Short & Long Answer Questions: Motion in a Plane | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Why cannot be vectors added algebraically?
Answer. Apart from magnitude, the vectors also have directions, so they cannot be added algebraically.
Q.2. State the essential condition for the addition of vectors.
Answer. The essential condition for the addition of vectors is that they must represent the physical quantities of the same nature.
Q.3. Is time a vector quantity? Give reason.
Answer. No, time flows from past to present and present to the future. Thus the direction of time flow is unique and does not need to be specified. Hence time is not a vector, though it has a direction.
Q.4. Is pressure a vector? Give reason.
Answer. No, The pressure is always taken to be normal to the plane of the area on which it is acting. As this direction is unique, it does need any specification. So pressure is not a vector.
Q.5. Can two vectors of different magnitudes be combined to give zero resultant?
Answer. No, two vectors of different magnitudes cannot be combined to give zero resultant. This is because the effect of vectors cancels out only when they act in the opposite direction and have the same magnitude.
Q.6. When is the magnitude of the resultant of two vectors equal to either of them?
Answer. When two vectors of equal magnitude are inclined to each other at an angle of 1200, the magnitude of their resultant is equal to that of either vector.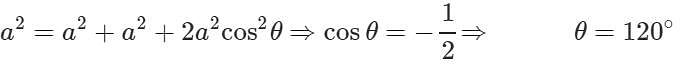
Q.7. Are the magnitude and direction of 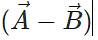 same as that of
same as that of 
Answer. The vectors  and
and 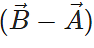 have equal magnitude but opposite directions.
have equal magnitude but opposite directions.
Q.8. Can 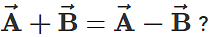
Answer. Yes. The equality holds when 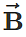 is a null vector.
is a null vector.
Q.9. When is the magnitude of 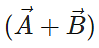 equal to the magnitude of
equal to the magnitude of  ?
?
Answer. When the vectors 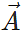 and
and 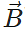 are perpendicular to each other,
are perpendicular to each other, 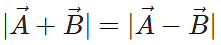
Q.10 Under what condition will the directions of sum and difference of two vectors be same?
Answer: When the two vectors are unequal in magnitude and are in the same direction.
Q.11 Can we add a velocity vector to a displacement vector?
Answer: No, only vectors representing physical quantities of same nature can be added together.
Q.12 What is the minimum number of coplanar vectors of different magnitudes which can give zero resultant?
Answer: Three. If three vectors can be represented by the three sides of a triangle taken in the same order, then their resultant is a zero vector.
Q.13  what can we say about the direction of these vectors?
what can we say about the direction of these vectors?
Answer: The three vectors have the same direction
Q.14 What is the resultant of vector 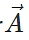 multiplied by real number m?
multiplied by real number m?
Answer: The resultant vector m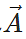 has magnitude m times that of
has magnitude m times that of 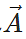 . It has same direction as that of
. It has same direction as that of 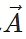 if m is positive. It has a direction opposite to that of
if m is positive. It has a direction opposite to that of 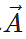 if m is negative.
if m is negative.
Q.15 Can a vector be multiplied by both dimensional and non-dimensional scalars?
Answer: Yes. When a vector is multiplied by a dimensional scalar, the resultant has different dimensions. When the vector is multiplied by a non-dimensional scalar, its dimensions remain unchanged.
Q.16 What is the maximum number of components into which a vector can be resolved?
Answer: Infinite.
Q.17 If  and Δ
and Δ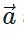 are directed opposite to each other, what is the relation between Δ
are directed opposite to each other, what is the relation between Δ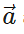 and |Δ
and |Δ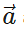 |?
|?
Answer:
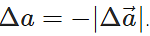
Q.18 Give two conditions necessary for a given quantity to be a vector.
Answer: (i) The quantity must have both magnitude and direction.
(ii) It must obey the laws of vector addition.
Q.19 Is finite rotation a vector?
Answer: No. This is because the addition of two finite rotations about different axes does not obey commutative law.
