Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Tissues
| Table of contents |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
| Activity-Based Questions |

|
| Value-Based Questions |

|
Q1. Name the tissues responsible for the movement of the body.
Ans: Muscle tissue and nervous tissue are the primary tissues responsible for body movement.
- Muscle tissueis divided into three types:
- Striated muscle (voluntary muscles that we control, like those in our limbs)
- Smooth muscle (involuntary muscles found in organs)
- Cardiac muscle (the muscle of the heart)
- Nervous tissue consists of neurons that transmit signals rapidly throughout the body.
- Neurons allow us to control muscle movement by sending nerve impulses.
The combination of muscle and nervous tissue is essential for coordinated movement and response to stimuli.
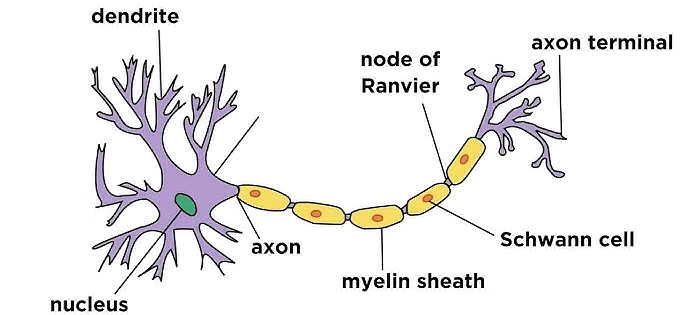
Q2. What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron is the basic unit of nervous tissue. It has a unique structure comprising:
- Cell body: Contains the nucleus and cytoplasm.
- Axon: A long, thread-like part that transmits signals.
- Dendrites: Short, branched parts that receive signals from other neurons.

Neurons can be quite long, with some measuring up to a metre. They are bundled together by connective tissue to form nerves. The signals that travel along these fibres are known as nerve impulses, which enable muscle movement and rapid responses to stimuli.
Q3. Name the types of simple tissues.
Ans: The types of simple tissues in plants are:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Q4. Name the types of complex tissues.
Ans: Complex tissues in plants consist of more than one type of cell that work together to perform a specific function. The main types of complex tissues are:
- Xylem - Responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
- Phloem - Transports food produced in the leaves to other areas of the plant.
Both xylem and phloem are part of the vascular bundle, which is essential for the plant's nutrient and water transport system.
Q5. Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: Apical meristem is found at the growing tips of stems and roots. It plays a crucial role in:
- Increasing the length of the stem.
- Increasing the length of the root.
Additionally, the lateral meristem (cambium) is responsible for increasing the girth of stems and roots, while the intercalary meristem is located near the nodes in some plants.
Q6. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans: The husk of a coconut is primarily made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
This tissue has the following characteristics:
- It consists of dead cells that provide strength.
- The cells are long and narrow with thickened walls due to lignin.
- These thick walls often leave no internal space within the cells.
- Sclerenchyma is also found in stems, around vascular bundles, and in the hard coverings of seeds and nuts.
Overall, this tissue plays a crucial role in providing support to various plant parts.
Q7. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The phloem is made up of several important cell types:
- Sieve tubes: These are tubular cells with perforated walls that facilitate the transport of food.
- Companion cells: These cells support sieve tubes and help in the transport process.
- Phloem parenchyma: This type of cell stores food and assists in transport.
- Phloem fibres: These provide structural support to the phloem.
All phloem cells, except for phloem fibres, are living cells, playing a crucial role in moving nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Q8. Define aerenchyma.
Ans: Aerenchyma is a type of parenchyma tissue that contains large air-filled cavities.
This tissue is particularly important for aquatic plants, as it:
- Facilitates floating in water.
- Helps in the exchange of gases.
In some cases, aerenchyma can also contain chlorophyll, allowing it to perform photosynthesis, and is then referred to as chlorenchyma.
Q9. What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Ans: Tissues play a crucial role in multicellular organisms by:
- Facilitating growth and development of organs.
