Short & Long Answer Questions: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles & Techniques | Organic Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Q.1 Ethyne is a stronger acid than propyne. Explain.
Answer: Terminal alkynes (R−C≡C−H) are weakly acidic in nature because of sp-hybridised state of the triple bonded carbon atom. Due to substantial s-character (50%), the triple bonded carbon is electronegative in nature and this enables the release of H+ ion from ≡C−H bond. However, ethyne is a stronger acid than propyne. This is attributed to the electron releasing +I effect of the methyl group which tends to increase the electron density on the triple bonded carbon atom in propyne. The release of H+ion from propyne is more difficult than from ethyne or it is a weaker acid than ethyne.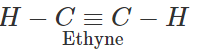
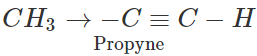
Q.2 Electromeric effect is a temporary effect. Assign reason.
Answer: The electromeric effect is noticed in the organic compounds containing multiple bond i. e., double bond (> C = C < or > C = O) or triple bond (−C≡N) under the influence of the attacking reagent. The moment the attacking reagent is removed, pi (π) electron pair comes back to its original position forming multiple bond again. Therefore, electromeric effect is a temporary effect.
Q.3 Alcohols are weaker acids than water. Why?
Answer: In alcohol (R→−O−H), the alkyl group has +I effect. It increases the electron density on the oxygen atom. As a result, the release of H+ ion from alcohol is more difficult than from water or alcohol is a weaker acid.
Q.4 Ethylamine is a stronger base than acetamide. Assign reason.
Answer: In acetamide, the carbonyl group is electron withdrawing in nature. It decreases the electron density on the nitrogen atom of the amino group due to conjugation. On the other hand, in ethylamine, the ethyl group has 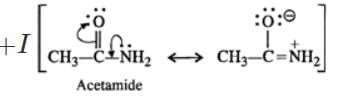
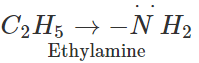 effect and it increases the electron density on the nitrogen atom. Therefore, electron releasing tendency is more in ethylamine than in acetamide or the former is a stronger base.
effect and it increases the electron density on the nitrogen atom. Therefore, electron releasing tendency is more in ethylamine than in acetamide or the former is a stronger base.
Q.5 Higher alkyl substituted alkene is formed in greater proportion than the lower alkyl substituted alkene. Justify.
Answer: In alkyl substituted alkene, the α-hydrogen atoms of the methyl group are involved in the hyper conjugation with the pi(π) electron pair of the double bond. As a result, the stability of alkene increases. Greater the number of such groups more will be the stability of alkene. Thus, the relative order of stability of the following alkenes is: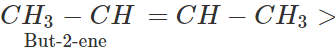
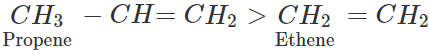
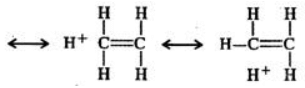
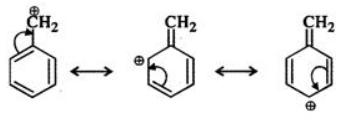
Q.6 Benzyl carbocation is more stable than ethyl carbocation. Justify.
Answer: In ethyl carbocation, there is only hyper-conjugation of the three α-hydrogen atoms and as a result, the following contributing structures are feasible.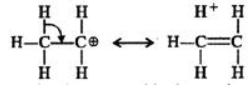
But benzyl carbocation is more stable due to the presence of resonance and the following resonating structures are possible:
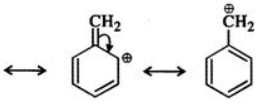
Q.7 How will you separate a mixture of benzoic acid and naphthalene?
Answer: Both these solids sublime on heating. Therefore, these cannot be separated by sublimation. The mixture is heated with water when only benzoic acid will dissolve. Upon filtration, naphthalene is separated and the solution upon cooling gives crystals of benzoic acid. Alternatively the mixture is reacted with strong aqueous sodium hydroxide when benzoic acid is converted to soluble sodium benzoate while napthalene is unaffected. It can be separated by filtration. The filtrate is then treated with dilute HCl to regenerate benzoic acid.