Q.20 Can the scalar product of two vectors be negative?
Answer: Yes, the scalar product is negative when the angle between two vectors lies between 900 and 2700.
Q.21 What is the dot product of two per-perpendicular vectors 
Answer: Zero, as 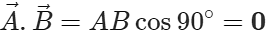
Q.22 What is the dot product of two similar unit vectors?
Answer: Unity. For example, 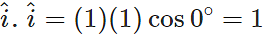
Q.23 What is the dot product of two dissimilar unit vectors? Or Calculate the value of 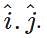
Answer: Zero. For example, 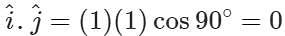
Q.24 If 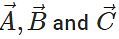 are non-zero vectors and
are non-zero vectors and 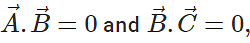
then find out the value of 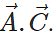
Answer:
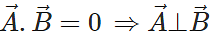
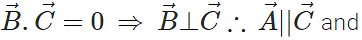
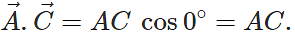
Q.25 What is the magnitude and direction of 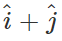
Answer: 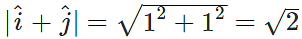 If the vector i^+j^ makes angle β with x-axis, then
If the vector i^+j^ makes angle β with x-axis, then
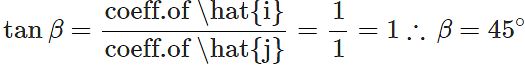
Q.26 What is the angle made by vector 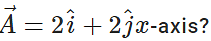
Answer: The angle θ between 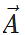 and x-axis is given by
and x-axis is given by
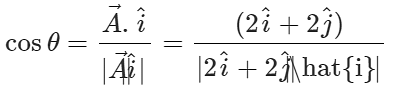
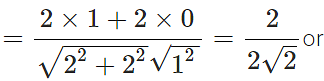
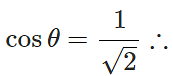
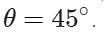
Q.27 What should be the angle θ between two vectors 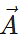 and
and 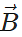 for their resultant
for their resultant 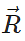 to be maximum?
to be maximum?
Answer:

R will be maximum when cosθ=+1 or θ=0∘ Rmax=A+B
Q.28 What is the effect on the magnitude of the resultant of two vectors when the angle θ between them is increased from 00 to 1800?
Answer: As the angle θ increases from 00 to 1800, the value of cosθ decreases, so the magnitude R of the resultant also decreases.
Q.29 Two persons are pulling the ends of string in such a way that the string is stretched horizontally. When a weight of 10 kg is suspended in the middle of the string, the string does not remain horizontal. Can the persons make it horizontal again by putting it with a greater force?
Answer: No, the vertical weight cannot be balanced by the horizontal force, however large the two forces may be.
Q.30 What is the vector sum of n co-planar forces, each of magnitude F, if each force makes an angle of 2π/n with the preceding force?
Answer: Total angle between n coplanar forces =(2π/n)×n=2π. This shows that forces can be represented by the n sides of a closed polygon taken in the same order. So the resultant force is zero.
Q.31 If  and
and 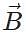 are two length vectors, then what is the geometrical significance of
are two length vectors, then what is the geometrical significance of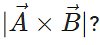
Answer: 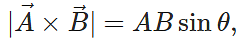 this gives area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides
this gives area of the parallelogram with adjacent sides 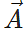 and
and 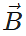 .
.
Q.32 What is the unit vector perpendicular to the plane of vectors?
Answer:
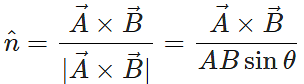
Q.33 What is the value of 
Answer: Zero, because 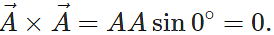
Q.34 What is the condition for two vectors to be collinear?
Answer: For two given vectors to be collinear, their cross-product must be zero.
Q.35 Find the value of 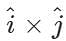 .
.
