ICAI Notes- Human Activities- 2 | Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation PDF Download
Distinguishing Characteristics of Business vis-à-vis Other Economic Occupations
Whilst business as an economic occupation is vastly diverse, yet only a small portion of population, more so urban educated population engages in it. For example, of all of you pursuing Chartered Accountancy, only a small percentage is going to start a business. Since CA is a professional qualification, most likely you are going to practice as an independent professional or would take up a paid employment somewhere. We have thus introduced two other distinct occupations, viz., employment and profession. A brief description of these two occupations would be in order before we elaborate the distinguishing characteristics of business.
- Employment: Employment is a contract of service between the employee and the employer. The contract elaborates job description and the periodic compensation known as wages & salaries (the term wages usually denotes factory workers; salary denotes office staff, managers, etc.). One has to undergo a detailed process of Recruitment & Selection for one’s engagement in employment. Usually minimum qualifications- educational/ technical/ professional and prior work experience are prescribed. Freshers may be initially recruited as interns and required to undergo training. And one is expected to performas per the terms of employment and the performance targets assigned from time to time. There is a minimum assured income, tenure certainty and reasonable opportunities for career progression via promotions.
- Profession: Profession is rendering of services of a specialised nature, necessitating prescribed qualifications, for a fee under a Certificate of Practice from an established certification / accreditation / examination & assessment body that also imposes a code of conduct. Professions can be pursued as independent practice or under a contract of employment too. Accountancy, Architecture, Designing, Engineering, Law, Medicine and increasingly even Management are assuming the attributes of a profession. In certain professions e.g. medicine, if in employment, the professionals are entitled to ‘non-practising allowance’ too.
The word profession or professional in common parlance is used to distinguish
from one’s amateurish/ substandard performance or practice as a partime/ hobby.
Professionalism is often associated with perfectionism. The word is also used
derogatively to denote that one greedily works for money. Historically however,
professions emerged in pursuit of nobility; demonstrated highest level of integrity and ethics; and hence were held in very high esteem and social status /respect. Chartered Accountants for example, represent a noble profession for ensuring truthfulness and fairness in the conduct of business and hence instrumental in ensuring its trustworthiness; and, hence the integrity of the entire economic system. The logo of the Institute from The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) is suggestive of the vigilance
expected from the CAs.
Having clarified the meaning and nature of employment and profession as economic occupations, we are now in a position to delve deeper into the nature of business. Before we do that, it would be useful to do a recapitulation of the main points of difference between business, profession and employment (Recap #1).
Recap #1: Distinction between Business, Profession and Employment
S. No. | Basis of distinction | Business | Profession | Employment |
1 | Meaning | Entire spectrum of market oriented activities coming under industry, trade and commerce. | Independent rendering of services of specialised nature based on prescribed qualifications under the aegis of a professional body that also prescribes a code of conduct. | Rendering of services under a contract of employment for wages / salaries. Also, called wage- employment. |
2 | Mode of establishment | Entrepreneur's decision and other legal formalities, if necessary | Membership of a professional body and certificate of practice. | Letter of Appointment and service agreement. |
3 | Source of livelihood | Profit | Professional Fee. | Wages & Salaries. |
4 | Prescribed qualifications | None | Strictly prescribed | Minimum qualifications for each type of job |
5 | Ethical guidance | Founder's values | Professional codes | Employer's codes |
6 | Investment | Substantial requirement | Some requirement e.g. Office/ Chamber / Clinic | None |
7 | Personal autonomy / freedom | The most- you are your own boss | Quite a bit | Not much |
8 | Popular psychological motive | Economic achievement | Service to the clients/ society | Livelihood |
9 | Certainty of income | Least. However either way. | Quite a bit | The most. Contractually determined periodic income |
10 | Stability of tenure / Durability of occupation | Uncertain | Quite certain | Quite certain |
11 | Transfer of interest/ succession | Possible | Not possible | Not possible |
- Job creator, not job seeker: Business as an institution is a source of sustenance directly to the business owners and employees and indirectly to all those who derive opportunities from it. This is a unique characteristic of business that separates it from other occupations. Yes, professionals in practice may also generate some employment but certainly not in numbers that business is capable of generating.
