Short & Long Answer Questions: Biomolecules | Organic Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Q.101 In what way enzymes differ from ordinary catalysts?
Answer: Enzymes are biochemical catalysts. They have high molecular mass whereas a catalyst may not be a biomolecule and may not have high molecular mass. Enzymes are required in very small quantity and work at optimum temperature and pH whereas ordinary catalyst works in all conditions.
Q.102 D-glucose is an aldohexose? Why does it react with HCN but not with NaHSO3?
Answer: D-glucose exists in two cyclic forms α- and β- in which the aldehydic group is involved in the formation of a ring and is not free. Therefore, it does not react with NaHSO3. However, with reagents like HCN and phenylhydrazine, the ring structure cleaves and the aldehydic group becomes free. Therefore, D-glucose does react with HCN.
Q.103 How will you show that D-glucose is a reducing sugar?
Answer: D-glucose forms silver mirror with Tollen's reagent and gives a red precipitate with Fehling's solution. This shows that D-glucose is a reducing sugar. The reaction with Tollen's reagent is given :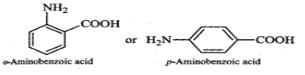
Q.104 (a) Name the type of linkages responsible for the formation of primary and secondary structures of proteins. (b) On electrolysis in acidic solution, α-amino acids migrate towards cathode while in alkaline medium, they migrate towards anode. Explain. (c) What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each.
Answer: (a) Peptide linkages (−CO−NH−) are present in the primary structures of proteins while the secondary structures of proteins involve hydrogen bonding.
(b) An α-amino acid has a dipolar structure. In acidic medium, it exists as a positive ion.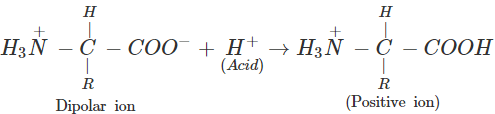
In electric field, the positive ion moves towards cathode. In alkaline medium, the dipolar ion changes to anion and moves towards anode under the influence of applied electric field.
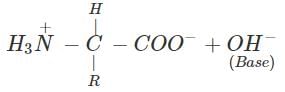
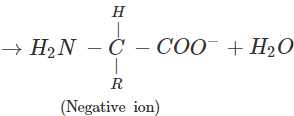
(c) Amino acids which are not synthesized by the body are called essential acids. For example, Leucine and Lysine. Amino acids which are synthesized by the body are known as non-essential amino acids. For example, Glycine and Alanine.
Q.105 A tripeptide on complete hydrolysis gives glycine, alanine and phenylalanine. Using three letter symbols, write the possible sequence of the tripeptide.
Answer: Three letters symbols of the amino acids are Gly, Ala and Phe. The possible sequences of the amino acids are: (i) Gly-Ala-Phe (ii) Gly-Phe-Ala (iii) Ala-Gly-Phe (iv) Ala-Phe-Gly (v) Phe-Gly-Ala (vi) Phe-Ala-Gly.
Q.106 What is isoelectric point of amino acid? How does it help in the separation of amino acids?
Answer: The pH at which a particular amino acid does not migrate under the influence of an electric field is called isoelectric point of amino acid. For example, isoelectric point of glycine is 6.1. At the isoelectric point, an amino acid does not dissolve in water. This property helps in the separation of different amino acids formed by the hydrolysis of proteins.
Q.107 Name three vitamins which are water soluble and three which are soluble in fat.
Answer: Water soluble vitamins: Vitamin C, B1 and B2. Fat soluble vitamins: Vitamin A, D and E.
Q.108 Name the diseases caused due to the deficiency of vitamin B12 and Vitamin C.
Answer: Vitamin B12 deficiency causes pernicious anaemia. Vitamin C deficiency causes diseases relating to teeth such as Scurvy, Pyorrhea etc.
Q.109 What type of substance is phenyl alanine hydroxylase? What is its importance for us?
Answer: It is an enzyme. The deficiency of the enzyme causes disease phenyl ketourea.