Answer: 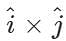 =(1)(1) sin90∘
=(1)(1) sin90∘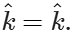
Q.36 What is 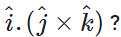
Answer: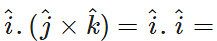 (1)(1)cos0∘=1
(1)(1)cos0∘=1
Q.37 Under what condition will the equality: 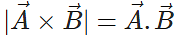 hold good?
hold good?
Answer:
 ∴ ABsinθ=ABcosθ or tanθ=1
∴ ABsinθ=ABcosθ or tanθ=1
⇒θ=45∘.
Q.38 What is the angle between 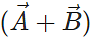 and
and 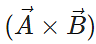 ?
?
Answer: The resultant vector 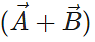 lies in the plane of
lies in the plane of 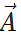 and
and 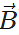 , while the cross product
, while the cross product 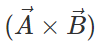 is perpendicular to this plane. So the angle between
is perpendicular to this plane. So the angle between 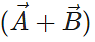 and
and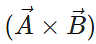 is 90∘.
is 90∘.
Q.39 Can there be motion in two dimensions with acceleration only in one dimension?
Answer: Yes, in a projectile motion, the acceleration acts vertically downwards while the projectile follows a parabolic path.
Q.40 Can the direction of velocity of a body change when the acceleration is constant?
Answer: Yes, in projectile motion the direction of velocity changes from point to point, but its acceleration is always constant and acts vertically downwards.
Q.41 Is the rocket in flight an example of projectile?
Answer: No, because it is propelled by combustion of fuel and does not move under the effect of gravity alone.
Q.42 A stone is thrown vertically upwards and then it returns to the thrower. Is it a projectile?
Answer: It is not a projectile, because a projectile should have two-component velocities in two mutually perpendicular directions, but in this case, the body has velocity only in one direction while going up or coming downwards.
Q.43 Why does a projectile fired along the horizontal not follow a straight line path?
Answer: Because the projectile fired horizontally is constantly acted upon by acceleration due to gravity acting vertically downwards.
Q.44 A body projected horizontally moves with the same horizontal velocity although it is under the action of force of gravity. Why?
Answer: The force of gravity acts in the vertically downward direction and has no effect on the horizontal component of velocity, and this makes the body to move with constant horizontal velocity.
Q.45 What is the angle between the direction of velocity and acceleration at the highest point of a projectile path?
Answer: 90∘. At the highest point, the vertical component of velocity becomes zero, the projectile has only a horizontal velocity while the acceleration due to gravity acts vertically downwards.
Q.46 A bullet is dropped from a certain height and at the same time, another bullet is fired horizontally from the same height. Which one will hit the ground earlier and why?
Answer: Since the heights of both bullets from the ground are the same, the time taken by both of them to reach the ground will be the same.
Q.47 A stone dropped from the window of a stationary bus takes 5 seconds to reach the ground. In what time the stone will reach the ground when the bus is moving with (a) constant velocity of 80 kmh−1 (b) constant acceleration of 2 kmh−2 ?
Answer: (a) 5 seconds (b) 5 seconds.
In both cases, initial vertical velocity is zero, downward acceleration is equal to ′g′ and also vertical distance covered is same.
Q.48 A bomb thrown as projectile explodes in mid-air. What is the path traced by the center of mass of the fragments assuming the friction to be negligible?
Answer: The path traced by the center of mass of the fragments is a parabola.
Q.49 At what point in its trajectory does a projectile have its (i) minimum speed (ii) maximum speed?
Answer: For a projectile given angular projection, the horizontal component of velocity remains constant throughout while the vertical component first decreases, becomes zero at the highest point and then increases again. Hence
(i) Projectile has minimum speed at the highest point of its trajectory.
(ii) Projectile has maximum speed at the point of projection and at the point where it returns to the horizontal plane of projection.
Q.50 What will be the effect on horizontal range of a projectile when its initial velocity is doubled, keeping the angle of projection same?
Answer: 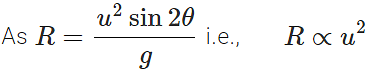
When u is doubled, the horizontal range becomes four times the original horizontal range.
