Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 Question Answers - Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
Short Q & A :
Q1: Why is the Frigid Zone very cold?
Ans: The Frigid Zone is very cold because it is near the poles, where the sun's rays are always slanting and provide less heat.
Q2: What are Latitudes & longitudes?
Ans:
- Latitudes are imaginary horizontal lines that run around the Earth parallel to the Equator, from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- Longitudes are imaginary vertical lines that run from the North Pole to the South Pole. The Prime Meridian, which is at 0°, is the starting point for measuring longitude.

Q3: What is the difference between the local time and standard time of a place?
Ans:
- Local Time: Local time is the real-time of a place according to its corresponding longitudes. Every place has its unique local time. Places having the same meridian of longitude have the same local time.
- Standard Time: The standard time of a place is the time of that time zone in which that place lies. In countries with large east-west extant variations in local time present; to overcome this problem standard time of a specific time zone is taken as the standard time of that place.
Q4: Why is it necessary to have standard time?
Ans: Standard time is necessary because:
(i) The different meridians having different times is likely to create problems for trains & flights.
(ii) To maintain uniformity in the country and the world.
Q5: If a person goes from west longitudes to east longitude he needs to
(a) Increase time in his watch
(b) Decrease time in his watch
Ans: (b) Decrease time in his watch.
When a person travels from west longitudes to east longitudes, they are moving ahead in time zones. As a result, they need to adjust their watch by decreasing the time to match the local time in the new eastern longitude.
Q6: Suppose the time at 30° east is 2 p.m. then what is the time at Greenwich?
(a) 2 p.m.
(b) 12 p.m.
(c) 1 p.m.
(d) Cannot find
Ans: (b)
Earth moves 360° in 24 hours,
So 15° in an hour and 1° in four minutes
30° east means 30 × 4 = 120 minutes ahead of Greenwich
So where at 30° east time is 2 p.m.
So at Greenwich time = 2 pm – 2 hours = 12 p.m.
Q7: How has 90 latitude been calculated in each hemisphere?
Ans: The equator represents the zero-degree latitude. Since the distance from the equator to either of the poles is one-fourth of a circle around the earth, it will measure 1/4th of 360 degrees, i.e. 90°.
Q8: Define a globe.
Ans: A globe is a model of the earth. It shows the earth in its actual shape. It is a simple and accurate way to represent the earth. It is not fixed and can be rotated in the same way as a top spin.
Features of the globe:
• The globe is small in size and therefore very convenient to carry and use.
• It clearly depicts all the features of the earth.
• Globes show countries, continents and oceans in their correct shape.
Q9: What is Prime Meridian?
Ans. The Prime Meridian is said to be the reference point, with a longitude of 0 degrees. We have 180 degrees eastward and 180 degrees westward from this prime Meridian. The earth is supposed to be divided into equal halves by the prime meridian and the 180 degree meridian.
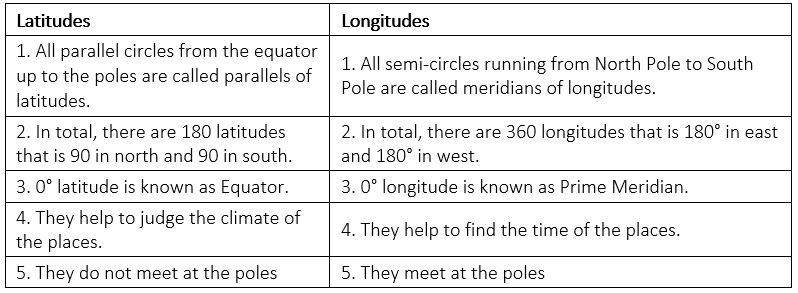
Q10: Distinguish between parallels of latitudes and meridians of longitudes.
Ans.
Q11: Why do places beyond the Tropics have moderate temperatures?
Ans: The mid-day sun never shines overhead on any latitude beyond the tropics. The angle of the sun's rays goes on decreasing towards the poles. As a result, the places between the tropics to the Arctic Circle and to Antarctic Circle have moderate temperatures.
Q12: How latitude and longitude are expressed?
Ans: Latitudes and longitudes are expressed in degrees. However, the increments of less than one degree can be expressed as a decimal or minutes and seconds. There are 60 minutes in a degree and 60 seconds in a minute. Longitudes can be written with an E or W for east or west. Latitudes have N or S for north or south.
Q13: Which longitude is taken as the International Date Line and why?
Ans: The International Date Line (IDL) is an imaginary line on the surface of the Earth opposite the Prime Meridian, where the date changes as one travels across east or west.