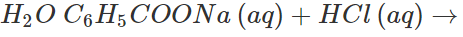
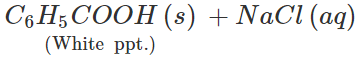
Q.8 Give the IUPAC name of the saturated hydrocarbon having the following carbon skeleton.
Answer: 5-Ethyl-2, 3, 4-trimethyloctane
Q.9 Give the IUPAC name for the amine.
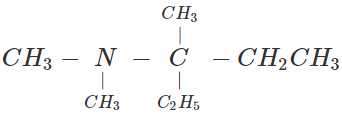
Answer: N, N, 3-Trimethylpentan-3-amine (Alphabets are given preference over numerals).
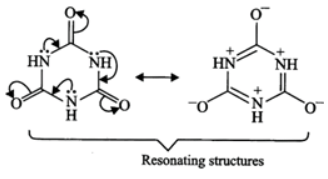
Q.10 Write resonance structures of the given compound.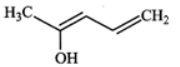
Answer: The following four resonance structures can be written for the given compound.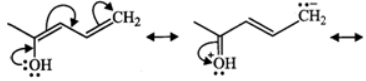
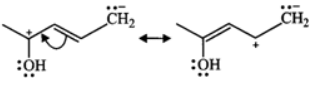
Q.11 (a) Write down resonating structure and tautomer of 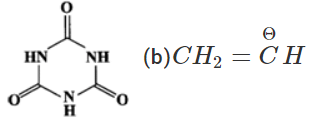 is more basic than HC≡C−. Explain why.
is more basic than HC≡C−. Explain why.
Answer: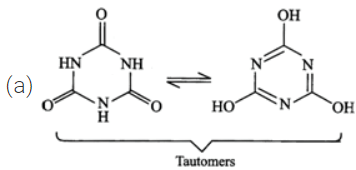
(b)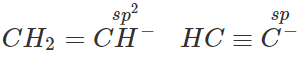 Since, sp-carbon is more electronegative than sp2-carbon, therefore, CH≡C− is less willing to donate a pair of electrons than H2C=CH−. In other words, H2C=CH− is more basic than HC≡C−.
Since, sp-carbon is more electronegative than sp2-carbon, therefore, CH≡C− is less willing to donate a pair of electrons than H2C=CH−. In other words, H2C=CH− is more basic than HC≡C−.
Q.12 Which of the following pairs do not constitute resonance structures? (a)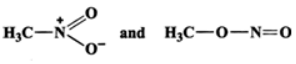

 (d) CH3CH=CHCH3andCH3CH2CH=CH2
(d) CH3CH=CHCH3andCH3CH2CH=CH2
Answer: (a) The two structures differ in the position of atoms and hence they are not resonance structures. In fact, these are functional isomers, i.e., CH3−NO2 having nitro (−NO2) group as the functional group and CH3−ONO having nitrite (O=N−O−) as the functional group. (b) 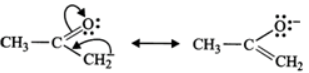 These two are resonance structures because they differ in the position of electrons only and not atoms. (c) These are not resonance structures since they differ in the position of atoms. They are, in fact, tautomers.
These two are resonance structures because they differ in the position of electrons only and not atoms. (c) These are not resonance structures since they differ in the position of atoms. They are, in fact, tautomers. 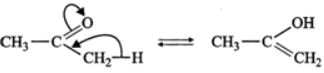 (d) These are not resonance structures since these differ in the position of double bond. In fact, these are position isomers.
(d) These are not resonance structures since these differ in the position of double bond. In fact, these are position isomers.
Q.13 Explain the following: (i)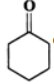 exists in keto form but
exists in keto form but 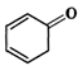 exists in enol form. (ii) CH2=CH−is a better nucleophile than HC≡C−.
exists in enol form. (ii) CH2=CH−is a better nucleophile than HC≡C−.
Answer: (i)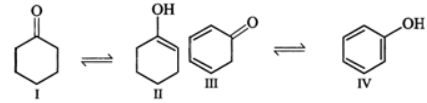 Enol form (II) is not stabilized and hence it exists in the keto form (I) Enol form (IV) is stabilized by resonance energy (150.6kJmol−1) of the benzene ring and hence (III) exists in the enol form (IV) (ii) In H2C=CH−, the carbon atom carrying the -ve charge is sp2-hybridized while in HC≡C−, the carbon atom carrying the -ve charge is sp-hybridized. Since a sp2-hybridized carbon is less electronegative than a sp-hybridized carbon, therefore, H2C=CH−is a better nucleophile than HC≡C−.
