JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Motion | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate a for some time after which it decelerates at a constant rate b to come to rest. If the total time lapse is t seconds, evaluate. (1978) (i) maximum velocity reached, and (ii) the total distance travelled.
Ans.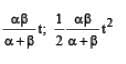
Solution. 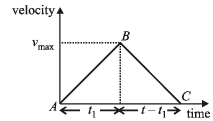
Distance travelled = area of Δ ABC

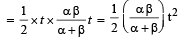
Q.2.The displacement x of particle moving in one dimension, under the action of a constant force is related to the time t by the equation t =√x+ 3 where x is in meters and t in seconds. Find
(i) The displacement of the particle when its velocity is zero, and
(ii) The work done by the force in the first 6 seconds.
Ans.(i) 0 ; (ii) 0
Solution. 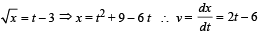
(i) For velocity to be zero, 2 t – 6 = 0 ⇨ t = 3 sec.
The displacement is x = 9 + 9 – 6 × 3 = 0
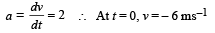
At t = 6 sec, v = 6 ms–1
∴ Work done = Change in K.E. = [K.Ef – K.Ei]
Q.3. Answer the following giving reasons in brief : 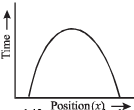
Is the time variation of position, shown in the figure observed in nature? (1979)
Ans. No
Solution. 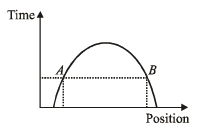
As shown, at a given instant of time, the body is at two different positions A and B which is not possible.
Q.4. Particles P and Q of mass 20 gm and 40 gm respectively are simultaneously projected from points A and B on the ground.
The initial velocities of P and Q make 45° and 135° angles respectively with the horizontal AB as shown in the figure.
Each particle has an initial speed of 49 m/s. The separation AB is 245 m.
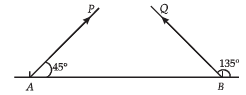
Both particle travel in the same vertical plane and undergo a collision After the collision, P retraces its path, Determine the position of Q when it hits the ground. How much time after the collision does the particle Q take to reach the ground? Take g = 9.8 m/s2.
Ans. mid point of AB, 3.53 sec.
Solution. If a body dr ops fr om a h eigh t H above the ground then the time taken by it to reach the ground
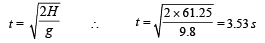
Q.5. Two towers AB and CD are situated a distance d apart as shown in figure.
AB is 20 m high and CD is 30 m high from the ground. An object of mass m is thrown from the top of AB horizontally with a velocity of 10 m/s towards CD. (1994 - 6 Marks) Simultaneously another object of mass 2 m is thrown from the top of CD at an angle of 60° to the horizontal towards AB with the same magnitude of initial velocity as that of the first object. The two objects move in the same vertical plane, collide in mid-air and stick to each other. 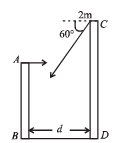
(i) Calculate the distance ‘d’ between the towers and,
(ii) Find the position where the objects hit the ground.
Ans. 17.32, 11.547 m from B
Solution.
(i) Let t be the time taken for collision.
For mass m thrown horizontally from A.
For horizontal motion PM = 10 t ... (i) For vertical motion uy = 0; sy = y; ay = g; ty = t
∴ y = 1/ 2 gt2 ... (ii)
vy = uy + ay t = gt ... (iii)

For mass 2m thrown from C
For horizontal motion QM = [10 cos 60°] t ... (iv)
For vertical motion vy = 10 sin 60° = 5√ 3 ; ay = g sy = y + 10; ty = t
Now, vy = 5√ 3 + gt ... (v)
and (sy) = uyt + 1/2 ay t 2
⇒ y + 10 = 5√3 1/2 gt2 ... (vi)
From (ii) and (vi)
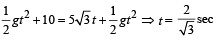
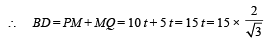
= 10√3 = 17.32 m
(ii) Applying conservation of linear momentum (during collision of the masses at M) in the horizontal direction
m × 10 – 2 m 10 cos 60° = 3 m × vx
⇨ 10 m – 10 m = 3 m × vx ⇨ vx = 0
Since, the horizontal momentum comes out to be zero, the combination of masses will drop vertically downwards and fall at E.