- Enabling the organisation of different organ systems.
- Allowing cells to perform specific functions efficiently.
In summary, tissues are essential for the proper functioning and coordination of various biological processes in complex organisms.
Q10. Name the two types of tissues.
Ans: Types of Tissues
Plant Tissues
- Divided into two main types: meristematic and permanent.
- Meristematic tissue is found in growing areas and is capable of division.
- Permanents tissuesarise from meristematic tissue and are classified into:
- Simple tissues:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Complex tissues:
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Simple tissues:
Animal Tissues
- Includes four main types:
- Epithelial (e.g., squamous, cuboidal, columnar)
- Connective (e.g., areolar, adipose, bone)
- Muscular (e.g., striated, unstriated, cardiac)
- Nervous (made of neurons)
Q11. Name the two types of plant tissue.
Ans: Plant tissues are classified into two main types:
- Meristematic tissue: This is the dividing tissue found in the growing regions of plants.
- Permanant tissue: This tissue forms when meristematic tissue loses its ability to divide. It is further classified into:
- Simple tissues: Includes parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
- Complex tissues: Includes xylem and phloem.
Q12. What is differentiation?
Ans: The process by which cells acquire a specific shape, size, and function is known as differentiation. This occurs when:
- Cells formed from meristematic tissue lose their ability to divide.
- They take on distinct roles, leading to the formation of permanent tissues.
Differentiation is essential for the development of various types of tissues in plants and animals, allowing for the specialisation of cells to perform specific functions efficiently.
Q13. Name the three types of meristematic tissues.
Ans: The three types of meristematic tissues are:
- Apical meristem - Located at the tips of roots and shoots.
- Lateral meristem - Found along the sides of stems.
- Intercalary meristem - Present at the nodes of plants.
Q14. Where is apical tissue found?
Ans: Apical tissue is found at the tips of:
- Roots
- Stems
This tissue is responsible for the growth in length of these plant parts.
Q15. What are tracheids?
Ans: Tracheids are specialised cells found in the xylem of plants. They have the following characteristics:
- They are elongated with tapering ends.
- Tracheids have thick walls, which provide structural support.
- Many tracheids are dead cells when mature, allowing for efficient water transport.
- They are tubular structures that facilitate the movement of water and minerals vertically within the plant.
Q16. What are guard cells?
Ans: Guard cells are specialised cells that surround each stoma, which are small pores found on the surface of leaves.
- They have a kidney shape and play a crucial role in regulating gas exchange.
- Guard cells control the opening and closing of stomata, allowing carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis and oxygen out.
- They also help manage transpiration, which is the loss of water vapour from the plant.
Q17. Epithelial tissue is the simplest tissue. Write (F) for false or (T) for true.
Ans: True
Epithelial tissue is indeed the simplest type of tissue. Here are some key points:
- It consists of a single layer of cells.
- All cells in epithelial tissue are similar in structure.
- This tissue serves as a protective barrier and is involved in absorption and secretion.
Q18. What are the functions of cuboidal epithelium?
Ans: The cuboidal epithelium serves several important functions:
- Facilitates absorption of substances.
- Involved in excretion processes.
- Plays a role in secretion of various substances.
- Provides mechanical support to surrounding tissues.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Give four differences between bone and cartilage.
Ans: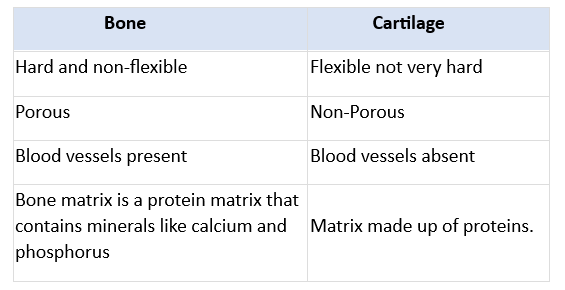
Q2. Give the functions of bone.
Ans: The functions of bone include:
- Shape: It gives shape to the body.
- Support: It provides skeletal support.