Q.110 Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
Answer: Carbohydrates are generally optically active as they contain one or more chiral carbon atoms in their molecules.
Q.111 What are the constituents of sucrose?
Answer: Sucrose (C12H22O11) has two constituents glucose and fructose linked to each other by glycosidic linkage.
Q.112 Name two classes of nitrogen containing bases present in nucleic acids.
Answer: These are purines and pyrimidines. For structures, consult section 15.9.
Q.113 What are polysaccharides. Name one polysaccharide and mention its importance?
Answer: For the definition, consult section 15.4. Starch is a polysaccharide. It is a reserve food material.
Q.114 Name two different types of RNA molecules found in the cells of organisms.
Answer: These are: Messenger RNA (m-RNA) and Ribosomal RNA (r-RNA).
Q.115 State one use of enzyme streptokinase in medicines.
Answer: The enzyme streptokinase can dissolve blood clots. It is a useful medicine for checking heart attacks due to the blood clotting.
Q.116 What is the structural feature characterizing reducing sugars?
Answer: The main structural feature of reducing sugars is the presence of an aldehyde group (−CHO) such as in glucose, mannose, galactose, etc. or the α-ketol grouping (−CO−CH2OH)as present in fructose.
Q.117 Fructose contains a keto group but still it reduces Tollens' reagent. Explain.
Answer: Under the basic conditions of Tollens' reagent, fructose undergoes Lobry de Bruyn van Eikenstein rearrangement (refer to 'Competition Focus', page 14/88). As a result, fructose gives an equilibrium mixture of fructose, glucose and mannose. Since both glucose and mannose contain - CHO group, therefore, they reduce Tollens' reagent.
Q.118 Glycine exists as a zwitter ion but o-and p-aminobenzoic acids do not. Explain.
Answer: In o- or p-aminobenzoic acids, the lone pair of electrons on the NH2 group is donated towards the benzene ring. As a result, acidic character of−COOH group and basic character of −NH2 group decreases. Therefore, the weakly acidic −COOH group cannot transfer a H+ion to the weakly basic −NH2 group. Thus, o- or p-aminobenzoic acids do not exist as zwitter ions.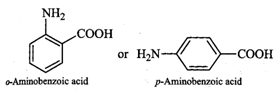
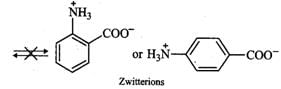
However, in glycine, no such electron withdrawing benzene ring is present. As a result, −NH2 group is sufficiently basic and hence accepts a proton form −COOH group to form a zwitter ion.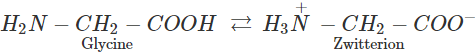
Q.119 Can the acid chloride of an α-amino acid be made by treating it with SOCl2?
Answer: No. Two molecules of the initially formed α-amino acid chloride react with each other to form a dipeptide acid chloride which, in turn, reacts further to form tetrapeptide acid chloride, etc.
NH2−CHR−COOH+SOCl2→NH2−CHR−COCl+SO2+HCl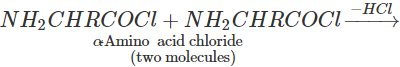

Q.120 Is a diet consisting mainly of rice an adequate diet? Why or Why not?
Answer: A diet consisting mainly of rice is not an adequate diet because it is deficient in lysine and threonine which are essential amino acids required for growth and maintenance of health and hence their deficiency has to be supplemented by other protein rich diets like pulses, etc.
Q.121 If one strand of a DNA has the sequence -ATGCTTCA-what is the sequence of the bases in the complementary strand?
Answer: We know that in DNA molecule, adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). Thus, Sequence of bases in one strand : A T G C T T C A ∴ Sequence of bases in the complementary strand : T A C G A A G T Thus, the sequence of bases in the complementary strand is TACGAAGT.
Q.122 What changes occur in the nature of egg proteins on boiling?