Q.51 A projectile is fired at an angle of 15∘ to the horizontal with the speed υ. If another projectile is projected with the same speed, then at what angle with the horizontal it must be projected so as to have the same range?
Answer: For the same R and υ, the sum of the two angles of projection is 90∘. As one angle is of 15∘, others should be 90∘−15∘ =75∘.
Q.52 Is the maximum height attained by projectile is largest when its horizontal range is maximum?
Answer: No. Horizontal range is maximum when θ=45∘ and maximum height attained by projectile is largest when θ=90∘.
Q.53 What will be the effect on maximum height of a projectile when its angle of projection is changed from 30∘ to 60∘, keeping the same initial velocity of projection?
Answer: Maximum height, 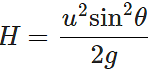
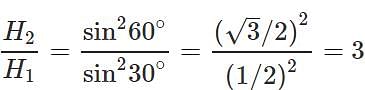 Thus the maximum height becomes three times the original maximum height.
Thus the maximum height becomes three times the original maximum height.
Q.54 A body is projected with speed u at an angle θ to the horizontal to have maximum range. What is the velocity at the highest point?
Answer: For maximum horizontal range, θ=45∘ Velocity at highest point = Horizontal component of velocity =u cos 45∘=u/√2
Q.55 What is the angle of projection for a projectile motion whose range R is n times the maximum height H?
Answer: Here R=nH or 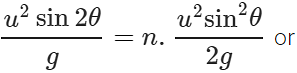
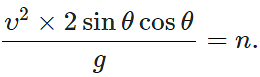
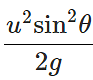 ortanθ = 4/n ⇒ θ=tan−1(4/n)
ortanθ = 4/n ⇒ θ=tan−1(4/n)
Q.56 The greatest height to which a man can throw a stone is h. What will be the greatest distance up to which he can throw the stone?
Answer: Maximum height attained, 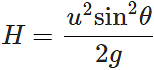
Clearly, H will be maximum when sinθ=1
∴ Hmax= u2/g =2h.
Q.57 A particle is projected at an angle θ from the horizontal with kinetic energy K. What is the kinetic energy of the particle at the highest point?
Answer: If the particle is projected with velocity υ, then its initial kinetic energy is K=1/2 mυ2 Velocity of the projectile at the highest point =υcosθ
∴K.E. of the particle at the highest point = 1/2 m(υcosθ)2=(1/2 mυ2)cos2θ=Kcos2θ.
Q.58 A man can jump on the moon six times as high as on the earth. Why?
Answer: Maximum height attained on earth, 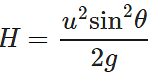 Acceleration due to gravity on moon, g′=g/6
Acceleration due to gravity on moon, g′=g/6
∴ Maximum height attained on moon:
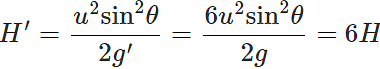
So, one can jump on moon six times as high as on earth.
Q.59 A projectile of mass m is fired with velocity υ at an angle θ with the horizontal. What is the change in momentum as it rises to the highest point of the trajectory?
Answer: Horizontal component of velocity remains constant. The vertical component is υ sin θ at the point of projection and zero at the highest point. Magnitude of change in momentum =m(υsinθ−0)=mυsinθ (in the vertical direction).
Q.60 A projectile of mass m is thrown with velocity υ from the ground at an angle of 45∘ with the horizontal. What is the magnitude of change in momentum between leaving and arriving back at the ground?
Answer: The vertical component of velocity at the point of projection is υ sin θ and at the point of return is −υ sin θ.
∴ Magnitude of change in momentum =m(υsinθ+υsinθ)= 2mυ sinθ = 2mυ sin45∘=√2mυ (in the vertical direction).
Q.61 A block slides down a smooth inclined plane when released from the top while another falls freely from the same point. Which one of them will strike the ground earlier?