- Muscle anchoring: It anchors the muscles.
- Protection: It protects vital organs like the brain and lungs.
Q3. Give the functions of cartilage.
Ans: Functions of cartilage:
- Support and flexibility for various body parts.
- Smoothens surfaces at joints for easier movement.
Q4. Fill in the blanks:
(i) Water and minerals are conducted by ………………….
(ii) In higher plants food is conducted by ……………………..
(iii) Blood is a ……………. tissue.
(iv) Bone consists of………….cells.
(v) Cartilage consists of………………..cells.
(vi) Fibres are absent in………….type of connective tissue.
Ans: (i) Xylem
(ii) Phloem
(iii) Connective
(iv) Osteocyte
(v) Chondrocyte
(vi) Blood
Q5. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Functions of areolar tissue:
- Assists in the repair of tissues after an injury.
- Helps in combating foreign toxins.
- Anchors skin to the underlying muscles.
Q6. Name the tissues for the following: (a) Stores fat in an animal body. (b) Divides and re-divides to grow in plants. (c) Tissue that joins bone to bone. (d) Covers the external surface of an animal body.
Ans:
- Adipose tissue - This tissue stores fat in the animal body.
- Meristematic tissue - This tissue divides and re-divides to promote growth in plants.
- Ligament - This tissue connects bone to bone.
- Epithelial tissue - This tissue covers the external surface of an animal body.
Q7. What is stomata?
Ans: Stomata are tiny openings found on the surface of leaves. They play a crucial role in:
- Gas exchange: Allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to enter and exit the leaf.
- Transpiration: Enabling the loss of water vapour from the plant.
Each stoma is surrounded by two guard cells, which regulate its opening and closing, ensuring that the plant maintains a balance between gas exchange and water loss.
Q8. Why does epidermal tissue have no intercellular space?
Ans: The epidermal tissue serves as a protective outer layer for plants, safeguarding their internal structures. It plays a crucial role in:
- Preventing water loss
- Shielding against mechanical injury
- Defending against parasitic fungi
To effectively perform these protective functions, epidermal cells form a continuous layer without any intercellular spaces. This ensures that the tissue remains intact and functional.
Most epidermal cells are relatively flat, with thicker outer and side walls compared to the inner walls. In some plants, especially those in dry environments, the epidermis may be thicker to enhance water retention.
Additionally, small pores known as stomata are present in the epidermis, allowing for gas exchange and transpiration.
Q9. Name and give the function of each cell of the xylem.
Ans: Xylem consists of four main types of cells:
- Tracheids and vessels: These cells transport water and minerals vertically throughout the plant.
- Xylem parenchyma: This type stores food and aids in the lateral movement of water.
- Xylem fibres: These cells provide support to the plant structure.
Q10. What is the function and location of stratified squamous epithelium?
Ans:
Stratified squamous epithelium is a type of tissue found primarily in the skin. Its main features include:
- Composed of multiple layers of cells.
- Designed to protect against wear and tear.
- Also lines areas such as the oesophagus and the mouth.
This structure helps to prevent damage from physical abrasion and provides a barrier to external elements.
Q11. Give the difference between ligament and tendon.
Ans:
Q12. Give the difference between striated muscles and unstriated muscles.
Ans: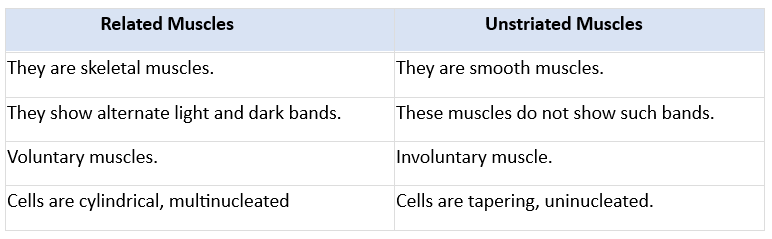
Q13. State the difference between bone and blood.
