JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids- 3 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.31. Suggest appopriate structures for the missing compounds. (The number of carbon atoms remains the same throughout the reactions.) (1996 - 3 Marks)
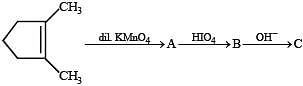
Solution.
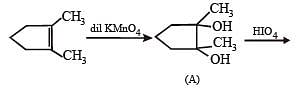
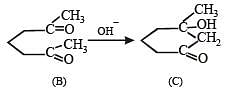
The last step is intramolecular aldol condensation.
Q.32. An ester A (C4H8O2), on treatment with excess methyl magnesium chloride followed by acidification, gives an alcohol B as the sole organic product. Alcohol B, on oxidation with NaOCl followed by acidification, gives acetic acid. Deduce the structures of A and B. Show the reactions involved. (1998 - 6 Marks)
Ans.
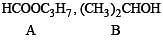
Solution. We know that esters on treatment with excess of methyl magnesium chloride either give secondary alcohols (from alkyl formates) or tertiary alcohols (from esters other than formates). However, tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidised, hence the alcohol should be secondary alcohol and thus ester is alkyl formate. Hence ester A (C4H8O2) should be HCOOC3H7. Thus the various reactions and nature of compound B can be established as below.
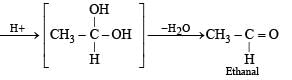
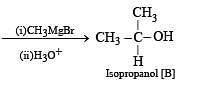
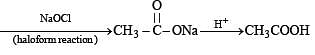
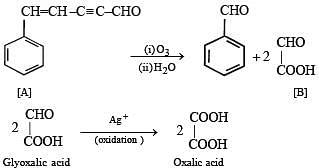
Q.33. An aldehyde A (C11H8O), which does not undergo self aldol condensation, gives benzaldehyde and two moles of B on ozonolysis. Compound B, on oxidation with silver ion gives oxalic acid. Identify the compounds A and B. (1998 - 2 Marks)
Ans. 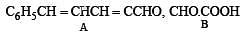
Solution.
Following informations are provided by the problem.
(i) Sin ce al deh yde A (C11H8O) gives C6H5CHO on ozonolysis, it must have a benzene nucleus and a side chain. The side chain should have five carbon (C11–C6 =C5), three hydrogen (H8-H5=H3) and one oxygen atom, i.e., it should be C5H3O. Further the compound A has an aldehydic group, so the side chain can be written as C4H2CHO.
(ii) Formation of two moles of B from one mole of A by ozonolysis indicates that the side chain must possess two unsaturated linkages, one of which must be alkyne type, suggested by very low number of hydrogen atoms.
(iii) Further since the aldehyde A does not undergo aldol condensation, a -hydrogen is absent and hence triple bond should be present between C2 and C3.
(iv) Thus the side chain C4H2CHO of A can be written as – CH = CH – C ≡ C – CHO.
(v) Thus compound A should possess following structure which explains all the given reactions.
Q.34. Write the intermediate steps for the following reaction. (1998 - 2 Marks)
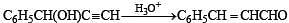
Solution.
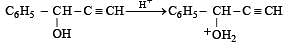
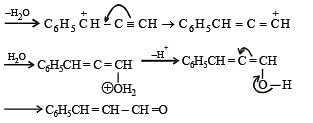
Q.35. Complete the following reaction with appropriate structures of products/reagents : (1998 - 2 + 2 Marks)
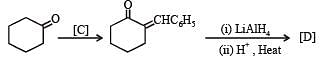
Solution.
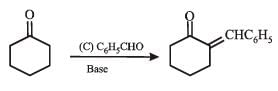
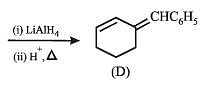
LiAlH4 reduces only ketonic group to 2° alcoholic group without affecting double bond.
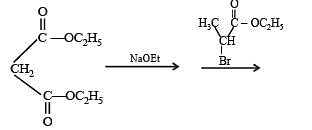
Q.36. Complete the following reaction with appropriate reagents : (1999 - 3 Marks)
Solution. 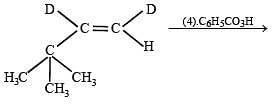
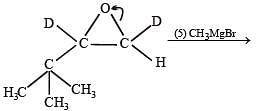
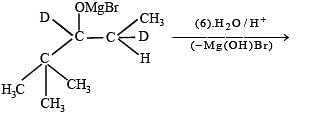
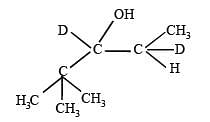
Q. 37. Explain briefly the formation of the products giving the structures of the intermediates.
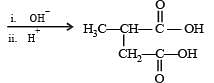 (1999 - 5 Marks)
(1999 - 5 Marks)
Solution.
