JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Electrostatics- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.13. A circular ring of radius R with uniform positive charge density λ per unit length is located in the y-z plane with its centre at the origin O. A particle of mass m and positive charge q is projected from the point P (R√ 3,0,0) on the positive x-axis directly towards O, with an initial speed v.
Find the smallest (non-zero) value of the speed v such that the particle does not return to P. (1993-4 Marks)
Ans.
Solution. Potential energy can be found at the initial point A and final point O. The difference in potential energy has to be provided by the K.E. of the charge at A.
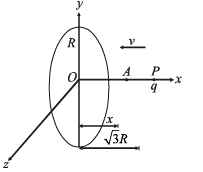
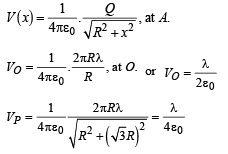
Potential difference between points O and P = V
∴ V = VO-VP
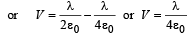
The kinetic energy of the charged particle is converted into its potential energy at O.
∴ Potential energy of charge (q) = qV
Kinetic energy of charged particle = 1/2 mv2
For minimum speed of particle so that it does not return to P,
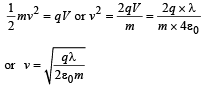
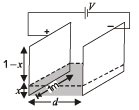
Q.14. Two square metal plates of side 1 m are kept 0.01 m apart like a parallel plate capacitor in air in such a way that one of their edges is perpendicular to an oil surface in a tank filled with an insulating oil. The plates are connected to a battery of emf 500 V. The plates are then lowered vertically into the oil at a speed of 0.001 ms–1. Calculate the current drawn from the battery during the process. (Dielectric constant of oil = 11, ε0 = 8.85 × 10–12C2N–1m–1) (1994 - 6 Marks)
Ans. 4.425 × 10–9 A.
Solution. The adjacent figure is a case of parallel plate capacitor. The combined capacitance will be
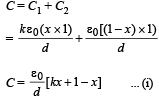
Differentiating the above quation w.r.t. time
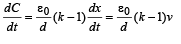
where v = dx/dt
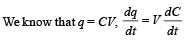
From (iii) and (iv)
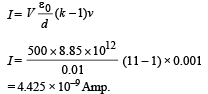
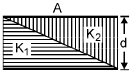
Q.15. The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with plate area A and separation d is C. The space between the plates is filled with two wedges of dielectric constants K1 and K2, respectively. Find the capacitance of the resulting capacitor. (1996 - 2 Marks)
Ans.
Solution. Case (i) When no dielectric :
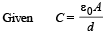
Case (ii) When dielectric is filled : A small dotted element of thickness dx is considered as shown in the figure.
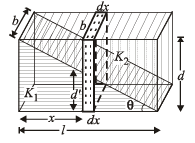
The small capacitance of the dotted portion 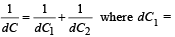 capacitance of capacitor with dielectric K1
capacitance of capacitor with dielectric K1
dC2 = capacitance of capacitor with dielectric K2.
Let ℓ, b the len gth an d br eadth of the capacitor plate.
Therefore ℓ × b=A.
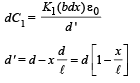
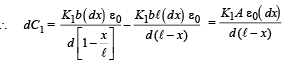
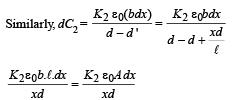
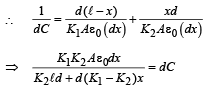
To find the capacitance of the whole capacitor, we integrate the above equation.
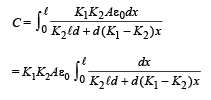
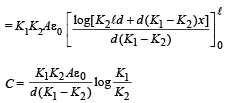
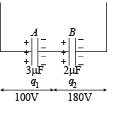
Q.16. Two capacitors A and B with capacities 3 μF and 2 μF are charged to a potential difference of 100 V and 180 V respectively. The plates of the capacitors are connected as shown in the figure with one wire from each capacitor free.
The upper plate of A is positive and that of B is negative. An uncharged 2 μF capacitor C with lead wires falls on the free ends to complete the circuit. Calculate (1997 - 5 Marks)
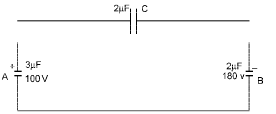
(i) the final charge on the three capacitors. and
(ii) the amount of electrostatic energy stored in the system before and after the completion of the circuit.
Ans. (i) 90 × 10–6 C, 210 × 10–6 C, 150 × 10–6 C
(ii) 4.74 × 10–2 J, 1.8 × 10–2 J
Solution. (i) KEY CONCEPT : Use charge conservation to solve this problem.