Ans: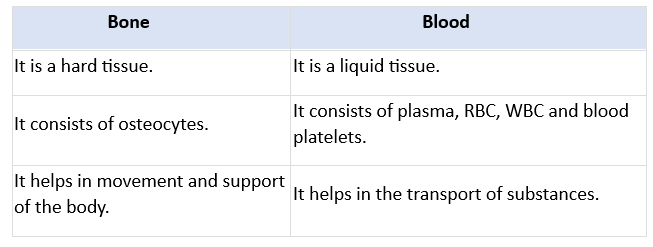
Q14. Name all different types of tissues present in animals.
Ans:
There are four main types of tissues in animals:
- Epithelial tissue: This tissue forms the outer and inner linings of the body, covering organs and cavities.
- Muscular tissue: Composed of muscle cells, this tissue is responsible for movement.
- Connective tissue: This type connects different organs and supports the body. Examples include blood, bone, and cartilage.
- Nervous tissue: Made up of nerve cells, this tissue is essential for the nervous system and for transmitting impulses.
Q15. Why is blood called connective tissue?
Ans:
Blood is classified as a connective tissue due to its unique composition and functions:
- It consists of cells suspended in a fluid called plasma.
- The main components of blood include:
- Red blood cells (RBCs)
- White blood cells (WBCs)
- Platelets
- Plasma serves as a medium that connects and transports various substances throughout the body, including:
- Oxygen
- Nutrients
- Hormones
- Waste products
This connective function is essential for maintaining the body's overall health and facilitating communication between different organs.
Q16. Name three types of muscle tissues and give the function of each.
Ans:
- Striated muscle:
These muscles have alternating light and dark bands, known as striations. They are voluntary and primarily found in skeletal tissues, aiding in the movement of the body and bones.
- Smooth muscle:
These are involuntary muscles that control movements such as the passage of food in the alimentary canal and the contraction of blood vessels. They are located in the iris, uterus, and other organs.
- Cardiac muscle:
This type of muscle is found only in the heart. It is responsible for the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart throughout life.
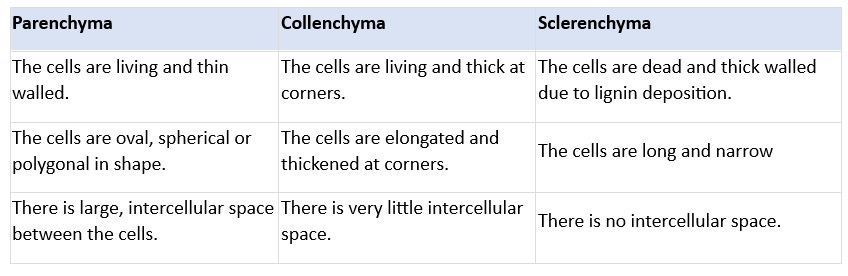
Q17. State the difference between simple tissues of plants.
Ans: The simple tissues of plants include:
- Parenchyma: This is the most common type of simple tissue. It consists of living cells with thin walls, usually arranged loosely, allowing for large intercellular spaces. Parenchyma primarily stores food.
- Collenchyma: This tissue provides flexibility and support to plants. It is found in leaf stalks just below the epidermis and consists of living cells that are elongated and thickened at the corners, with minimal intercellular space.
- Sclerenchyma: This tissue makes plants hard and stiff. Composed of dead cells with thick lignified walls, sclerenchyma has very little internal space. It is commonly found in stems and the husk of coconuts.
Q18. With the help of a diagram show the difference between striated muscle fiber, smooth muscle fiber and cardiac muscle fiber.