Answer: Acceleration of the freely falling block is g while that of the block sliding down the smooth inclined plane is gsinθ. Asg>gsinθ, so the block falling freely will reach the ground earlier.
Q.62 Why does a tennis ball bounce higher on hills than in plains?
Answer: Maximum height attained by a projectile ∝ 1/g As the value of g is less on hills than on plains, so a tennis ball bounces higher on hills than on plains.
Q.63 A stone is thrown horizontally with a speed 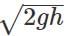 from the top of a wall of height h. It strikes the level ground through the foot of the wall at a distance x from the wall. What is the value of x?
from the top of a wall of height h. It strikes the level ground through the foot of the wall at a distance x from the wall. What is the value of x?
Answer:
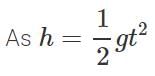
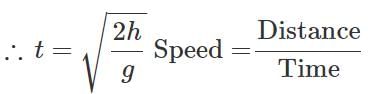
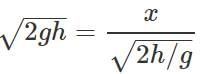 or
or 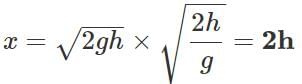
Q.64 The velocity of a particle is constant in magnitude but not in direction. What is the nature of trajectory?
Answer: The particle moves on a curved path. The instantaneous direction will be tangential to the path at every point.
Q.65 What is the angle between velocity vector and acceleration vector in uniform circular motion?
Answer: 900.
Q.66 For uniform circular motion, does the direction of centripetal acceleration depends upon the sense of rotation?
Answer: The direction of centripetal acceleration does not depend on the clockwise or anticlockwise sense of rotation of the body. It always acts along the radius towards the center of the circle.
Q.67 If both the speed and radius of the circular path of a body are doubled, how will the centripetal acceleration change?
Answer: Original centripetal acceleration, a = v2/r New centripetal acceleration,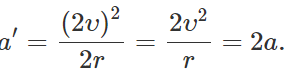
Q.68 A stone tied to the end of a string is whirled in a circle. If the string breaks, the stone flies away tangentially. Why?
Answer: The instantaneous velocity of the stone going around the circular path is always along tangent to the circle. When the string breaks, the centripetal force ceases. Due to inertia, the stone continues its motion along tangent to the circular path.
Q.69 When a knife is sharpened with the help of a rotating grinding stone, the spark always travels tangentially to it. Why?
Answer: When a knife is sharpened, the red hot particles of the grinding stone get separated as sparks. As these particles are in circular motion, hence their velocities are directed tangentially to the grinding stone.
Q.70 Which of the following quantities are independent of the choice of orientation of the coordinate axes : 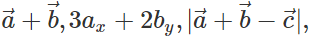 angle between
angle between 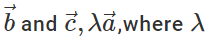 is a scalar?
is a scalar?
Answer: A vector, its magnitude and the angle between two vectors do not depend on the choice of the orientation of the coordinate axes, so 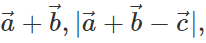 angle between
angle between 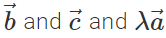 are independent of the orientation of the coordinate axes. But the quantity
are independent of the orientation of the coordinate axes. But the quantity 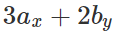 depends upon the magnitude of the components along x- and y-axes, so it will change with the change in coordinate axes.
depends upon the magnitude of the components along x- and y-axes, so it will change with the change in coordinate axes.
Q.71 Do  lie in the same plane. Give reason.
lie in the same plane. Give reason.
Answer: Yes, because 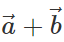 is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn with
is represented by the diagonal of the parallelogram drawn with 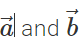 as adjacent sides. The diagonal passes through the common tail of
as adjacent sides. The diagonal passes through the common tail of 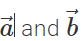 . However,
. However, 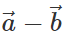 is represented by the other diagonal of the same parallelogram not passing through the common tail of
is represented by the other diagonal of the same parallelogram not passing through the common tail of 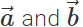 Thus both
Thus both 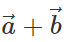 and
and 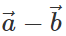 lie in plane of the same parallelogram.
lie in plane of the same parallelogram.