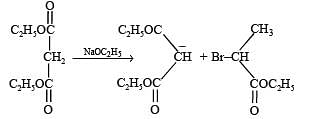
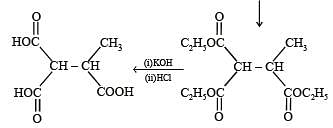
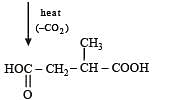
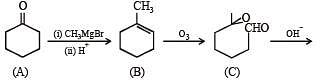
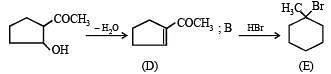
Q.38. An organ ic compound A, C6H10O on r eacti on wit h CH3MgBr followed by acid treatment gives compound B. The compound B on ozonolysis gives compound C, which in presence of a base gives 1-acetylcyclopentene D. The compound B on reaction with HBr gives compound E. Write the structures of A, B, C and E. Show how D is formed from C ? (2000 - 5 Marks)
Solution. TIPS/Formulae :
The given reaction can be summarised as below :
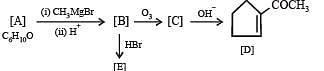
Conclusions from the set of reactions
(i) Carbon-hydrogen ratio of A indicates that it is a cyclic compound
(ii) Reaction of A with CH3MgBr indicates that it should have a ketonic group.
(iii) As B undergoes ozonolysis to form C, It must have a double bond, and C must have two carbonyl groups.
(iv) Reaction of C (a dicarbonyl compound) with a base gives a cyclic compound, it indicates that intramolecular condensation have occurred during this conversion.
Thus A is cyclohexanone which explains all the given reactions.
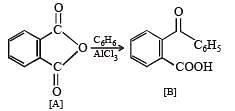
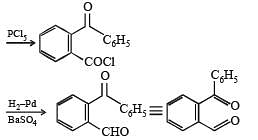
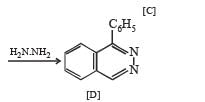
Q.39. An organic compound A, C8H4O3, in dry benzene in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives compound B. The compound B on treatment with PCl5, followed by reaction with H2/Pd (BaSO4) gives compound C, which on reaction with hydrazine gives a cyclic compound D (C14H10N2).
Identify A, B, C and D. Explain the formation of D from C. (2000 - 5 Marks)
Solution.
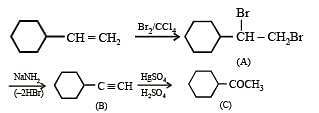
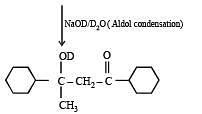
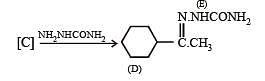
Q.40. Identify (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E) in the following schemes and write their structures :
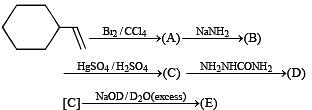
Solution.
Q.41. Identify (X), (Y) and (Z) in the following synthetic scheme and write their structures.
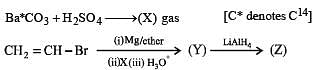 (2001 - 5 Marks)
(2001 - 5 Marks)
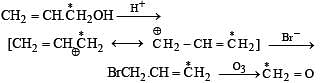
Explain the formation of labelled formaldehyde (H2C*O) as one of the products when compound (Z) is treated with HBr and subsequently ozonolysed. Mark the C* carbon in the entire scheme.
Ans. 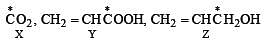
Solution.
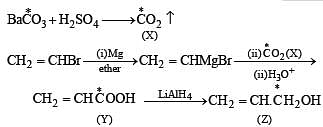
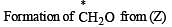
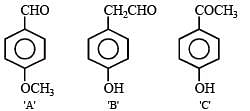
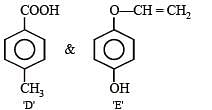
Q.42. Five isomeric para-disubstituted aromatic compounds A to E with molecular formula C8H8O2 were given for identification. Based on the following observations, give structures of the compounds. (2002 - 5 Marks)
(i) Both A and B form a silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent; also B gives a positive test with FeCl3 solution.
