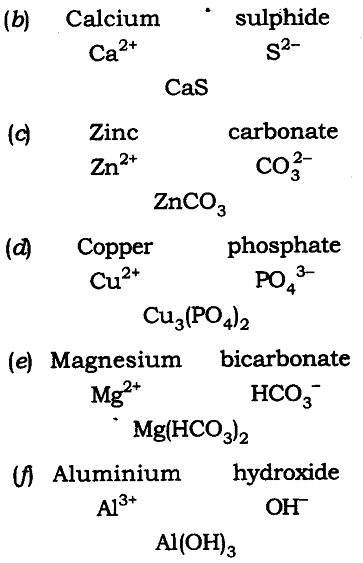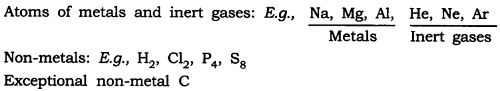Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Atoms and Molecules
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Define the law of conservation of mass.
Ans: In a chemical reaction mass can neither be created nor destroyed.
E.g., 2Na + Cl2——–> 2NaCl
2 x 23 + 2 x 35.5 ——> 2(23 + 35.5)
Q2. Explain the law of constant proportion.
Ans: In a chemical substance, the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
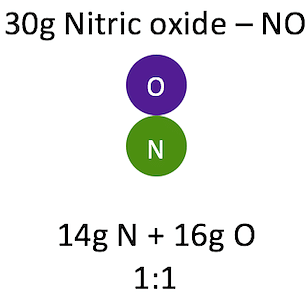
Example: In nitric oxide, the ratio of the mass of nitrogen to the mass of oxygen N: O is always 1:1.
Q3. Who coined the term atom?
Ans: John Dalton coined the term atom.
Q4. Define atom.
Ans: The smallest particle of matter, which can take part in a chemical reaction is called an atom.
Q5. Define molecule.
Ans: The smallest particle of an element or compound which can exist independently is called a molecule.
Q6. Define atomicity.
Ans: The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity.
Q7. What is an atomic mass unit?
Ans: The sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance is expressed in the atomic mass unit. E.g., H20 = 1 x 2 + 16 = 18 amu
Q8. Give one example of cation and anion.
Ans: Cation => Na+
Anion => Cl–
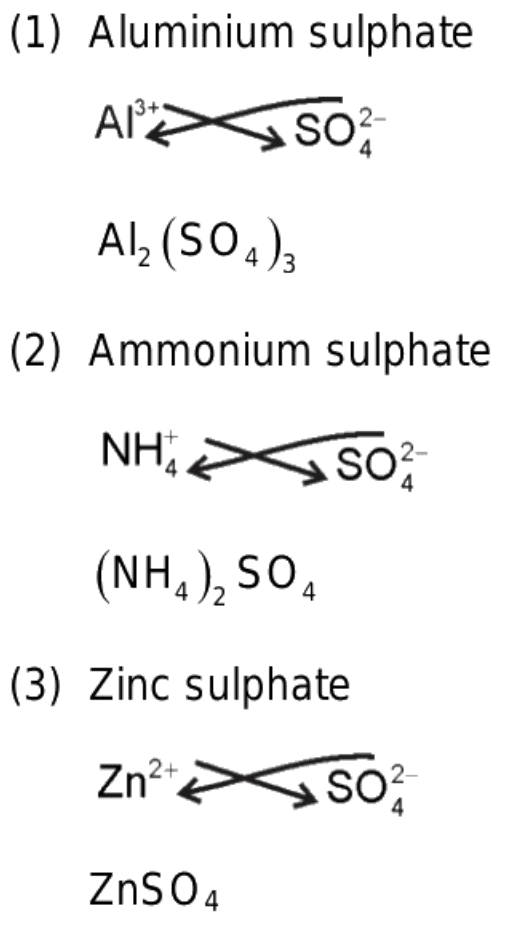
Q9. Give the chemical formula for ammonium sulphate.