- Provides momentum to economic growth: What is economic growth? It is persistent increase in a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). What is GDP? It is the value of all the goods & services produced in a country during a particular period. Business output comprehensively contributes toward GDP and economic growth. How is economic growth distinguishable from economic development? Whereas growth merely implies increase in GDP numbers, economic development implies diversification of an economy’s capabilities and improvement in the quality of lives of its people. Business, through research & development, education, and training & development of employees and by sheer guts and courage of experimenting and innovation brings about development. In fact, it is pertinent now to introduce the term entrepreneur here. In common parlance, the terms ‘business person’ and ‘entrepreneur’ are synonymous. Even we shall be using these two terms interchangeably. However, entrepreneurs are better characterised more by their problem solving, new opportunity seeking behaviour that draws on their creativity and innovation.
- Investment intensive: Starting a business requires a sizeable investment of funds in accommodation, plant & machinery, inventories, etc. In accounting, investment requirements are estimated as the sum of fixed assets and net current assets. Indeed, investments are necessary for technological up gradation, modernisation and expansion. However, size of investment usually varies with the scale of business. That is why in India Micro, Small, Medium and Large Enterprises are defined with respect to the size of investment- more specifically investment in Plant & Machinery for manufacturing enterprises and investment in Equipment for service enterprises. Many a people believe that the lack of investible funds or capital is a strong barrier to start a business.
- Gestation and uncertainties: Investment takes time to fructify. And it is uncertain whether it will yield the returns as expected. For example, it will take time to construct and ready a hotel before it is opened for occupancy. And it is uncertain if all the rooms would be occupied all the time. In fact, it is also uncertain if the occupancy ratio (room nights occupied / room nights capacity) would be adequate. In economics and finance, one distinguishes between risk and uncertainty. Risk can be calculated in advance, uncertainty cannot.
- Systematic, organised, efficiency oriented activity: Business is not a random, stray, unorganised and occasional activity. It is a consciously created system of production. Thus, firm infrastructure needs to be in place, supply chain of materials needs to be developed, these materials need to be processed or transformed, products need to be marketed and sold, payments need to be collected, etc. All these tasks have to be divided into specialised functions, means of coordination need be devised so that the business is able to deliver the promised products and services on day-to-day basis efficiently- on time, of consistent quality and exceeding performance expectations. In fact, the phrase ‘business like’ (of a person) means ‘carrying out tasks efficiently without wasting time or being distracted by personal or other concerns; systematic and practical (Oxford Dictionary).’
Business is systematic in the literal sense of the term system- an integrated, unified whole comprising of interrelated, interdependent and interacting parts just as an automobile system. Viewed thus, for the business to perform well, it needs be ensured that all the parts perform their respective functions well and in sync with each other- be it production, sales, marketing and the like. Imagine, if the production function is not in sync with marketing and hence unable to fulfil the orders generated by it? Moreover, whilst each function performs its task it is important that one does not lose sight of the overall objective of the firm. Unlike an automobile, however, business is an open system as it interacts with the environment. For example, business has to interact with the customers to get the vital feedback, product modification and win their continuing patronage. - Objective oriented/ purposeful: profit is said to the defining motive behind business. In economics, objective of the firm is set as maximisation of profits. profits characterize income from business just as wages & salaries characterize labour; rent characterizes land; and interest characterizes capital. It is the residue occurring to the business owners after all other factors of production have been paid off. What are the profits for? These are for organizing production, undertaking risks and uncertainty bearing. Let’s reflect deeper on the purpose of business. We have seen above, that business as an institution and more so through its entrepreneurial endeavours brings about a qualitative change called development. We have seen that entrepreneurial businesspersons are efficiency seekers, problem solvers and innovators. These intangible aspects of business’s performance impart deeper meaning to business and its purpose.