Enol form (II) is not stabilized and hence it exists in the keto form (I) Enol form (IV) is stabilized by resonance energy (150.6kJmol−1) of the benzene ring and hence (III) exists in the enol form (IV) (ii) In H2C=CH−, the carbon atom carrying the -ve charge is sp2-hybridized while in HC≡C−, the carbon atom carrying the -ve charge is sp-hybridized. Since a sp2-hybridized carbon is less electronegative than a sp-hybridized carbon, therefore, H2C=CH−is a better nucleophile than HC≡C−.
Q.14 When do we use a fluted filter paper or hot water funnel for filtration?
Answer: To avoid crystallization during filtration, fluted filter paper is used when the volume of the solution to be filtered is small and hot water funnel when the volume is large.
Q.15 How will you purify a liquid having non-volatile impurities?
Answer: Simple distillation will give us the pure liquid while the non- volatile impurities will remain in the flask as residue.
Q.16 Suggest a method to purify : (i) Camphor containing traces of common salt. (ii) Kerosene oil containing water. (iii) A liquid which decomposes at its boiling point.
Answer: (i) Sublimation. Camphor sublimes while common salt remains as residue in the china dish. (ii) Since the two liquids are immiscible, the technique of solvent extraction with a separating funnel is used. The mixture is thoroughly shaken and the separating funnel is allowed to stand. Kerosene being lighter than water forms the upper layer while water forms the lower layer. The lower water layer is run off when kerosene oil is obtained. It is dried over anhydrous CaCl2 or MgSO4 and then distilled to give pure kerosene oil. (iii) Distillation under reduced pressure.
Q.17 A mixture contains two components A and B. The solubilities of A and B in water near their boiling point are 10 grams per 100 mL and 2 g per 100 mL respectively. How will you separate A and B from this mixture?
Answer: Fractional crystallization. When the saturated hot solution of this mixture is allowed to cool, the less soluble component B crystallizes out first leaving the more soluble component A in the mother liquor.
Q.18 Suggest methods for the separation of the following mixtures. (i) A mixture of liquid A (b.p. 365 K) and liquid B (b.p. 356 K). (ii) A mixture of liquid C (b.p. 353 K) and liquid D (b.p. 413 K).
Answer: (i) Fractional distillation because the boiling points of the two liquids differ by just 9∘. (ii) Simple distillation since the boiling points of the two liquids are widely apart.
Q.19 How will you purify essential oils?
Answer: Essential oils are volatile and are insoluble in water. Therefore, they are purified by steam distillation.
Q.20 How will you separate a mixture of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol?
Answer: Steam distillation. o-Nitrophenol being steam volatile distils over along with water while p-nitrophenol being non-volatile remains in the flask.
Q.21 (a) Write the IUPAC name of (i) 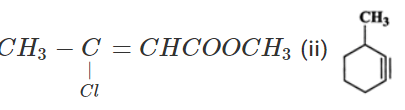 (b) Out of
(b) Out of  which will be eluted first in moderately polar solvent and why?
which will be eluted first in moderately polar solvent and why?
Answer: (a) (i) Methyl 3-chlorobut-2-en-1-oate (ii) 3-Methylcyclohexyne (b) 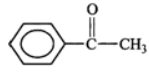 has significant dipole moment while
has significant dipole moment while 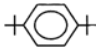 being symmetrical has zero dipole moment. Therefore, di-tert-butyl benzene is non-polar and hence will not be adsorbed strongly on the adsorbent and hence it will be eluted first in moderately polar solvent.
being symmetrical has zero dipole moment. Therefore, di-tert-butyl benzene is non-polar and hence will not be adsorbed strongly on the adsorbent and hence it will be eluted first in moderately polar solvent.
Q.22 A liquid (1.0 g) has three components. Which technique will you employ to separate them?
Answer: Column chromatography.
Q.23 The Rf value of A and B in a mixture determined by TLC in a solvent mixture are 0.65 and 0.42 respectively. If the mixture is separated by column chromatography using the same solvent mixture as a mobile phase, which of the two components, A or B, will elute first? Explain.