Ans: Ammonium sulphate
NH4+ SO42-Chemical formula —-> (NH4)2S04.
Q10. Find the molecular mass of H20.
Ans: Molecular mass of H20
= (2 x 1) + (16)
= 2 + 16 = 18 u
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Give the unit to measure the size of an atom and give the size of a hydrogen atom.
Ans: The unit to measure the size of an atom is nanometer, and the size of a hydrogen atom is 10-10m.
Q2. What is IUPAC, give its one function?
Ans: IUPAC is International Union for Pure and Applied Chemistry. IUPAC is an international scientific organisation which approves names of elements, symbols andunits,
Q3. Give the Latin name for sodium, potassium, and iron.
Ans: Sodium —> Natrium
Potassium —> Kalium
Iron —> Ferrum
Q4. What is the ratio by mass of combining elements in H2O, CO2and NH3?
Ans: H2O ratio by mass of combining elements 2: 16 —>1: 8 (H: O)
CO2 ratio by mass of combining elements 12: 32—> 3: 08 (C: O)
NH3 ratio by mass of combining elements 14 : 3—>14 : 3 (N: H)
Q5. What is a polyatomic ion? Give one example.
Ans: A group of atoms carrying a charge is known as a polyatomic ion.
E.g., Ammonium – NH4+
Nitrate – N03–
Q6. Write down the formula for:
Copper nitrate, calcium sulphate and aluminium hydroxide.
Ans: Chemical formula:
Copper nitrate —> Cu(N03)2
Calcium sulphate —> CaS04Aluminium hydroxide —> Al(OH)3
Q7. What is formula unit mass? How is it different from molecular mass?
Ans: The formula unit mass of a substance is a sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit of a compound. The constituent particles of formula unit mass are ions and the constituent particles of molecular mass are atoms.
Q8. What are the rules for writing the symbol of an element?
Ans: IUPAC —> International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry approves name of elements.
Symbols are the first one or two letters of the element’s name in English. The first letter of a symbol is always written as a capital letter (upper case) and the second letter as a small letter (lower case).
e.g., Hydrogen —> H Helium —> He
Some symbols are taken from the names of elements in Latin, German or Greek.
e.g., Symbol of iron is Fe, its Latin name is Ferrum.
The symbol of sodium is Na, its Latin name is Natrium.
Q9. Explain relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass.
Ans: Relative atomic mass: It can be defined as the number of times one atom of a given element is heavier than 1/12 th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. Relative Molecular Mass: It is defined as the number of times one molecule
of a substance or given element is heavier than 1/12 th of the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
Q10. The formula of carbon dioxide is CO2. What information do you get from this formula?
Ans: (i) CO2represents carbon-dioxide.
(ii) CO2is one molecule of carbon dioxide.
(iii) CO2is one mole of carbon dioxide i.e., it contains 6.022 x 1023 molecules of carbon dioxide.
(iv) CO2contains 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen.
(v) CO2represents 44 g of molar mass.
Q11. State 3 points of difference between an atom and an ion.
Ans:
Atom Ion An atom has no charge. An ion has either positive or negative charge. Number of electrons = number of protons. Number of electrons ≠ number of protons. Atom is reactive Ion is stable
Q12. Calculate the formula unit mass of NaCl and CaCl2.
(Na = 23, Cl = 35.5, Ca = 40)
Ans: Formula unit mass of NaCl = 23 + 35.5
= 58.5 u
Formula unit mass of CaCl2= 40 + (2 x 35.5)
= 40 + 71 = 111 u
Q13.The ratio by mass for hydrogen and oxygen in water is given as 1 : 8 respectively. Calculate the ratio by number of atoms for a water molecule.
Ans: The ratio by the number of atoms for a water molecule are:
Element Ratio by mass Atomic mass Mass ratio/Atomic mass Simplest ratio H 1 1 1/1 = 1 2 O 8 16 8/16 = 1/2 1 Thus, the ratio by the number of atoms for water is H: O = 2: 1.