Q.72 Can we apply the commutative and associative laws to vector subtraction also?
Answer: (i) No, we cannot apply commutative law to vector subtraction because 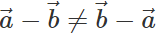 (ii) Yes, association law can be applied to vector subtraction because
(ii) Yes, association law can be applied to vector subtraction because
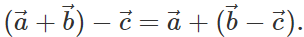
Q.73 Can three vectors not in one plane give a zero resultant? Can four vectors do so?
Answer: No, three vectors not in one plane cannot give a zero resultant because the resultant of two vectors will not lie in the plane of the third vector and hence cannot cancel its effect. The resultant of four vectors not in one plane may be a zero vector.
Q.74 What is the difference between the following two data : (i) 8 (5 km/hr, east) (ii) (8 hr) (5 km/hr, east)?
Answer: (i) It is the product of a pure number and a vector (velocity), hence the unit of product is the same as that of vector i.e., the product is a velocity of 40 km/hr, towards east. (ii) It is the product of a scalar (time) and a vector (velocity). Hence the unit of the product will be hr × (km/hr). Thus the product is a displacement of magnitude 40 km, towards east.
Q.75 Under what condition does the equality: 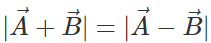 hold good?
hold good?
Answer: 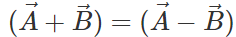
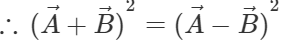 or
or 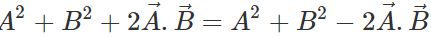 or
or 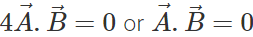
This implies that  are perpendicular to each other.
are perpendicular to each other.
Q.76 The sum and difference of two vectors are perpendicular to each other. Prove that the vectors are equal in magnitude.
Answer: As the vectors  are perpendicular to each other, therefore
are perpendicular to each other, therefore 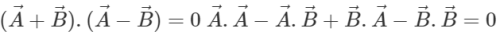 or
or
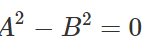
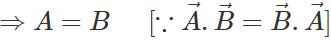 .
.
Q.77 Find the conditions for two vectors to be (i) parallel and (ii) perpendicular to each other.
Answer: and
and 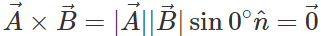 Hence if two vectors are parallel, then their cross product must be zero.
Hence if two vectors are parallel, then their cross product must be zero.
(ii) If 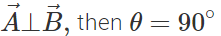 and
and 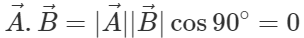 Hence if two vectors are perpendicular, then their dot product must be zero.
Hence if two vectors are perpendicular, then their dot product must be zero.
Q.78 The magnitude of vector 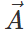 is 2.5 meter and is directed towards east. What will be the magnitudes and directions of the following :
is 2.5 meter and is directed towards east. What will be the magnitudes and directions of the following : 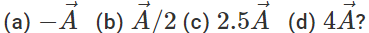
Answer: (a) 2.5 m due west. (b) 1.25 due east. (c) 6.25 m due west. (d) 10 m due east.
Q.79 A person sitting in a moving train throws a ball vertically upwards. How will the ball appear to move to an observer (i) sitting inside the train (ii) standing outside the train? Give reason.
Answer: (i) To the observer inside the train, the ball will appear to move straight vertically upwards and then downwards because with respect to an observer sitting inside the train, the ball has only one velocity acting vertically downward. (ii) To the observer outside the train, the ball will appear to move along the parabolic path because with respect to the observer outside the train, the ball has both horizontal and vertical components of velocity.
Q.80 A bob hung from the ceiling of a room by a string is performing simple harmonic oscillations. What will be the trajectory of the bob, if the string is cut, when bob is (i) at one of its extreme positions, (ii) at its mean position?
