Modals & Auxiliaries | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Auxillary Verbs? |

|
| Kinds of Auxiliaries Verbs |

|
| 1. Primary Auxiliaries |

|
| 2. Modal Auxiliaries |

|
| Uses of Modal Auxiliaries |

|
| Rules to use Modal Verbs |

|
| Examples of Modal Auxiliaries |

|
What are Auxillary Verbs?
Auxiliary verbs are the helping verbs used in sentences along with the verbs to set the mood, tense, tone etc. of the sentence.
For example, if you use the auxiliary ‘might’, it indicates a slight probability. But if you use the auxiliary ‘will’, it indicates a strong affirmation.
Auxiliary verbs, add functional or grammatical meaning to the clauses in which they appear. They perform their functions in several different ways:
- By expressing tense ( providing a time reference, i.e. past, present, or future)
- Grammatical aspect (expresses how verb relates to the flow of time)
- Modality (quantifies verbs)
- Voice (describes the relationship between the action expressed by the verb and the participants identified by the verb’s subject, object, etc.)
- Adds emphasis to a sentence
Kinds of Auxiliaries Verbs
There are two types of Auxiliaries:
1. Primary Auxiliaries
2. Modal Auxiliaries
1. Primary Auxiliaries
Primary Auxiliaries are used as main verbs to denote time (present, past and future). These are known as primary because they are the most frequently occurring auxiliaries and are used in their different forms in the English language.
Example:
I am watching cricket on TV.
His grandfather was watering the plants on the balcony.
Be
The forms of “be” are:
(a) Present tense: is, am, are
(b) Past tense: was, were
(c) Past participle: been
(i) To form continuous tense:
He is reading a book.
We were reading a book.
He has been reading a book.
(ii) For passive voice:
The work is done.
The work is being done.
(iii) To express a previous plan or agreement:
You were to visit the dentist.
I am to go to Delhi.
(iv) To express a command:
You are to get the work done by tonight.
The plumber is to repair the pipeline tomorrow.
(v) To express feelings, age, size, weight, price, time etc.
Today is a cold day.
I am not happy.
My weight is 60 kgs.Have
The forms of “have” are:
(a) Present tense: has, have
(b) Past tense: had
(c) Past participle: had
(i) To form perfect tense:
He has read the book.
We had done our household chores.
(ii) To form passive voice:
The work has been done.
The room had been cleaned.
(iii) To express a compulsion:
He had to go.
You have to obey the law.
(iv) To express a job got to be done:
I have my room cleaned every week.
She has bread and butter for breakfast.
(v) To express the consumption of food, drinks, events etc.
I have tea in the morning.
He had the party at his house.
You have a test tomorrow.Question for Modals & AuxiliariesTry yourself:She ……………arrived yet.View SolutionDo
The forms of “do” are:
(a) Present tense: do
(b) Past tense: did
(c) Past participle: done
(i) In additions to avoid repetition of verbs:
He likes to read and so do I.
You liked to dance and so did she.
(ii) In question tags and short answers:
You liked the film; didn’t you?
Yes, I did.
(iii) To form interrogative and negative forms of present and past indefinite tenses and imperatives:
Do not lean over the fence.
He does not work. Does he?
(iv) To stress some action in the present and past indefinite tenses and in imperatives:
I do go to the class every day.
I did the work daily.
Do finish the work for me.
2. Modal Auxiliaries
The modal auxiliary verbs are used to show possibility, necessity, willingness, or capability. A modal auxiliary verb does not change form (to indicate singular or plural) or change tense (to indicate time). Modal auxiliary verbs are used in the following sentences:
- Modal Auxiliaries denote certain feelings, moods and possibilities.
- Unlike be, have, and do, the modal auxiliaries cannot function as main verbs except in a few cases.
- The modal auxiliary words are: may, can might, could, will, would, shall, should, must, used to, need, dare, ought to, used to, etc.
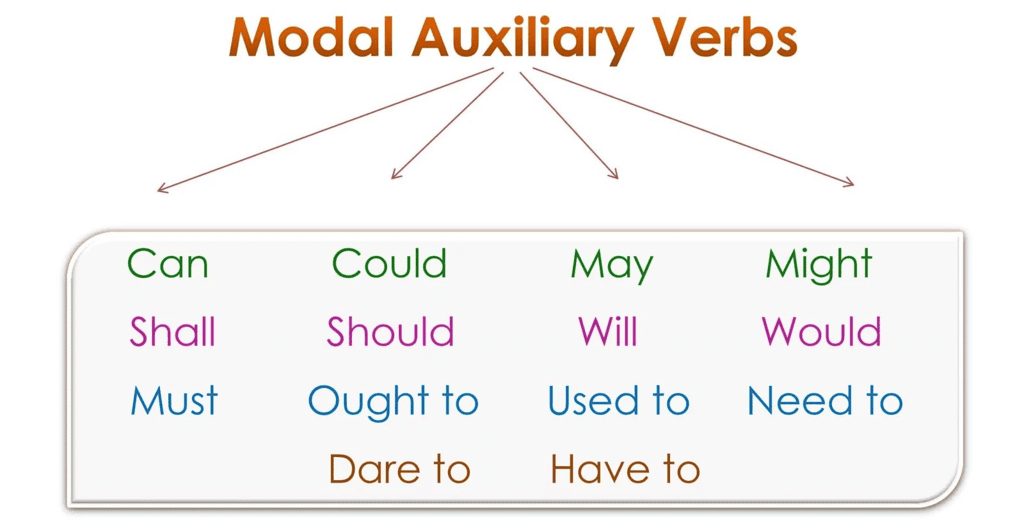
- Modals use such ideas as ability or capacity, probability or possibility, permission, command, compulsion, duty, obligation, propriety, etc.
- He should come and see his boss.
- He could come and see his boss tomorrow too.
In the above examples, words in bold represent modal. - In most of the cases, modals indicate present or future time however sometimes they also represent past times.
Uses of Modal Auxiliaries
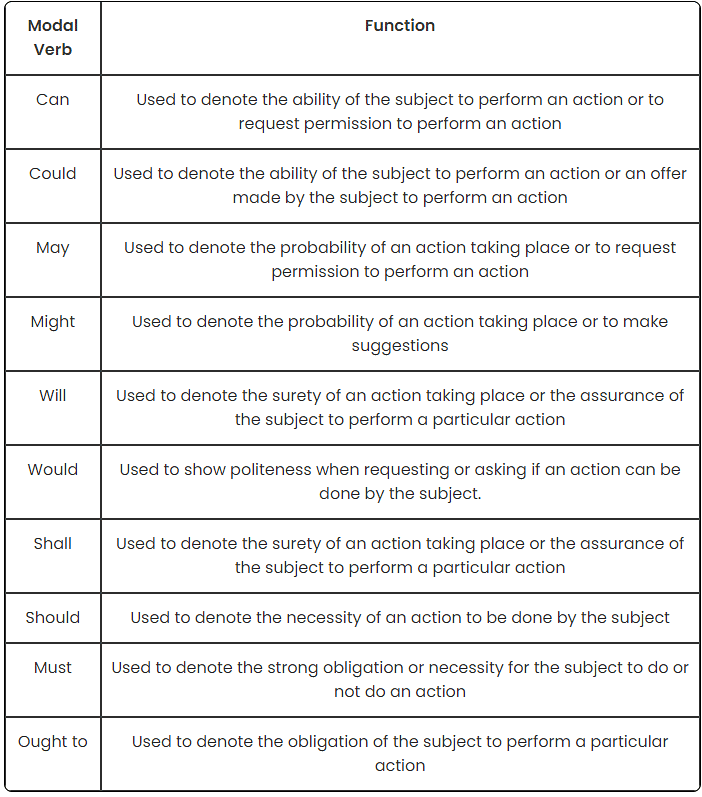
Rules to use Modal Verbs
Rule 1: All modal auxiliaries are followed by the base form of the verb.
Modal + Verb
Example:
I will build the house next year.
You can come to our house in the evening.
Rule 2: Two modal verbs cannot go together. One complete sentence can have only one modal verb.
Example:
Windsurfing can be difficult.
Examples of Modal Auxiliaries
1. Will you go to college?
2. Would you be able to lend me a pencil?
3. Shall I do the homework?
4. You should try the chocolate cake, it’s delicious.
5. Lisa can speak French fluently.
6. He could do it.
7. Alisha may come here today.
8. I might go to the beach this weekend if the weather is nice.
9. You must obey your parents.
10. I dare you to try spicy salsa!
11. You need not come here.
12. My mother used to tell me moral stories.
13. You ought to work hard for your exam.
|
111 videos|450 docs|90 tests
|
FAQs on Modals & Auxiliaries - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What are primary auxiliaries? |  |
| 2. What are modal auxiliaries? |  |
| 3. What are the uses of modal auxiliaries? |  |
| 4. What are the rules to use modal verbs? |  |
| 5. How do modals differ from primary auxiliaries? |  |





















