Interest on Capital & Methods for Interest on Capital | Crash Course of Accountancy - Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Interest on capital Accounting treatment
· P & L appropriation a/c Dr. side
· Capital / current a/c Cr. Side
Journal entry
Entry for Interest on Capital :—
(i) On allowing Interest on Capital :
Interest on Capital A/c Dr.
To Partner’s Capital A/c
(Interest on Capital at ....% p.a.)
(ii) On closure of Interest on Capital A/c :
Profit & Loss Appropriation A/c Dr.
To Interest on Capital A/c
Methods for interest on capital
Direct method
Interest on capital = capital X ROI/100 X M/12
Example – A was having a capital of Rs.3,00,000 on 1st april 2014. During the year A introduced Rs.1,00,000 as additional capital on 1st December 2014.
Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution
For 8months (from 1april to 1december)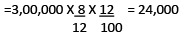
For 4months (from 1december to 31march)-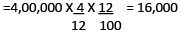
Total= 24,000 + 16,000 = 40,000
Product method
Interest on capital = total capital X ROI/100 X 1/12
Example – A was having a capital of Rs.3,00,000 on 1st april 2014. During the year A introduced Rs.1,00,000 as additional capital on 1st December 2014.
Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution-
Amount | Months | Product |
3,00,000 | 8 | 24,00,000 |
4,00,000 | 4 | 16,00,000 |
Total capital | 40,00,000 |
Interest on capital = 
CASE 1
A & B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ration of 3:2 with capitals of Rs.3,00,000 and Rs.2,00,000 on 1st april 2014. Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution –
A’s Interest on capital = 3,00,000 ∗ 12/100 = 36,000 B’s Interest on capital = 2,00,000 ∗ 12/100 = 24,000
CASE 2
A & B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ration of 3:2 with capitals of Rs.3,00,000 and Rs.2,00,000 on 1st april 2014. During the year A introduced Rs.1,00,000 as additional capital on 1st December 2014 and B had withdrawn Rs.50,000 from his capital on 31st dec 2014. Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution –
A’s Interest on capital = 40,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 40,000
Amount | Months | Product |
3,00,000 | 8 | 24,00,000 |
4,00,000 | 4 | 16,00,000 |
Total capital | 40,00,000 |
B’s Interest on capital = 22,50,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 22,500
Amount | Months | Product |
2,00,000 | 9 | 18,00,000 |
1,50,000 | 3 | 4,50,000 |
Total capital | 22,50,000 |
CASE 3
A,B & C are partners sharing profits and losses in the ration of 3:2:1 with capitals of Rs.3,00,000, Rs.2,00,000 and Rs.2,00,000 on 1st april 2014. During the year A & B both had introduced Rs.1,00,000 as additional capital on 1st October 2014 , B had withdrawn Rs.50,000 from his capital and C had introduced Rs.1,00,000 as additional capital on 31st dec 2014. Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution-
A’s Interest on capital = 42,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 42,000
Amount | Months | Product |
3,00,000 | 6 | 18,00,000 |
4,00,000 | 6 | 24,00,000 |
Total capital | 42,00,000 |
B’s Interest on capital = 28,50,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 28,500
Amount | Months | Product |
2,00,000 | 6 | 12,00,000 |
3,00,000 | 3 | 9,00,000 |
2,50,000 | 3 | 7,50,000 |
Total capital | 28,50,000 |
C’s Interest on capital = 27,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 27,000
Amount | Months | Product |
2,00,000 | 9 | 18,00,000 |
3,00,000 | 3 | 9,00,000 |
Total capital | 27,00,000 |
CASE 4
A & B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ration of 3:2 with capitals of Rs.3,00,000 and Rs.5,00,000 on 1st april 2014. On 30th September they decided to adjust their capital in their ratio by bringing or withdrawing in cash. Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution-
For adjustment add the capitals of A & B
Step 1 Find the Total capital of the firm = A +B (3,00,000+ 5,00,000)= 8,00,000
Step 2 divide the total capital in their profit sharing ratio i.e. 3:2
A’s share = 8,00,000 X 3/5 = 4,80,000
B’s share = 8,00,000 X 2/5 = 3,20,000
Step 3 Find surplus and deficit = old capital – new capital
A = 3,00,000 – 4,80,000 = -1,80,000 (deficit)
B = 5,00,000 – 3,20,000 = 1,80,000 (surplus)
A’s Interest on capital = 46,80,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 46,800
Amount | Months | Product |
3,00,000 | 6 | 18,00,000 |
4,80,000 | 6 | 28,80,000 |
Total capital | 46,80,000 |
B’s Interest on capital = 49,20,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 49,200
Amount | Months | Product |
5,00,000 | 6 | 30,00,000 |
3,20,000 | 6 | 19,20,000 |
Total capital | 49,20,000 |
CASE 5
A & B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ration of 3:2 with capitals of Rs.3,00,000 and Rs.5,00,000 on 1st april 2014. On 31th December they decided to fix their capital at Rs.10,00,000 and decided to adjust this in their profit sharing ratio by bringing or withdrawing in cash. Provide interest on capital to the partners @ 12% p.a. for the year ending on 31st march 2015.