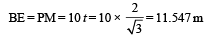
Q.6.Two guns, situated on the top of a hill of height 10 m, fire one shot each with the same speed 5 √3 m s–1 at some interval of time. One gun fires horizontally and other fires upwards at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. The shots collide in air at a point P. Find (i) the time-interval between the firings, and (ii) the coordinates of the point P. Take origin of the coordinate system at the foot of the hill right below the muzzle and trajectories in x-y plane. (1996 - 5 Marks)
Ans.1 sec, (5√3 , 5) in metres
Solution.
For Bullet A. Let t be the time taken by bullet A to reach P.
Vertical motion
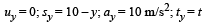
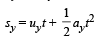
10 – y = 5 t2
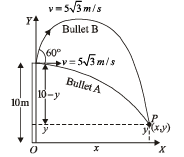
Horizontal motion x = 5√3 t ... (ii)
For bullet B.
Let (t + t') be the time taken by bullet B to reach P Vertical Motion Let us consider upward direction negative and downward positive. Then
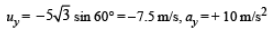
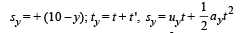
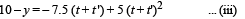
Horizontal motion
x = (5 √3 cos 60°) (t + t ')
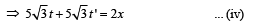
Substituting the value of x from (ii) in (iv), we get
5√3t + 5√3t '= 10√3t
⇒ t = t '
Putting t = t ' in eq. (iii) y – 10 = 15 t – 20 t2 ... (v)
Adding (i) and (v)
0 = 15 t – 15 t2 ⇒ t = 1 sec.
(ii) Putting t = 1 in eq. (ii), we get x = 5√3
Putting t = 1 in eq. (i), we get y = 5
Therefore, the coordinates of point P are ( 5√3 , 5) in metres.
Q.7.A large, heavy box is sliding without friction down a smooth plane of inclination q. From a point P on the bottom of the box, a particle is projected inside the box. The initial speed of the particle with respect to the box is u, and the direction of projection makes an angle a with the bottom as shown in Figure. (1998 - 8 Marks)
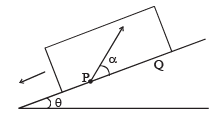
(a) Find the distance along the bottom of the box between the point of projection P and the point Q where the particle lands. (Assume that the particle does not hit any other surface of the box. Neglect air resistance.)
(b) If the horizontal displacement of the particle as seen by an observer on the ground is zero, find the speed of the box with respect to the ground at the instant when particle was projected.
Ans.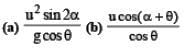
Solution.
(a) u is the relative velocity of the particle with respect to the box. Resolve u. ux is the relative velocity of particle with respect to the box in x-direction. uy is the relative velocity with respect to the box in y-direction.
Since, there is no velocity of the box in the y-direction, therefore this is the vertical velocity of the particle with respect to ground also.
Y-direction motion (Taking relative terms w.r.t. box)
uy = + u sinα
ay = – g cos∅
sy = 0 (activity is taken till the time the particle comes back to the box.)
ty = t
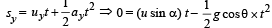
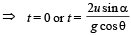
X - direction motion (Taking relative terms w.r.t. box)
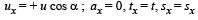
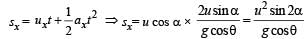
(b) For the observer (on ground) to see the horizontal displacement to be zero, the distance travelled by the box in time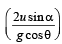 should be equal to the range of the particle.
should be equal to the range of the particle.
Let the speed of the box at the time of projection of particle be U. Then for the motion of box with respect to ground.

