NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - (Part - 2) - Light
Page No. 213
Q11. Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 16.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher’s advice?
Ans: Laser light is harmful to the human eyes because its intensity is very high. It can cause damage to the retina and lead to blindness. Hence, it is advisable not to look at a laser beam directly.
Q12. Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Ans: To protect our eyes, the given points should be taken into account:
- Visit an eye specialist regularly.
- Avoid reading in dim light and very bright light.
- Avoid direct exposure to sunlight to the eye.
- Clean your eyes with cold water quickly if dust particles or small insects enter your eye. Do
- not rub your eyes.
- Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm between the book and your eyes while reading.
Q13. What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
Ans:
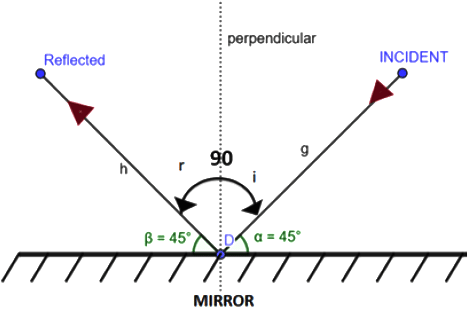
We know that angle of incident ray is equal to angle of reflected ray i.e. ∠i = ∠r
Here, it is given that ∠i + ∠r = 90°
⇒ ∠i + ∠i = 90°
⇒ 2∠i = 90°
⇒ ∠i = 45°
Q14. How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
Ans: Infinite or multiple images of the candle will be formed because of multiple reflections between the mirrors. When two mirrors are placed parallel to each other, then infinite numbers of images are formed.
Q15. Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in Fig. 16.19. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.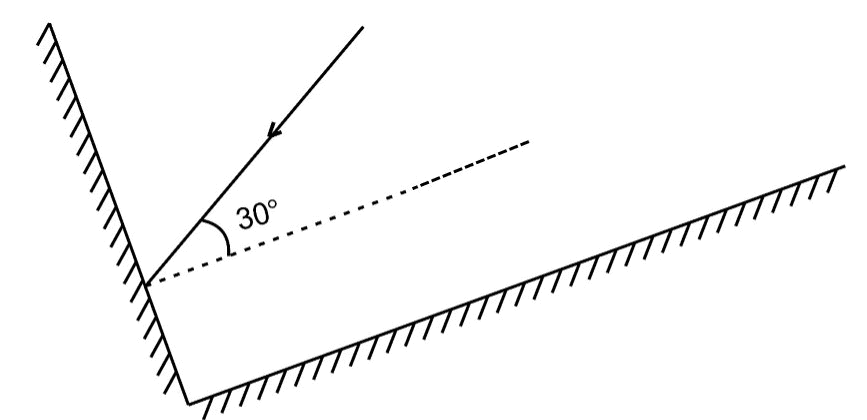 Ans: The first law of reflection is used to obtain the path of reflected light.
Ans: The first law of reflection is used to obtain the path of reflected light.
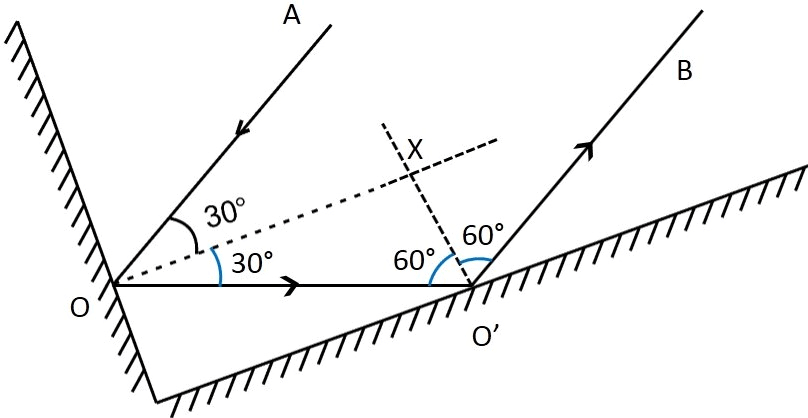 It can be observed that the given ray of light will reflect from the second mirror at an angle 60°.
It can be observed that the given ray of light will reflect from the second mirror at an angle 60°.
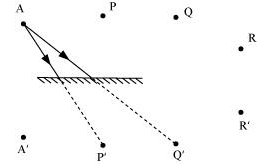
Q16. Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in Fig. 16.20. Can he see himself in the mirror? Also, can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R?
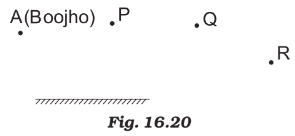
Ans: A plane mirror forms a virtual image behind the mirror. The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. A cannot see his image because the length of the mirror is too short on his side. However, he can see the objects placed at points P and Q, but cannot see the object placed at point R (as shown in the given figure).
Q17. (a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (Fig. 16.21).
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
 Ans:
Ans:
(a) Image of the object placed at A is formed behind the mirror. The distance of the image from the mirror is equal to the distance of A from the mirror. Image of A is shown in the given figure.
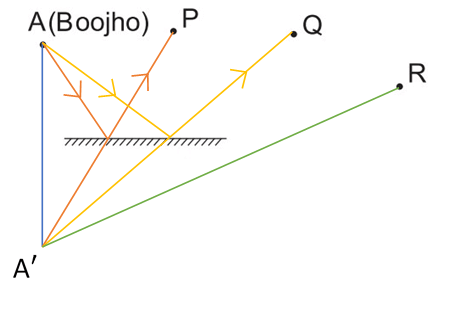 (b) Yes. Paheli at B can see this image.
(b) Yes. Paheli at B can see this image.
(c) Yes. Boojho at C can see this image.
(d) If we trace the reflected rays from B and C backwards, they converge at a point behind the mirror. The position of image A remains fixed even if Paheli moves.
|
90 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science - (Part - 2) - Light
| 1. What is light and how does it travel? |  |
| 2. What are the different colors of light and how do they form? |  |
| 3. How does the human eye perceive light? |  |
| 4. What is the concept of reflection of light? |  |
| 5. How does refraction of light occur? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|













