Phase Equilibrium, Phase Rule & Degrees of Freedom | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Phase Equilibrium |

|
| Phase Rule |

|
| Terms used in Phase Rule |

|
| Advantages of Phase Rule |

|
| Limitations of Phase Rule: |

|
| Phase Diagram |

|
Phase Equilibrium
Phase equilibrium is the study of the equilibrium which exists between or within different states of matter namely solid, liquid and gas.
- Equilibrium is defined as a stage when the chemical potential of any component present in the system stays steady with time.
- Phase is a region where the intermolecular interaction is spatially uniform or in other words physical and chemical properties of the system are the same throughout the region.
- Within the same state, a component can exist in two different phases such as allotropes of an element.
- Also, two immiscible compounds in the same liquid state can coexist in two phases.
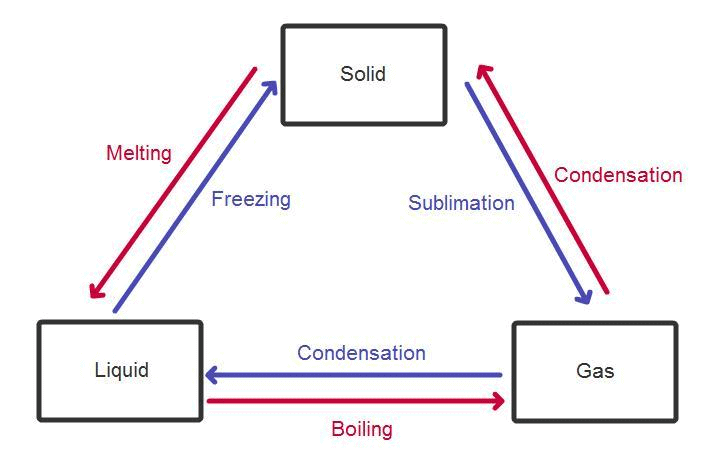
Applications of Phase Equilibrium
- Phase equilibrium has a wide range of applications in industries including the production of different allotropes of carbon, lowering of the freezing point of water by dissolving salt (brine), purification of components by distillation, usage of emulsions in food production, pharmaceutical industry, etc.
- Solid-solid phase equilibrium has a special place in metallurgy and is used to make alloys of different physical and chemical properties.
- For instance, melting point of alloys of copper and silver is lower than the melting point of either copper or silver.
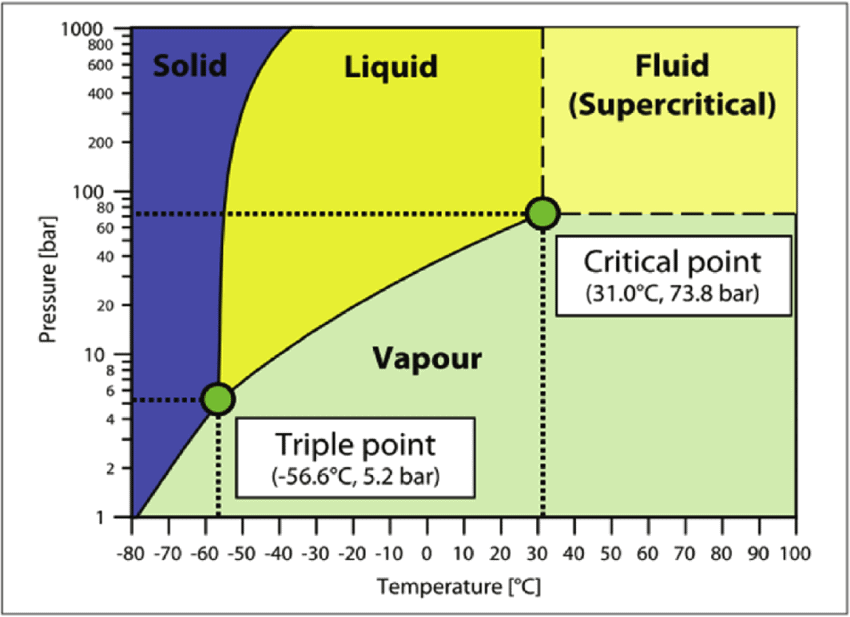 Phase Diagram of CO2
Phase Diagram of CO2
Phase Rule
Gibbs phase rule states that if the equilibrium in a heterogeneous system is not affected by gravity or by electrical and magnetic forces, the number of degree of freedom is given by the equation
- Gibbs' phase rule was proposed by Josiah Willard Gibbs in his landmark paper titled On the Equilibrium of Heterogeneous Substances, published from 1875 to 1878.
- The rule applies to non-reactive multi-component heterogeneous systems in thermodynamic equilibrium and is given by equality.
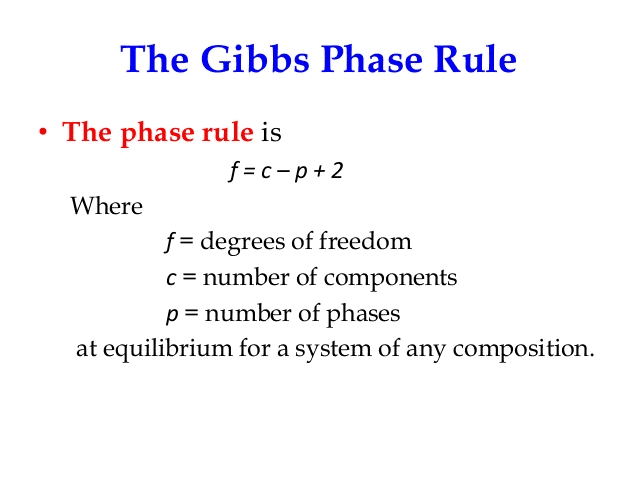
- The number of degrees of freedom is the number of independent intensive variables, i.e. the largest number of thermodynamic parameters such as temperature or pressure that can be varied simultaneously and arbitrarily without determining one another.
- An example of a one-component system is a system involving one pure chemical, while two-component systems, such as mixtures of water and ethanol, have two chemically independent components, and so on.
- Typical phases are solids, liquids, and gases.
Terms used in Phase Rule
Before studying the phase rule, it is necessary to explain the meaning of phase, component, and degree of freedom.
Phase
The homogenous, physically distinct, and mechanical separable parts of the heterogeneous system in equilibrium are called phases.
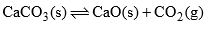
There are three phases in equilibrium state two solids and one is gas (CO2), water system can be expressed as
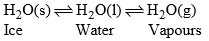
In this system, there are three phases viz solid, liquid and vapors.
Component & Number of Components
In a heterogeneous system, in equilibrium the minimum number of variables that are necessary to explain the chemical composition of a phase, by a chemical equation, is called component, the meaning of component can be understood by taking the following examples:
(a) Ice-water-vapours system
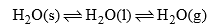
This system has three phases i.e. solid (ice) liquid (water) and gas (vapour). The chemical composition of each phase can be expressed by H2O in the form of a chemical equation.
Phase | Component |
H2O(s) | H2O |
H2O(l) | H2O |
H2O(g) | H2O |
Thus water system is a one-component system.
(b) When solid NH4Cl is heated in a closed vessel, the following equilibrium establishes:
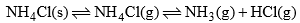
This system has two phases i.e. solid NH4Cl and a mixture of gases NH3 and HCl. Here, although the system has three components, but the chemical composition of both phases can be expressed by a single component i.e. NH4Cl. Since NH3 and HCl are in equimolar ratio
Phase Component
NH4Cl(s) = NH4Cl
NH3(g) + HCl(g) = NH4Cl
Thus, this system is also a one-component system.
Note: It some additional amount of either NH3(g) or HCl(g) is added in this system at equilibrium then each phase can be not expressed by NH4Cl, then one more component will be required and a number of components will be two in the system.
(c) When solid CaCO3 is heated in a closed vessel, the following heterogeneous equilibrium establishes:
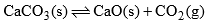
- This system consists of three phases i.e. solid CaCO3, solid CaO and gaseous CO2. Although system has three components but they are not independent of each other. Any of these two can be independently variable.
- Thus out of three, two components may be selected to express the composition of any phase. Thus the number of components in this system are two
(i) When CaCO3 and CaO are taken as components
Phase | Component |
CaCO3(g) | CaCO3+0CaO |
CaO(s) | CaCO3 + CaO |
CO2(s) | CaCO3 – CaO |
(ii) When CaO and CO2 are taken as components
Phase | Component |
CaCO3(s) | CaCO3 + 0CO2 |
CaO(s) | CaCO3 – CO2
|
CO2(g) | CaCO3 + CO2 |
Therefore, minimum number of components which are required to express any phase is two and the system is a bi-component system
(d) Sodium Sulphate-water system:
It may have different phases as Na2SO4.7H2O, Na2SO4.10H2O, Na2SO4 solution, ice, vapors, etc. Any phase can be expressed by chemical formulae of Na2SO4 and H2O
Therefore it is also a two-component system.
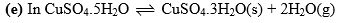 the system also the number of components are two. Number of components may also be calculated by the following formula
the system also the number of components are two. Number of components may also be calculated by the following formula
When components do not ionize
C = C’ – m
Where C = number of components
C’ = total number of undissociated components
m = Number of chemical equations which correlate undissociated species with each other
Degree of Freedom
The degree of freedom or variance of a system is defined as the smallest number of independent variables such as pressure, temperature, and concentration that must be specified in order to describe completely the state of a system.
Following examples will illustrate the meaning of degree of freedom in a better may:
- A system aqueous solution of KCl has two degrees of freedom i.e. temperature and composition (Concentration of solution). If the solution is saturated, then only one variable temperature is necessary to express the system. Thus the saturated solution of KCl is monovarient and unsaturated solution is bivariant.