Answer: (i) When the string is cut in one of the extreme positions of the bob, the bob will fall vertically downwards. The reason is that when the bob reaches its extreme positions, it comes to rest for a moment. If the string is cut, it will be simply the case of a body falling freely under gravity. (ii) When the string is cut in mean position of the bob, then the bob will move on parabolic path. The reason is that when the bob is at its mean position, it has a velocity parallel to the horizontal. If the string is cut, it will be simply the case of a projectile fired parallel to the horizontal.
Q.81 Prove that the horizontal range is same when angle of projection is (i) greater than 45∘ by certain value and (ii) less than 45∘ by the same value.
Answer: (i) When the angle of projection, θ=45∘+α,, the horizontal range is 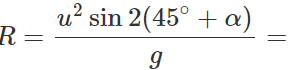
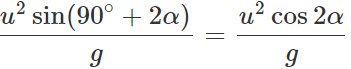
(ii) When the angle of projection, θ=45∘−α,, the horizontal range is 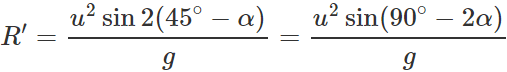
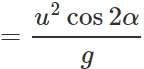 Clearly, R′=R.
Clearly, R′=R.
Q.82 Two bombs of 5 kg and 10 kg are thrown from a cannon with the same velocity in the same direction, (i) Which bomb will reach the ground first? (ii) If the bombs are thrown in the same direction with different velocity, what would be the effect?
Answer: (i) Both the bombs will reach the ground simultaneously because the time of flight does not depend upon mass of the projectile. (ii) On throwing with different velocities, the bomb thrown with lesser velocity will reach the ground earlier. 
Q.83 Two bodies are thrown with the same initial velocity at angles α and (90∘ − α) with the horizontal. What will be the ratio of (i) maximum heights attained by them and (ii) their horizontal ranges?
Answer: (i) When the angle of projection α, the maximum height is H1= 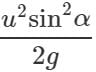 When the angle of projection is(90∘ − α), the maximum height is
When the angle of projection is(90∘ − α), the maximum height is
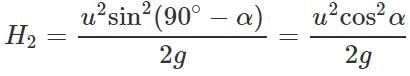
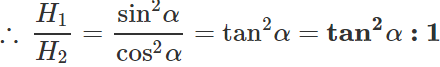 (ii) When the angle of projection is a, the horizontal range is
(ii) When the angle of projection is a, the horizontal range is 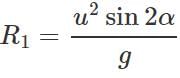 When the angle of projection is(90∘−α), the horizontal range is
When the angle of projection is(90∘−α), the horizontal range is 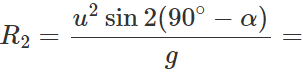
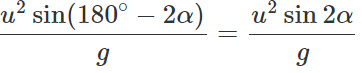
∴ R1:R2=1:1
Q.84 At which points on the projectile trajectory is the (i) potential energy maximum (ii) kinetic energy minimum and (iii) total energy maximum?
Answer: (i) P.E. of a projectile is maximum at its highest point because of its maximum height. It is given by (P.E.)H=mgH=mg. 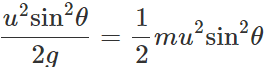
(ii) K.E. of a projectile is minimum (not zero) at its highest point because of its minimum velocity.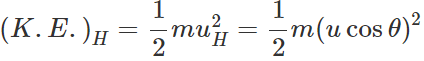
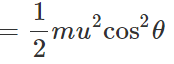
(ii) Total energy at highest point =(P.E.)H+(K.E)H = 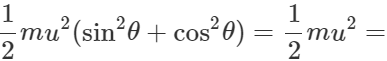
Total energy at the point of projection Hence total energy of a projectile is conserved at all points of its motion. The K.E. is maximum at the point of projection.
Q.85 A body A of mass m is thrown with velocity υ at an angle 30∘ to the horizontal and another body B of the same mass is thrown with velocity υ at an angle of 60∘ to the horizontal, find the ratio of the horizontal range and maximum height of A and B.
