of these two daughter nuclides are 1.2 and 98.8 respectively. What are the decay constants (l) for each of the separate paths? (1996 - 2 Marks)
Solution:
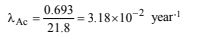

19. The ionisation constant of 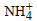 in water is 5.6×10–10 at 25°C. The rate constant for the reaction of
in water is 5.6×10–10 at 25°C. The rate constant for the reaction of 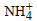 and OH- to form NH3 and H2O at 25°C is 3.4×1010 L mol–1s–1. Calculate the rate constant for proton transfer from water to NH3. (1996 - 3 Marks)
and OH- to form NH3 and H2O at 25°C is 3.4×1010 L mol–1s–1. Calculate the rate constant for proton transfer from water to NH3. (1996 - 3 Marks)
Solution:
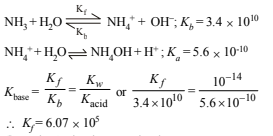
20. The rate constant for the first order decomposition of a certain reaction is described by the equation
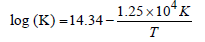 (1997 - 5 Marks)
(1997 - 5 Marks)
(i) What is the energy of activation for this reaction?
(ii) At what temperature will its half-life period be 256 minutes?
Solution:
(i) The Arrhenius equation is
k = A exp (–Ea/RT)
Taking natural logarithm, we get
ln k = ln A – Ea/RT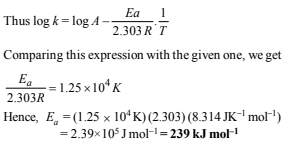
(ii) The reaction is first order as the unit of rate constant is s–1. For a first order reaction,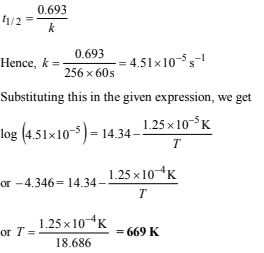
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Subjective Type Questions: Chemical Kinetics & Nuclear Chemistry- 2 - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What is chemical kinetics and why is it important in chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction? |  |
| 3. How can we determine the rate of a chemical reaction experimentally? |  |
| 4. What is nuclear chemistry and why is it important? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of radioactive decay? |  |
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