(ii) C gives positive iodoform test.
(iii) D is readily extracted in aqueous NaHCO3 solution.
(iv) E on acid hydrolysis gives 1,4-dihydroxybenzene.
Ans.
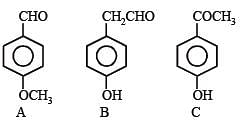
Solution. (i) As both the compounds A and B form a silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent, they have aldehydic group in their structure. In these compounds, B gives positive test with FeCl3 solution, so it must also have phenolic group in its structure.
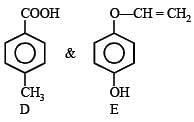
Hence, compound A is p-methoxybenzaldehyde and B is p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde.
(ii) Compound C gives positive iodoform test, so it must have CH3CO– group in its structure. Hence compound C is p-hydroxyphenylmethyl ketone.
(iii) Compound D is readily extracted in aqueous NaHCO3, so it must have -COOH group in its structure. So, compound D is p-methylbenzoic acid.
(iv) Compound E on hydrolysis gives 1,4-dihydroxybenzene.
So, compound E is p-hydroxyphenyl vinyl ether.
Hence the structures of all the five compounds are :
Q.43. Identify X, Y and Z in the following synthetic scheme and write their structures.
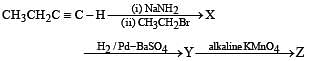
Is the compound Z optically active?
Ans. 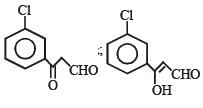
Solution. TIPS/Formulae : Meso forms are optically inactive.
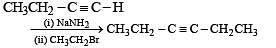
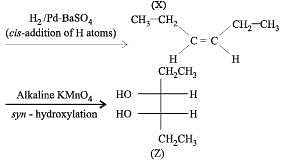
Z is in meso form having plane of symmetry. The upper half molecule is mirror image of the lower half molecule. The molecule is, therefore, optically inactive due to internal compensation.
Q.44. A racemic mixtur e of ( ± ) 2–ph enylpropan oic acid on esterification with (+) 2–butanol gives two esters. Mention the stereochemistry of the two esters produced. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Solution. The two enantiomers of 2-phenylpropan oic acid in the racemic mixture react with (+) – alcohol to form two diastereomers.

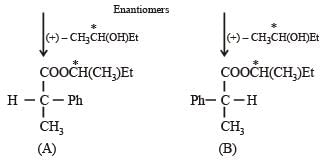
(A) and (B) are diasteromers.
The bonds attached to the chiral carbon in both the molecules are not broken during the esterification reaction. (+) – Acid reacts with (+) –alcohol to give an (+)–(+)–easter, while (–) acid reacts with (+) alcohol to give (–)–(+)–ester. These two esters are diastereoisomers.
Q.45. Compound A of molecular formula C9H7O2Cl exists in keto form and predominantly in enolic form ‘B’. On oxidation with KMnO4, ‘A’ gives m–chlorobenzoic acid. Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Solution.
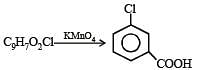
Hence compound should have following part structure
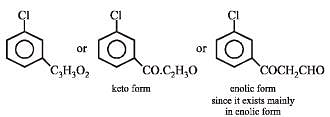
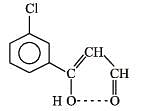
The enolic form of the compound is more stable than the keto form due to hydrogen bonding.
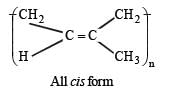
Q.46. A monomer of a polymer on ozonolysis gives two moles of CH2O and one mole of CH3COCHO. Write the structure of monomer and write all – ‘cis’ configuration of polymer chain.
Ans. H2C=C(CH3).CH = CH2
Solution.
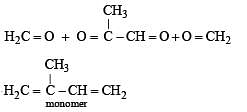
Thus the possible polymer should be
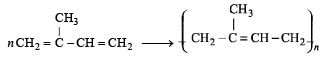
Structure of all cis configuration of the polymer.
|
446 docs|930 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