INITIALLY :
Charge on capacitor A
qA = 3 × 10–6 × 100 = 3 × 10–4C
Charge on capacitor B
qB = 2 × 10–6 × 180 = 3.6 × 10–4C
FINALLY :
Let the charge on capacitor A, C and B be q1, q2 and q3 respectively.
By charge conservation.
The sum of charge on +ve plate of capacitor A and C should be equal to qA
∴ q1 + q2 = 3 × 10–4C... (i)
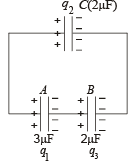
Similarly the sum of charge on –ve plates of capacitor C and B will be equal to qB
∴ – q2 – q3 = – 3.6 × 10–4C
⇒ q2 + q3 = 3.6 × 10–4C ... (ii)
Applying Kirchoff's law in the closed loop, we get
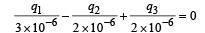
⇒ 2q1 – 3q2 + 3q3 = 0 ....(iii)
On solving (i), (ii) and (iii), we get
q1 = 90 × 10–6 C, q2 = 210 × 10–6 C, and q3 = 150 × 10–6 C,
(ii) Amount of electrostatic energy in the system initially
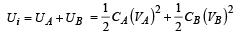
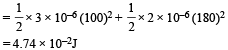
Amount of electrostatic energy stored finally
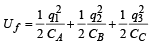
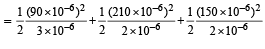
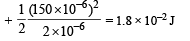
Q.17. A conducting sphere S1 of radius r is attached to an insulating handle. Another conducting sphere S2 of radius R is mounted on an insulating stand. S2 is initially uncharged.
S1 is given a charge Q, brought into contact with S2, and removed. S1 is recharged such that the charge on it is again Q; and it is again brought into contact with S2 and removed.
This procedure is repeated n times. (1998 - 8 Marks)
(a) Find the electrostatic energy of S2 after n such contacts with S1.
(b) What is the limiting value of this energy as n →∞ ?
Ans.
Solution. Limiting value of energy as n →∞.
Let us calculate qn when n tends to ∞.

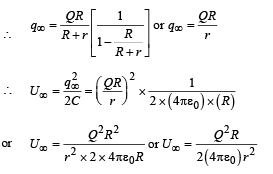
Q.18. A non-conducting disc of radius a and uniform positive surface charge density σ is placed on the ground, with its axis vertical. A particle of mass m and positive charge q is dropped, along the axis of the disc, from a height H with zero initial velocity. The particle has q/m = 4 ∈0g/σ (1999 - 10 Marks)
(a) Find the value of H if the particle just reaches the disc.
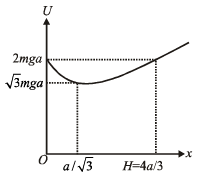
(b) Sketch the potential energy of the particle as a function of its height and find its equilibrium position
Ans.
Solution. (a) KEY CONCEPT : The K.E. of the particle, when it reaches the disc is zero.
Given that a = radius of disc, σ = surface charge density, q/m = 4ε0g/σ
Potential due to a charged disc at any axial point situated at a distance x from O is,
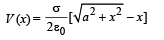
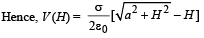
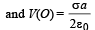
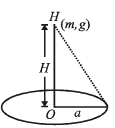
NOTE : According to law of conservation of energy, loss of gravitational potential energy = gain in electric potential energy
mgH = qΔV
= q [V(0) – V (H)]
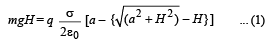
From the given relation 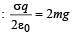
Putting this in equation (1), we get,
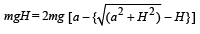
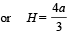 [∵H = O is not valid]
[∵H = O is not valid]
(b) Total potential energy of the particle at height H
U (x) = mgx + qV (x)
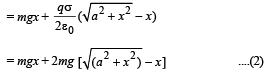
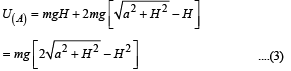
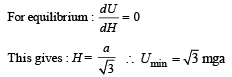
From equation (2), graph between U(x) and x is as shown above.
Q.19. Four point charges +8mC, –1mC, –1mC, and +8mC are fixed at the points 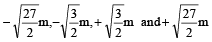 respectively on the y-axis. A particle of mass 6 × 10–4 kg and charge +0.1 μC moves along the -x direction. Its speed at x = + ∞ is V0. Find the least value of V0 for which the particle will cross the origin. Find also the kinetic energy of the particle at the origin. Assume that space is gravity free.
respectively on the y-axis. A particle of mass 6 × 10–4 kg and charge +0.1 μC moves along the -x direction. Its speed at x = + ∞ is V0. Find the least value of V0 for which the particle will cross the origin. Find also the kinetic energy of the particle at the origin. Assume that space is gravity free. (2000 - 10 Marks)
(2000 - 10 Marks)
Ans. 3 m/s, 3 × 10–4 J
Solution. Let the particle at some instant be at a point P distant x from the origin. As shown in the figure, there are two forces of repulsion acting due to two charges of + 8 mC. The net force is 2F cos α towards right.