Answer: Since the Rf value of A is 0.65, therefore, it is less strongly adsorbed as compared to component B with Rf value of 0.42. Therefore, on extraction of the column, A will elute first.
Q.24 A mixture contains benzoic acid and nitrobenzene. How can this mixture be separated into its constituents by the technique of extraction using an appropriate chemical reagent?
Answer: The mixture is shaken with a dilute solution of NaHCO3 and extracted with ether or chloroform when nitrobenzene goes into the organic layer. Distillation of the solvent gives nitrobenzene. The filtrate is acidified with dil. HCl when benzoic acid gets precipitated. The solution is cooled and benzoic acid is obtained by filtration.
Q.25 Without using column chromatography, how will you separate a mixture of camphor and benzoic acid?
Answer: Sublimation cannot be used since both camphor and benzoic acid sublime on heating. Therefore, a chemical method using NaHCO3 solution is used when benzoic acid dissolves leaving camphor behind. The filtrate is cooled and then acidified with dil. HCl to get benzoic acid.
Q.26 Name two compounds which do not contain halogen but give positive Beilstein test.
Answer: Urea and thiourea give positive Beilstein test due to the formation of volatile cupric cyanide.
Q.27 Will sodium cyanide give a positive Lassaigne's test for nitrogen?
Answer: Yes. During fusion with Na metal, the N of the organic compound is actually converted into NaCN which is the primary requirement for Lassaigne's test for nitrogen.
Q.28 How will you test the presence of nitrogen in hydrazine?
Answer: If hydrazine (NH2NH2)is fused with Na metal, it does not form NaCN since it does not contain carbon and hence will not give +ve test for nitrogen. In order to test the presence of N in such compounds, during fusion with Na, some charcoal or preferably starch (which contains C but not N, S, halogens, etc.) is added. Under these conditions, C of starch or charcoal combines with N of the compound to form NaCN which will now give a +ve test for nitrogen.
Q.29 Lassaigne's test is not shown by diazonium salts. Why?
Answer: Diazonium salts usually lose N2 on heating much before they have a chance to react with fused sodium metal. Therefore, diazonium salts do not show positive Lassaigne's test for nitrogen.
Q.30 Sometimes a red colour is not produced in the Lassaigne's test even if both nitrogen and sulphur are present in the organic compound. Explain.
Answer: In principle, if the organic compound contains both N and S, sodium thiocyanate should be formed in Lassaigne's test and this should give blood red colouration with 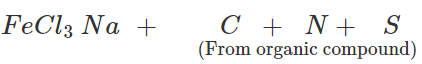
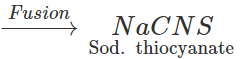 3NaCNS+FeCl3→
3NaCNS+FeCl3→ 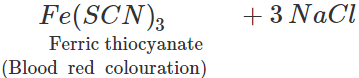 However, if blood red colouration is not obtained, it does not necessarily mean that S is absent. This is because in presence of excess of sodium metal, sodium thiocyanate initially formed, decomposes to form sodium cyanide and sodium sulphide. 2Na+2NaCNS
However, if blood red colouration is not obtained, it does not necessarily mean that S is absent. This is because in presence of excess of sodium metal, sodium thiocyanate initially formed, decomposes to form sodium cyanide and sodium sulphide. 2Na+2NaCNS 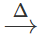 NaCN+Na2S As a result, blood red colouration is not obtained.
NaCN+Na2S As a result, blood red colouration is not obtained.
Q.31 Why is a freshly prepared saturated solution of ferrous sulphate used in the Lassaigne's test for nitrogen?
Answer: On keeping aq. FeSO4 solution, it undergoes oxidative-hydrolysis to form basic ferric sulphate 4FeSO4+2H2O+O2 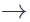 4Fe(OH)SO4 The pale yellow colour of Fe3+ ions interferes with the light green colour usually obtained in Lassaigne's test.
4Fe(OH)SO4 The pale yellow colour of Fe3+ ions interferes with the light green colour usually obtained in Lassaigne's test.
|
52 videos|128 docs|138 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles & Techniques - Organic Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What are some basic principles of organic chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are the techniques commonly used in organic chemistry? |  |
| 3. How do you name organic compounds? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of organic chemistry in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How can one determine the structure of an organic compound? |  |