- Roughly along 180° longitude, it almost corresponds to the time zone boundary separating -12 and +12 hours Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- Crossing the IDL, travelling east results in a day or 24 hours being added and crossing west results in a day being subtracted.
- The exact number of hours depends on the time zones.
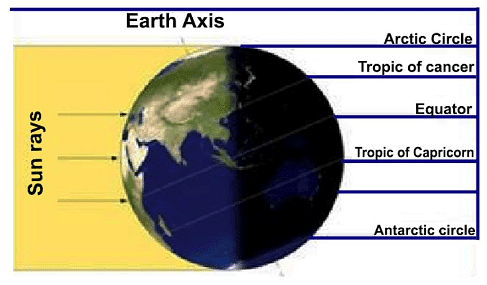
Q14: In the given diagram mark the important parallels of Latitudes.
(a) Equator
(b) Tropic of Cancer
(c) Tropic of Capricorn
(d) Arctic Circle
(e) Antarctic Circle

Ans:
Q15: How pole star can be useful in finding latitude?
Ans: For example, the Pole star will be around 52 degrees above the horizon from southern England, indicating a latitude of 52 degrees north. Near the North Pole, Polaris will be straight overhead, while at the Equator, it will be on the horizon.
Long Q & A:
Q1: What are the different heat zones of the earth? Describe each of them.
Ans: There are different heat zones of the earth. In these zones the sun’s rays fall differently causing different climatic patterns. These zones are: the Torrid Zone, the two Temperate Zones and the two Frigid Zones.
• Torrid Zone: This zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. This area receives the maximum heat because the sun shines overhead here. As a result, this zone is very hot.
• Temperate Zones: The areas bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere, and the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere have moderate temperatures because the sun never shines overhead here.
• Frigid Zones: Areas lying between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole in the Northern Hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole in the Southern Hemisphere, are very cold. It is because here the sun does not rise much above the horizon. Therefore, its rays are always slanting and provides less heat.
Q2: Why is latitude and longitude useful?
Ans:
• The Earth is divided into degrees of longitude and latitude which helps us measure location and time using a single standard.
• When used together, longitude and latitude define a specific location through geographical coordinates. These coordinates are what the Global Position System or GPS uses to provide an accurate locational relay.
• Longitude and latitude lines measure the distance from the Earth's Equator or central axis - running east to west - and the Prime Meridian in Greenwich, England - running north to south.
• They have been useful to navigators, geographers, cartographers and surveyors for a long time. Latitude and longitude are useful on a daily basis for a great number of people for global positioning system, GPS and computerized mapping.
• Using latitude and longitude, it is possible to calculate all sorts of things such as calculate the distances from city to city, calculate the distance from any point on earth to any other point.
Q3: Why is it necessary to have standard time? Also define Indian Standard Time (IST).
Ans: Indian Standard Time is abbreviated as IST. Every country must have a standard time zone. The following things will help to understand it:-
- Time zones are important when creating a schedule for trains and aircraft. It's difficult to build a time table without a common time because different time zones have different times.
- Standard time also aids in maintaining time consistency across the country.
- The standard meridian is located at a longitude of 82°30'E and is known as IST (Indian Standard Time). This meridian is used to calculate India's standard time.
Q4: Which meridian is taken as a standard meridian for India and why?
Ans: The standard meridian for India is 82°30' East.
Why is This Meridian Used?
Uniform Time Across the Country:
- Time Difference: India is a large country with a significant difference in sunrise times from the western part (like Gujarat) to the eastern part (like Arunachal Pradesh). This time difference can be up to 1 hour and 45 minutes.
Consistency:
- Single Time Zone: To ensure that everyone in the country follows the same time, no matter where they are, a single standard time is necessary. Using the standard meridian at 82°30' East helps in creating a uniform time for the entire country.
Location of the Meridian:
- Passing Through the Middle: The 82°30' East meridian is chosen because it is close to the center of India. It is situated near the Tropic of Cancer, which runs through the middle of the country. This helps in reducing the time difference across different regions of India.
By using the standard meridian at 82°30' East, India ensures that everyone follows the same time, making it easier to coordinate activities and schedules throughout the country.
|
67 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 Question Answers - Globe Latitudes and Longitudes
| 1. How are latitudes and longitudes used to locate a place on the globe? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Equator in relation to latitudes? |  |
| 3. How do latitudes and longitudes help in navigation and mapping? |  |
| 4. How are latitudes and longitudes different from each other? |  |
| 5. Can you determine the time difference between two locations using longitudes? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|


