Similarly there are two forces of attraction due to two charges of – 1 mC. The net force due to these force is 2F' cos β towards left.
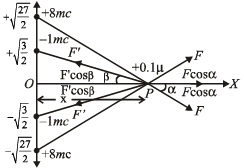
The net force on charge 0.1 µC is zero when 2F cos α = 2F' cos β
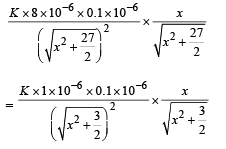
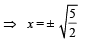
This means that we need to move the charge from – ∞ to 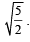 Thereafter the attractive forces will make the charge move to origin.
Thereafter the attractive forces will make the charge move to origin.
The electric potential of the four charges at 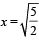 is
is
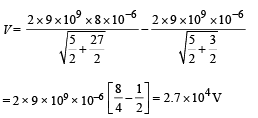
Kinetic energy is required to overcome the force of repulsion
from ∞ to 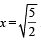
The work done in this process is W = q (V)
where V = p.d between ∞ and 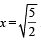
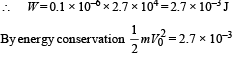
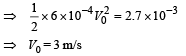
K.E. at the origin
Potential at origin
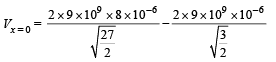
= 2.4 × 104
Again by energy conservation
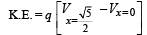
∴K.E. = 0.1 × 10–6 [2.7 × 104 – 2.4 × 104]
= 0.1 × 10–6 × 0.3 × 104
= 3 × 10–4 J
Q.20. Charges +q and –q are located at the corners of a cube of side as show in the figure. Find the work done to separate the charges to infinite distance. (2003 - 2 Marks)
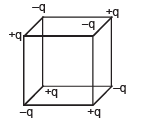
Ans.
Solution.
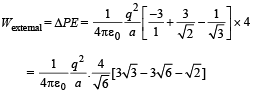
Q.21. A charge +Q is fixed at the origin of the co-ordinate system while a small electric dipole of dipole moment 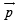 pointing away from the charge along the x-axis is set free from a point far away from the origin. (2003 - 4 Marks)
pointing away from the charge along the x-axis is set free from a point far away from the origin. (2003 - 4 Marks)
(a) Calculate the K.E. of the dipole when it reaches to a point (d, 0).
(b) Calculate the force on the charge +Q at this moment.
Ans.
Solution. (a) Potential energy of the dipole-charge system
Ui = 0 (since the charge is far away)
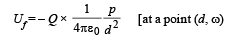
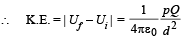
(b) Electric field at origin due to dipole
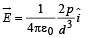
Thus, force on charge Q is given by
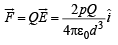
Q.22. Two uniformly charged large plane sheets S1 and S2 having charge densities σ1 and σ2 (σ1 > σ2) are placed at a distance d parallel to each other. A charge q0 is moved along a line of length a(a < d) at an angle 45º with the normal to S1. Calculate the work done by the electr ic field (2004)
Ans.
Solution.

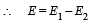
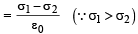
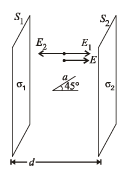
Work done by electric field
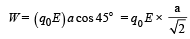
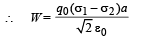
Q.23. A conducting liquid bubble of r adius a and th ickn ess t (t << a) is charged to potential V. If the bubble collapses to a droplet, find the potential on the droplet. (2005 - 2 Marks)
Ans.
Solution. LIQUID BUBBLE : The potential of the liquid bubble is V.
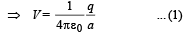
where q is the charge on the liquid bubble.
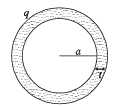
LIQUID DROPLET
The volume of liquid droplet = Volume (of the liquid) in liquid bubble.
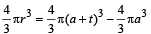
or, r3 = a3 + t3 + 3a2t + 3at2 – a3
or, r3 = 3a2t
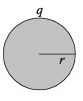
(Q t is very small as compared to a)
or, r = [3a2t]1/3 ... (iii)
NOTE : By charge conservation we can conclude that charge on liquid bubble is equal to charge on liquid droplet Let charge on liquid droplet is q.
∴ Potential on liquid droplet
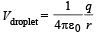
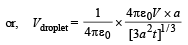 [From (i) and (ii)]
[From (i) and (ii)]
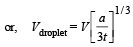
|
446 docs|929 tests
|





