Answer: On boiling, the globular proteins present in the egg undergo coagulation to form fibrous proteins. As a result, proteins lose their biological activity and thus get denatured. Chemically, during denaturation, the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins are destroyed but primary structure remains intact.
Q.123 Name the two components of starch. How do they differ from each other structurally?
Answer: Starch consists of two components, (i) amylose and (ii) amylopectin. Although, both these components are made up of α-D-glucose units yet they differ in the manner in which the different α-D-glucose units are linked to one another. Amylose is a linear condensation polymer of α D-glucose in which C1 of one glucose unit is attached to C4 of the other through α-glycosidic linkage as shown in Fig. 14.8, page 14/15. Amylopectin, on the other hand, is a highly branched polymer. It consists of a large number (several hundreds) of short chains each containing 20-25 glucose units which are joined together through α-glycosidic linkages involving C1 of one glucose unit with C4 of the other. The C1 of terminal glucose unit in each chain is further linked to C6 of some other glucose unit in the next chain through C1−C6 α−glycosidic linkage. This gives amylopectin a highly branched structure as shown in Fig. 14.9, page 14/15.
Q.124 Name the four bases present in DNA. Which of these is not present in RNA?
Answer: The four bases present in DNA are : Purines: adenine (A) and guanine (G); Pyrimidines: thymine (T) and cytosine (C). Out of these, thymine (T) is not present in RNA. Instead RNA contains uracil (U).
Q.125 Give reasons for the following (i) Glucose does not give 2, 4-DNP test and Schiff's test. (ii) Ammo acids have high melting points and are soluble in water. (iii) What is meant by the secondary structure of proteins?
Answer: (i) Glucose does not have open chain structure and hence it does not have a free −CHO group. Actually CHO group combines with C5−OH to form an hemiacetal. Thus, glucose largely exists in the cyclic hemiacetal form, with a small amount (< 0.5%) of the open chain form. Since the concentration of the open chain form is low and its reactions with 2, 4-DNP reagent and Schiff's reagent are reversible, therefore, formation of 2, 4-DNP derivative or restoration of pink colour of the Schiff's reagent cannot disturb the equilibrium to generate more of the open chain form from the cyclic hemiacetal forms and hence does not give 2, 4-DNP test/Schiff's test.
(ii) α-Amino acids contain both an acidic carboxyl group and a basic amino group. These two groups neutralize each other. As a result, α-amino acids largely exist as dipolar ions or zwitterions.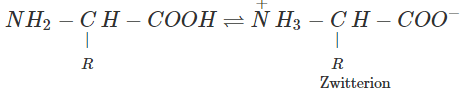
Due to dipole-dipole interactions, the molecules of α-amino acids are held together by strong forces of attraction and hence amino acids have high melting points. Further, due to strong interactions between the +ve and -ve poles of α-amino acids with polar water molecules, α-amino acids are moderately soluble in water. (iii) Secondary structure of proteins refers to the conformation or the shape which the polypeptide chains assume as a result of H-bonding. There are two types of secondary structures of proteins. These are α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure.
Q.126 What is the difference between hormones and vitamins?
Answer: The main points of difference are :
| Hormones | Vitamins |
| 1. They are produced in the ductless (endocrine) glands, e.g., testes of males and ovaries of females. | 1. They are not produced in the body but have to be supplied in food (except vitamin D which may be supplied in the food or produced in skin by irradiation of sterols present in oils and fats with UV light). |
| 2. They are not stored in the body but are continuously produced. | 2. They may remain stored (except vitamin C and some vitamins of group B) to fight out the diseases. |
|
52 videos|124 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: Biomolecules - Organic Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What are biomolecules and what role do they play in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How are carbohydrates classified and what are their functions in the body? |  |
| 3. What is the structure of a lipid molecule and what are their functions in living organisms? |  |
| 4. How are proteins formed and what are their functions in the body? |  |
| 5. What are nucleic acids and what is their role in genetic information transmission? |  |

