Solution-
Step 1 Find the Total capital of the firm =10,00,000 (given)
Step 2 divide the total capital in their profit sharing ratio i.e. 3:2
A’s share = 10,00,000 X 3/5 = 6,00,000
B’s share = 10,00,000 X 2/5 = 4,00,000
Step 3 Find surplus and deficit = old capital – new capital
A = 3,00,000 – 6,00,000 = -3,00,000 (deficit)
B = 5,00,000 – 4,00,000 = 1,00,000 (surplus)
A’s Interest on capital = 45,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 45,000
Amount | Months | Product |
3,00,000 | 9 | 27,00,000 |
6,00,000 | 3 | 18,00,000 |
Total capital | 45,00,000 |
B’s Interest on capital = 57,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 57,000
Amount | Months | Product |
5,00,000 | 9 | 45,00,000 |
4,00,000 | 3 | 12,00,000 |
Total capital | 57,00,000 |
CASE 6
A and B started partnership business on April 01, 2006 with capitals of Rs. 2,50,000 and Rs.1,50,000, respectively. On October 01, 2006, they decided that their capitals should be Rs. 2,00,000 each. The necessary adjustments in the capitals are made by introducing or withdrawing cash. Interest on capital is to be allowed @ 12% p.a. Calculate interest on capital as on March 31, 2007.
Solution
A’s Interest on capital = 27,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 27,000
Amount | Months | Product |
2,50,000 | 6 | 15,00,000 |
2,00,000 | 6 | 12,00,000 |
Total capital | 27,00,000 |
B’s Interest on capital = 21,00,000 ∗ 1/12 ∗ 12/100 = 21,000
Amount | Months | Product |
1,50,000 | 6 | 9,00,000 |
2,00,000 | 6 | 12,00,000 |
Total capital | 21,00,000 |
CASE 7
On March 31, 2006 after the close of accounts, the capitals of A, B and C stood in the books of the firm at Rs. 4,00,000, Rs.3,00,000 and Rs. 2,00,000, respectively. Subsequently, it was discovered that the interest on capital @ 10% p.a. had been omitted. The profit for the year amounted to Rs. 1,50,000 and the partner’s drawings had been A: Rs. 20,000, B Rs. 15,000 and C Rs. 10,000.Calculate interest on capital.
Solution-
Find opening capital of the firm (as interest on capital is always allowed on the opening capitals) Profits should be divided in the profit sharing ratio
Opening capital = closing capital –profits + drawings
Opening capital of A = 4,00,000 – 50,000 + 20,000 = 3,70,000
B= 3,00,000 – 50,000 + 15,000 = 2,65,000
C= 2,00,000 – 50,000 +10,000 = 1,60,000
A’s Interest on capital = 3,70,000 ∗ 10/100 = 37,000
B’s Interest on capital = 2,65,000 ∗ 10/100 = 26,500
C’s Interest on capital = 1,60,000 ∗ 10/100 = 16,000
|
79 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Interest on Capital & Methods for Interest on Capital - Crash Course of Accountancy - Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is interest on capital in commerce? |  |
| 2. How is interest on capital calculated? |  |
| 3. What are the methods for calculating interest on capital in commerce? |  |
| 4. Why is interest on capital important in commerce? |  |
| 5. Can interest on capital be deducted as an expense in business? |  |

