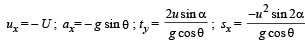
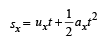
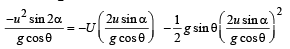
On solving we get U =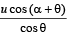
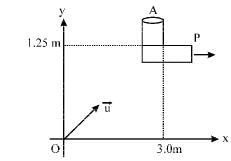
Q.8. An object A is kept fixed at the point x = 3 m and y = 1.25 m on a plank P raised above the ground. At time t = 0 the plank starts moving along the + x direction with an acceleration 1.5 m/s2. At the same instant a stone is projected from the origin with a velocity ur as shown. A stationary person on the ground observes the stone hitting the object during its downward motion at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. All the motions are in the X–Y plane. Find ur and the time after which the stone hits the object. Take g = 10 m/s (2000 - 10 Marks)
 Ans.
Ans.
Solution.
Let 't ' be the time after which the stone hits the object and θ be the angle which the velocity vector u makes with horizontal.

According to question, we have following three conditions. (i) Vertical displacement of stone is 1.25 m.
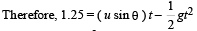
where g = 10 m/s2
or (u sinθ ) t = 1.25 + 5t2
(ii) Horizontal displacement of stone = 3 + displacement of object A.
Therefore, (u cos θ ) t= 3 + 1/2 at2
where a = 1.5 m/s2
or(u cos q )t = 3 + 0.75 t2 ... (ii)
Horizontal component of velocity of stone = vertical component (because velocity vector is inclined at 45° with horizontal.) Therefore (u cos θ) = gt – (u sinθ ) ... (iii)
(The right hand side is written gt – u sinθ because the stone is in its downward motion. Therefore, gt > u sinθ .
In upward motion usinθ > gt). Multiplying equation (iii) with t we can write, (u cosθ ) t + (u sin q ) t = 10 t2 ... (iv)
Now, (iv) – (ii) – (i) gives 4.25 t2 – 4.25 = 0 or t = 1s Substituting t = 1s in (i) and (ii), we get, u sin q = 6.25 m/s or uy = 6.25 m/s and u cos q = 3.75 m/s.
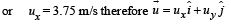
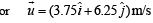
Q.9. On a frictionless horizontal surface, assumed to be th e x-y plane, a small trolley A is moving along a straight line parallel to the y-axis (see figure) with a constant velocity of (√ 3 -1) m/s. At a particular instant, when the line OA makes an angle of 45° with the x-axis, a ball is thrown along the surface from the origin O. Its velocity makes an angle f with the x-axis and it hits the trolley.
(a) The motion of the ball is observed from the frame of the trolley. Calculate the angle q made by the velocity vector of the ball with the x-axis in this frame.
(b) Find the speed of the ball with respect to the surface, ifφ = 4θ/4. (2002 - 5 Marks)
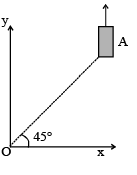
Ans. 45°, 2 m/sec.
Solution. (a) Let the ball strike the trolley at B. Let
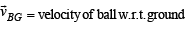
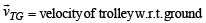
∴ Velocity of ball w.r.t. trolley
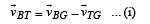
From triangle OAB
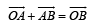
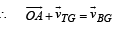
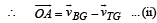
From (i) and (ii) 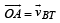
⇒ velocity of ball w.r.t. trolley makes an angle of 45° with the X-axis
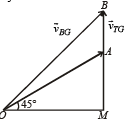
(b) Here q = 45°
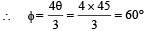
In ΔOMA,
θ = 45°⇨∠OAM = 45°
∴ ∠OAB = 135°
Also∠BOA = 60° – 45° = 15°
Using sine law in ΔOBA
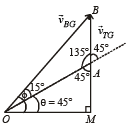
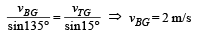
|
446 docs|930 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