Answer: For body A : θ = 30∘ Horizontal range, 
Maximum height, 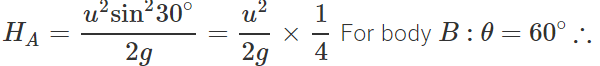
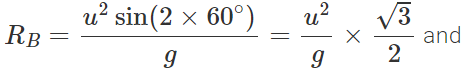
 Hence RA:RB=1:1 and HA:HB=1:3
Hence RA:RB=1:1 and HA:HB=1:3
Q.86 A ball of mass m is thrown vertically up. Another ball of mass 2m is thrown at an angle θ with the vertical. Both of them remain in air for the same period of time. What is the ratio of the heights attained by the two balls?
Answer: Time of flight of the ball thrown vertically upwards, 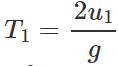 Time of flight of the ball thrown at an angle θ with the vertical , T2=
Time of flight of the ball thrown at an angle θ with the vertical , T2= 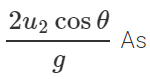
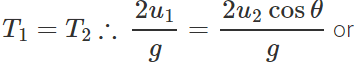 u1=u2cosθ Now
u1=u2cosθ Now 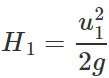 and
and 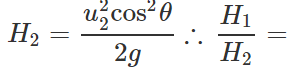
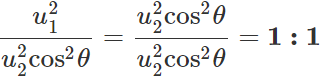
Q.87 Is it important in the long jump that how much height you take for jumping? What factors determine the span of a jump?
Answer: Yes, for the longest jump the player should throw himself at an angle of 45∘ with respect to horizontal. The vertical height for this angle is H=u2sin245∘/2g=u2/4g, where u is the velocity of projection. If the vertical height is different from u2/4g, then the angle will be different from 45∘ and the horizontal distance covered will also be less. Clearly, the span of jump depends upon (i) the initial velocity of the jump, (ii) the angle of projection.
Q.88 A body is thrown horizontally with a velocity υ from a tower of height H. After how much time and at what distance from the base of the tower will the body strike the ground?
Answer: Clearly, 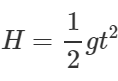
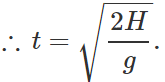 Distance from the base of the tower, x=υt=
Distance from the base of the tower, x=υt=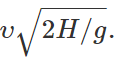
Q.89 A ball is thrown horizontally and at the same time another ball is dropped down from the top of a tower (i) will both the balls reach the ground at the time? (ii) Will both strike the ground with the same velocity?
Answer: (i)Yes, because the initial vertical velocity of both the balls is zero, and both will cover the same vertical distance under the same vertical acceleration g. (ii)No, because on striking the ground although their vertical velocities will be same but horizontal velocities will be different. Hence their resultant velocities will be different.
Q.90 A horizontal stream of water leaves an opening in the side of a tank. If the opening is h meters above the ground and the stream hits the ground D meter away, then what is the speed of water as it leaves the tank in terms of g, h and D?
Answer: The steam of water leaving the tank behaves like a horizontal projectile and follows parabolic path. 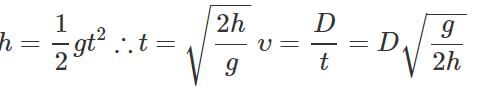
Q.91 A railway carriage moves over a straight, track with acceleration a. A passenger in the carriage drops a stone. What is the acceleration of the stone w. r. t. the carriage and the earth?
Answer: When the stone is dropped, it falls freely under the acceleration due to gravity g. With respect the earth, the acceleration of the stone is g. Inside the carriage, the stone possesses two accelerations: (i) Horizontal acceleration ′a′ due to the motion of the carriage. (ii) Vertical downward acceleration 'g' due to gravity. The acceleration of the stone w. r. t. the carriage =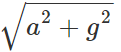
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: Motion in a Plane - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is motion in a plane? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of motion in a plane? |  |
| 3. How is velocity calculated in motion in a plane? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of acceleration in motion in a plane? |  |
| 5. How can we analyze the trajectory of an object in motion in a plane? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|


