Ans: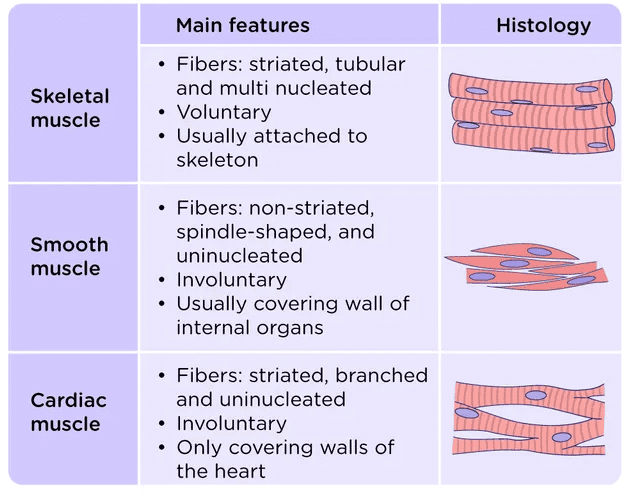
Q19. Name different types of meristematic tissue and draw a diagram to show their location.
Ans: The three types of meristematic tissue are:
- Apical meristem - Responsible for growth in length, found at the tips of roots and stems.
- Lateral meristem - Facilitates growth in thickness, located along the sides of stems and roots.
- Intercalary meristem - Promotes growth in internodes, typically found near the nodes of some plants.
These tissues are crucial for the plant's growth and development, as they produce new cells that eventually differentiate into various types of permanent tissues.
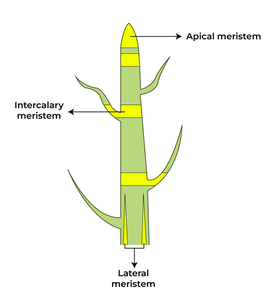 Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic Tissue
Q20. Explain the structure, function and location of nervous tissue.
Ans:
Structure: Nervous tissue is made up of cells known as neurons. Each neuron has:
- A cell body containing a nucleus and cytoplasm.
- A long, thin part called an axon.
- Many short, branched parts known as dendrites.
Location: Nervous tissue is found in:
- The brain
- The spinal cord
- Nerves throughout the body
Function: The primary roles of nervous tissue include:
- Receiving and transmitting stimuli quickly within the body.
- Facilitating movement by sending signals to muscles.
- Enabling responses to various stimuli.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Show the types of animal tissues using flow chart.
Ans: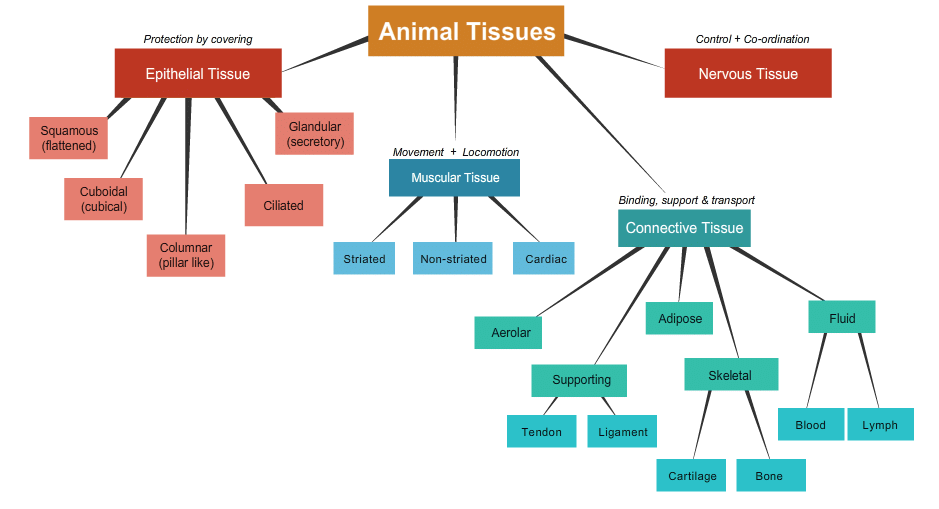
Q2. What is connective tissue? Explain its types.
Ans: Connective tissue is a type of tissue that supports, binds, and connects other tissues and organs in the body. It consists of various cells embedded in a matrix, which can vary in consistency.
- Blood: A fluid connective tissue that transports nutrients and oxygen.
- Bone: A rigid connective tissue with a hard matrix made of calcium and phosphorus, providing structure and support.