- Let there be a gas enclosed in a closed chamber. Two variables temperature and pressure are required to express this system. Third variable (composition) is not required since container has only one gas. If the system has a mixture of gases then third variable i.e. composition is also required and system becomes a trivariant system.
Advantages of Phase Rule
- It gives a simple method of classifying equilibrium states of system.
- Physical as well as chemical equilibria and can be studied by this rule.
- The phase rule is applicable to macroscopic systems. Therefore, it is not necessary to take into account about their molecular structure.
- It confirms that the different systems having the same number of degree of freedom behave in like manner.
- Phase rule takes no account of nature of the reactant or products in phase reactions.
- It predicts the behavior of the system when subjected to the variables such as pressure, temperature, and volume.
Limitations of Phase Rule:
- In phase rule only three variables temperature, pressure, and composition are considered. Phase rule does not consider the variable like electric, magnetic and radiation influence.
- As the phase rule is applicable to a single equilibrium state, it does not tell about the number of other equilibrium possible in the system.
- Gravitation force is not considered in phase rule.
- No liquid or solid phases should be finely divided otherwise their vapour pressure and surface tension will differ from their normal values.
- Certain limitations are to be imposed on phase rule in some circumstances. In this state, it is called phase rule under restricted conditions.
Phase Diagram
A phase-diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which thermodynamically distinct phases occur and coexist at equilibrium.
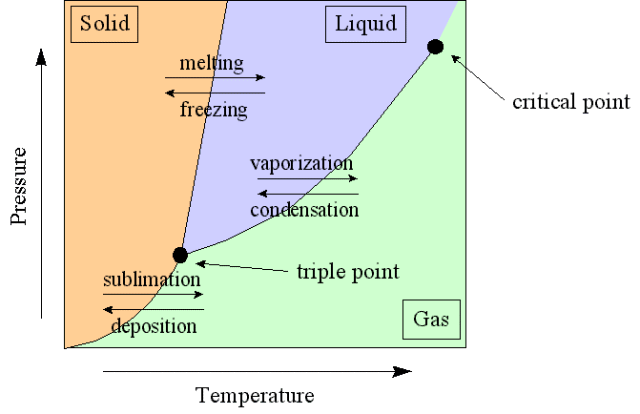
- Common components of a phase diagram are lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries, which refer to lines that mark conditions under which multiple phases can coexist at equilibrium. Phase transitions occur along lines of equilibrium.
- Triple points are points on phase diagrams where lines of equilibrium intersect. Triple points mark conditions at which three different phases can coexist. For example, the water phase diagram has a triple point corresponding to the single temperature and pressure at which solid, liquid, and gaseous water can coexist in stable equilibrium (273.16 K and partial vapor pressure of 611.657 Pa).
- The solidus is the temperature below which the substance is stable in the solid-state. The liquidus is the temperature above which the substance is stable in a liquid state. There may be a gap between the solidus and liquidus; within the gap, the substance consists of a mixture of crystals and liquid (like a "slurry").
- Working fluids are often categorized by on the basis of the shape of their phase diagram.
|
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Phase Equilibrium, Phase Rule & Degrees of Freedom - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is phase equilibrium? |  |
| 2. What is the phase rule? |  |
| 3. What are some terms used in the phase rule? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of the phase rule? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of the phase rule? |  |
