Q14. Write down the chemical formula for the following compounds:
(a) Aluminium carbonate
(b) Calcium sulphide
(c) Zinc carbonate
(d) Copper phosphate
(e) Magnesium bicarbonate
(f) Aluminium hydroxide.
Ans:The chemical formula are:
Q15. Explain the difference between 2[0] , 02and 03.
Ans: 2[O] —> It represents 2 atoms of oxygen (cannot exist independently).
O2—> It represents one molecule of oxygen (made up of 2 atoms) that can exist freely.
O3—> It represents one molecule of ozone (made up of 3 atoms) it can exist independently.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. (a) How do atoms exist?
(b) What is atomicity?
(c) What are polyatomic ions?
(a) Atoms of some elements are not able to exist independently. For such elements, atoms form molecules and ions. In the case of metals and inert gases, atoms can exist independently.
(b) The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity.
E.g., O3—> atomicity is 3
O2—> atomicity is 2
(c) Polyatomic ions: When more than two atoms combine together and act like an atom with a charge on it is called a polyatomic ion.
E.g., OH–, N03–, NH4+
Q2.Which are the six postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory?
Ans: Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory
1. The matter is composed of indivisible particles called atoms.
2. Atoms of the same element are similar in shape and mass but differ from the atoms of different elements.
3. Atoms can neither be created nor be destroyed.
4. Atoms of different elements combine in fixed, simple, whole-number ratios to form a compound.
5. Atoms of the same element can combine in more than one ratio to form two or more compounds.
6. The atom is the tiniest unit of matter that can take part in a chemical reaction.
Q3. What is an atomic mass unit’? How is it linked with relative atomic mass?
Ans: Atomic mass unit is defined as the 1 / 12 of the mass of carbon – 12 atom C – 12. The relative atomic mass of an element is the number of times one atom of the element is heavier than the 1 / 12 times the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
Q4. Write the formulae for the following and calculate the molecular mass for each of them.
(a) Caustic potash
(b) Baking powder
(c) Limestone
(d) Caustic soda
(e) Ethanol
(f) Common salt
Ans:
(a) The formulae of Caustic potash is KOH.
The molecular mass of Caustic potash is 39 + 16 + 1 = 56 u.
(b) The formulae of Baking powder is NaHCO3.
The molecular mass of Baking powder is 23 + 1 + 12 + 3 X 16 = 84 u.
(c) The formulae of Limestone is CaCO3.
The molecular mass of Limestone is 40 + 12 + 3 X 16 = 100 u.
(d) The formulae of Caustic soda is NaOH.
The molecular mass of Caustic soda is 23 + 16 + 1 = 40 u.
(e) The formulae of Ethanol is C2H5OH.
The molecular mass of 2 × 2 + 5 X 1 + 16 + 1 = 46 u.
(f) The formulae of Common salt is NaCl.
The molecular mass of Common salt is 23 + 35.5 = 58.5 u.
Ans:
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Atoms and Molecules
| 1. What are atoms and molecules? |  |
| 2. How do atoms and molecules differ? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between an element and a compound? |  |
| 4. How are atoms represented in chemical equations? |  |
| 5. Can atoms or molecules be created or destroyed? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
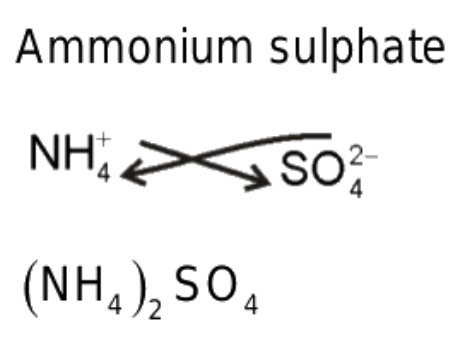 Chemical formula —-> (NH4)2S04.
Chemical formula —-> (NH4)2S04.