- Cartilage: A flexible connective tissue found in joints, the nose, and ears, with a matrix of proteins and sugars.
- Tendons: Connect muscles to bones, made of strong fibrous tissue.
- Ligaments: Connect bones to other bones, highly elastic and strong.
- Adipose tissue: Stores fat and provides insulation.
- Areolar tissue: A loose connective tissue that supports and binds other tissues.
The matrix of connective tissue varies depending on its function, ranging from jelly-like to dense or rigid. This diversity allows connective tissues to perform various roles in the body.
Q3. Describe the ‘epidermis’ in plants.
Ans: The epidermis is the outermost layer of a plant, consisting of a single layer of cells. It serves several important functions:
- The epidermis protects the internal parts of the plant.
- On aerial parts, it secretes a waxy, water-resistant layer that helps prevent water loss, mechanical injury, and invasion by parasitic fungi.
- In leaves, small pores called stomata are present, which facilitate gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) and transpiration (water loss).
- In roots, the epidermis has long hair-like structures that increase the surface area for water absorption.
- In desert plants, the epidermis features a thick waxy coating of cutin, which acts as a waterproofing agent.
Q4. Explain the 'complex tissue' of plants.
Ans: Complex tissues in plants consist of more than one type of cell that work together to perform a specific function. The main types of complex tissues are:
- Xylem: Responsible for transporting water and minerals.
- Phloem: Transports food throughout the plant.
The components of xylem include:
- Tracheids: Tubular structures that help in water transport.
- Vessels: Also assist in transporting water.
- Xylem parenchyma: Stores food and aids in lateral water movement.
- Xylem fibres: Provide structural support.
The phloem consists of:
- Sieve tubes: Tubular cells that transport food.
- Companion cells: Support sieve tubes in their function.
- Phloem fibres: Provide support.
- Phloem parenchyma: Involved in storage and transport.
In summary, complex tissues like xylem and phloem are essential for the plant's transportation and support systems.
Activity-Based Questions
Q1: Take two glass jars and fill them with water.
Now, take two onion bulbs and place one on each jar, as shown in the figure given below.
| Length | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 |
| Jar 1 | 3 cm | 3.5 cm | 4 cm | 4.5 cm | 5 cm | 5.2 cm | 5.4 cm |
| Jar 2 | 3 cm | 3.5 cm | 4 cm | 4.5 cm | 3.5 cm | 3.5 cm | 3.5 cm |
• Observe the growth of roots in both the bulbs for a few days.
• Measure the length of roots on day 1, 2 and 3.
• On day 4, cut the root tips of the onion bulb in jar 2 by about 1cm. After this, observe the growth of roots in both the jars and measure their lengths each day for five more days and record the observations in tables, like the table
From the above observations, answer the following questions:
(a) Which of the two onions has longer roots? Why?
(b) Do the roots continue growing even after we have removed their tips?
(c) Why would tips stop growing in jar 2 after we cut them?
Answer: (a) The onion in jar 1 has longer roots, as the growth of roots continues in it due to intact root tips.
(b) The roots did not continue to grow in jar 2 after cutting down their tips. (c) The tips of root stopped growing in jar 2 because the tips of these roots were cut down and the tissues which helps in the growth of roots i.e., meristematic tissues are removed from it.
(c) The tips of root stopped growing in jar 2 because the tips of these roots were cut down and the tissues which helps in the growth of roots i.e., meristematic tissues are removed from it.
Q2: Take a plant stem and with the help of your teacher cut into very thin slices or sections.
Now, stain the slices with safranin. Place one neatly cut section on a slide, and put a drop of glycerine.
Cover with a cover-slip and observe under a microscope. Observe the various types of cells and their arrangement.
Answer the following on the basis of your observations:
(a) Are all cells similar in structure?
(b) How many types of cells can be seen?