Idealistically, business must lead the world toward more egalitarian, participative and collective prosperity that is sustainable for generations. This ideal corresponds to the ideal of sustainable development that at business level may be interpreted as simultaneous pursuit of profitability, people well-being and planet sustainability (See Think #1).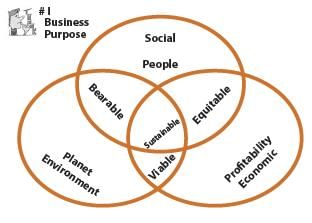
Think why is sustainable development necessary and how business, instead of focusing solely on profits must also attend to people’s problems and planet conservation? Think, why it is not sufficient that business and a country just balances economic (profitability) and social (people) concerns or economic and ecological concerns or social and ecological concerns only leaving out the third element. Whilst you think through, let us highlight the plurality of the objectives of business in Concept Elaboration #1.
Concept Elaboration #1: Objectives of Business
Considerations
#1. Interdependence. Business draws its factors of production from the society and is dependent on it for the sale of its goods & services.
#2. Multiple stakeholders. A firm is not only the owners. It is as much other investors /lenders, employees, customers, suppliers, competitors, the community and the larger society and the ecology of which business is a part
#3. Amount of profit. Profit is just about that much and that less an objective of business as is eating for living. Do we eat to live or live to eat? Likewise, profit is a minimum concept, in fact a cost, cost of being in and cost of staying in business.
#4. Primacy of Customer. If at all there is a single purpose of business, it is the creation and maintenance of customers through product quality, service, and delivering value for money.
#5. Performance is the precursor to profits. To be able to earn profit, the firm has to excel in all its functionalities, viz., procurement, production, sales & marketing, accounting & finance. Thus even if profit is the objective, it has to be broken down to the relevant objectives for each of these areas
Economic Objectives | Organic Objectives | Social Responsibilities | Legal, Ethical and Environmental Objectives |
| Sales, profits, return on investment, eficiency (resource conservation, achieving more from less) economic value added (profits in excess of cost of capital invested in business), market share | Survival, health (age of assets, fitness of human resources, reservescapital, general and contingency) growth, diversification of capabilities | Community service, education, health, sanitation, heritage conservation, community support during calamities & disasters, etc. Specific responsibilities toward employees, investors, customers, suppliers, competitors, etc. | Respect for law in letter and spirit, fair practices, transparency, truthfulness, honesty & integrity. Green technologies, productsusage & disposal, lower emissions, effective waste handling and disposal, preservation of air, water and soil quality |
| Responsible businesses: wishful thinking or meaningful enterprise? | |||
| Asbah- India’s first social enterprise focused on women  | ITC- The Greenest Hotel Chain in the World | Lemon Tree Hotels providing gainful employment to persons with disabilities | Hindustan Unilever Ltd.’s Project Shakti for Empowerment of Rural Women  |
The plurality of the objectives of business suggests that businesses must be assessed not only in terms of their economic returns but also their social and ecological returns. In fact, the trend surely is toward development of more holistic and more balanced measures of business performance. Having said so one has to be aware enough that there will always be unscrupulous persons in the mindless pursuit of greed. We should be able to discriminate between them and those who justly, fairly do their business and care for the community, society and the environment in which they live.
Some argue that to an extent responsible business behaviour depends on the ownership forms, more so corporate forms of business organisation. The argument is that corporations are regulated. There is a separation of ownership and management, the latter being professional and hence more aware and engaged in social and ecological issues. We do not intend to engage in this discussion. However, let’s get acquainted with the various forms of business organisation.
|
21 videos|91 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on ICAI Notes- Human Activities- 2 - Business and Commercial Knowledge (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation
| 1. What are the human activities discussed in the article? |  |
| 2. How do human activities affect the environment? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of overfishing? |  |
| 4. How can we reduce the negative impact of human activities on the environment? |  |
| 5. What role does the CA Foundation exam play in addressing the issue of human activities? |  |





















