True/False: Ray & Wave Optics | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
True/False
Q.1. The setting sun appears higher in the sky than it really is. (1980)
Ans. T
Solution. This is due to atmospheric refraction. The light coming from sun bends towards the normal. Therefore, sun appears higher.
Q.2. The intensity of light at a distance ‘r’ from the axis of a long cylindrical source is inversely proportional to ‘r’. (1981- 2 Marks)
Ans. T
Solution. KEY CONCEPT : Formula for intensity of a line source of power (P) at a distance r from the source is 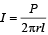
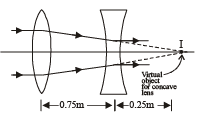
Q.3. A convex lens of focal length 1 meter and a concave lens of focal length 0.25 meter are kept 0.75 meter apart. A parallel beam of light first passes through the convex lens, then through the concave lens and comes to a focus 0.5 m away from the concave lens. (1983 - 2 Marks)
Ans. F
Solution. The image formed by the convex lens at the focus of the concave lens. Therefore I will act as a virtual object for concave lens and angle will be formed at infinity.
Q.4. A beam of white light passing through a hollow prism give no spectrum. (1983 - 2 Marks)
Ans. T
Solution. NOTE : For the light to split, the material through which the light passes should have refractive index greater than 1.
Since the prism is hollow, we get no spectrum. The thickness of glass slabs through which the prism is made can be neglected.
Q.5. The two slits in a Young’s double slit experiment are illuminated by two different sodium lamps emitting light of the same wavelength. No interference pattern will be observed on the screen. (1984- 2 Marks)
Ans. T
Solution. When the two slits of Young's double slit experiment are illuminated by two different sodium lamps, then the sources are not coherent and hence sustained interference pattern will not be achieved. It will change so quickly that there will be general illumination and hence interference pattern will not be observed.
Q.6. In a Young’s double slit experiment performed with a source of white light, only black and white fringes are observed. (1987 - 2 Marks)
Ans. F
Solution. In Young's double slit experiment if source is of white light than the central fringe is white with coloured fringes on either side.
Q.7. A parallel beam of white light fall on a combination of a concave and a convex lens, both of the same meterial. Their focal lengths are 15 cm and 30 cm respectively for the mean wavelength in white light. On the other side of the lens system, one sees coloured patterns with violet colour at the outer edge. (1988 - 2 Marks)
Ans. T
Solution.
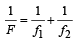
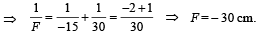
This combination behaves as a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
Since Fv < Fr.
∴One sees coloured pattern with violet colour at the outer edge.
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on True/False: Ray & Wave Optics - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What is the difference between ray optics and wave optics? |  |
| 2. What is the principle of reflection in ray optics? |  |
| 3. How does Snell's law explain the refraction of light in ray optics? |  |
| 4. What is the phenomenon of interference in wave optics? |  |
| 5. How does polarization of light occur in wave optics? |  |
|
347 docs|185 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