(c) Can we think of reasons why there would be so many types of cells?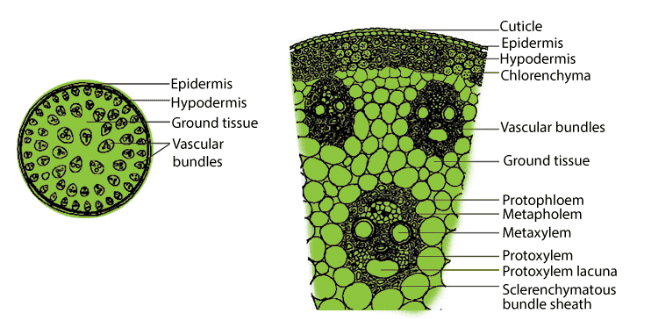 Transverse section and Longitudinal section of stem
Transverse section and Longitudinal section of stem
Answer:
(a) No, all cells are not similar in structure, we see variety of cells with different shape and size.
(b) We can see at least ten different types of cells in the slide.
(c) Yes, there are variety of cells so that each group of cell does a specific role in the overall growth of plant.
Q3: Take a freshly plucked leaf of Rheo.
Stretch and break it by applying pressure.
While breaking it, keep it stretched gently so that some peel or skin projects out from the cut.
Remove this peel and put it in a petridish filled with water.
Add a few drops of safranin.
Wait for a couple of minutes and then transfer it onto a slide. Gently place a cover slip over it.
Ans: (a) The slide shows epidermal cells with stomatal pores as shown in Fig. (a).
(b) On focusing stomata pores under microscope. We can see guard cells and stomata pore as shown in Fig. (b).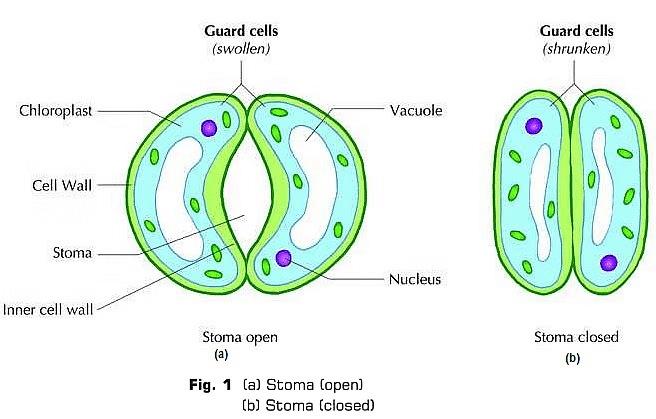
 |
Download the notes
Short & Long Answer Questions- Tissues
|
Download as PDF |
Value-Based Questions
Q1: A group of students completed the project of finding the botanical names of all the trees present in the school campus. They prepared metal plates with names carved on it, to fix it on the plant trunks. Shreya was concerned that if the metal plate is fixed into tree many cells of the tree may get damaged. But the group members explained her that the outer layer of trunk does not have living cells and there won’t be any damage to the tree.
(a) What type of cells are present on the outer layer of the bark/tree trunk?
(b) How does the cprk act as a protective tissue?
(c) What value of the group is seen in the above cast?
Ans: (a) On the outer layer of the tree trunk/bark all thick layer of dead cells is present which acts as protective tissue.
(b) In cork, all cells are dead without intercellular spaces, the walls of the cells have deposition of suberin.
(c) The students in a group show team effort, peer learning and co-operatiye.
Q2: A paralytic patient was unable to walk. ‘The family member of the atient took the outmost care of the patient.
(a) Name two tissues responsible for the movement of a body.
(b) Name the tissues present in brain and spine.
(c) What value of the family members is seen in the above case?
Ans: (a) The two tissues responsible for movement of the body are muscular tissue and nervous tissue.
(b) The tissues present in brain and spine are nervous tissues.
(c) The family members showed the value of being caring, responsible, dutiful and kind.
|
84 videos|384 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Tissues
| 1. What are the different types of plant tissues? |  |
| 2. What is the function of xylem in plants? |  |
| 3. How does phloem differ from xylem in terms of function? |  |
| 4. What are meristematic tissues and where are they found? |  |
| 5. Why are tissues important in the study of biology? |  |