Charging of a Body | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Charging by Friction |

|
| Charging by Conduction |

|
| Charging By Induction |

|
| Experiment to Demonstrate Induction |

|
All objects are electrically neutral, which means that they have an equal number of protons in the nucleus and electrons in the circular orbits of the atom. In the normal state, materials are electrically neutral, although they contain charges. To charge an object, we have to alter the charge balance of positive and negative charges. A body can be charged using (a) friction, (b) conduction, and(c) induction
Charging by Friction
The charging by friction process involves rubbing one neutral body with another(at least one of which should be an insulator). This results in the moving of electrons from one surface of one body to another.
- The transfer happens from a material in which electrons are held less tightly (lower work function or electron affinity) to a material in which electrons are held more tightly (higher work function or electron affinity).
- The body which gains electrons becomes negatively charged and the other becomes positively charged. This method is useful for charging insulators.
 Charging by Friction
Charging by Friction
- In this process actual transfer of electrons takes place.
- Although, the mass of electrons is negligibly small (me= 9.1 x 10-31 kg) a positively charged body has lost some electrons so its mass reduces slightly and a negatively charged body has gained some electrons so its mass increases slightly.
The table below shows the pairs of objects which get charged on rubbing against each other.
- Any two charged objects, in the same column will repel each other and any two charged objects from different columns will attract each other.
- For reference, one can remember the triboelectric series. When any two substances in the series are rubbed together, the one occurring earlier in the series acquires a positive charge and the one occurring later in the series acquires a negative charge.
 Triboelectric Series
Triboelectric Series
Charging by Conduction
Charging by conduction is a fundamental principle in the study of electrostatics and is often demonstrated in physics experiments. Charging by conduction refers to the process of charging an object by direct contact with a charged object. When a charged object comes into contact with a neutral object, the charge is transferred between them through the process of conduction. Here's how it typically works:
- Charged Object: Begin with an object that has an excess of electric charge (either positive or negative). This could be, for example, a charged metal rod.
- Neutral Object: Place a neutral (uncharged) object in direct contact with the charged object. The charges on the charged object will redistribute due to the proximity and contact with the neutral object.
- Charge Transfer: Electrons will move between the charged and neutral objects, redistributing the charge. If the charged object is negative, electrons will move to the neutral object, making it negative as well. If the charged object is positive, electrons will move from the neutral object to the charged object, making it positive.
- Result: After contact and charge transfer, both objects will be charged with the same type of charge.
 Charging by Conduction
Charging by Conduction
It's important to note that charging by conduction involves physical contact between the charged and neutral objects. If two identical-shaped conductors kept at large distances are connected, then they will have equal charges.
Charging By Induction
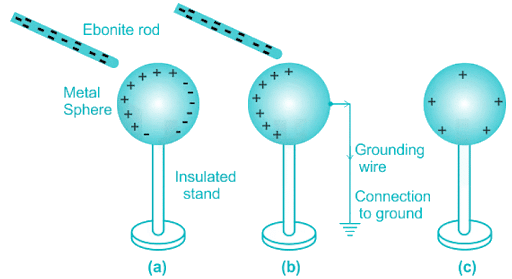
Charging by induction is a common phenomenon and is used in various devices like capacitors and other electrical applications. Charging by induction is a method of charging an object without direct contact. In this process, a charged object induces a charge on a neutral object without the need for physical contact. Here's how it works:
- Charged Object: Begin with an object that has an excess of electric charge (either positive or negative). For example, let's consider a negatively charged object (−).
- Neutral Object: Place a neutral (uncharged) object near the charged object but without allowing it to touch. This neutral object is initially without a net charge (0).
- Electron Movement: Due to the presence of the charged object, the electrons in the neutral object are repelled or attracted. If the charged object is negative, it will repel electrons in the neutral object, causing them to move away from the charged object.
- Induced Charge Separation: The movement of electrons within the neutral object results in a temporary separation of charges. The side of the neutral object closest to the charged object becomes oppositely charged (induced charge), while the opposite side becomes charged with the same type of charge as the charged object.
- Result: Even though there was no direct contact, the neutral object now has regions with opposite charges. The side facing the charged object has a charge opposite to that of the charged object, and the side away from the charged object has a charge of the same type.
 Charging by Induction
Charging by Induction
It's important to note that, in charging by induction, the neutral object does not gain or lose any electrons. The charges are merely redistributed temporarily due to the influence of the charged object. If you were to connect the neutral object to the ground or another conductive path, the induced charge could be separated, leaving the neutral object charged with the same type of charge as the inducing object.
Experiment to Demonstrate Induction
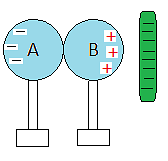
- Consider the two spheres above made with a metal.
- Since metal is a good conductor, it is a good choice for this experiment.
(i) They touch each other, so they become a single conductor.
(ii) We put them on insulated stands so charges or electricity does not travel to the ground.
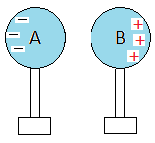
(iii) The two spheres right now form a neutral system. This means that there is the same number of electrons and protons in each sphere. - We get a rod that is negatively charged and we put it next to the two spheres. The rod is shown on the right in green. The lines inside the rod represent negative charges.

- Electrons in sphere B are repelled by the rod and move to sphere A to create an excessive charge called also net charge. This situation creates also a net charge in sphere B.
- We say that a charge has been induced on the spheres.
- We can separate the spheres while the rod is still there.

- Finally, we can remove the rod completely.
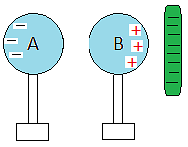
- The spheres will keep their charges and this is what we mean by charging by induction.
- The charges on the spheres are equal and opposite.
- The charges are equal because, for each single electron that goes to A and therefore creates a single negative net charge, it leaves B with a single positive charge.
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
FAQs on Charging of a Body - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. How does charging by friction work? |  |
| 2. What is charging by conduction? |  |
| 3. How does charging by induction differ from charging by conduction? |  |
| 4. Can a body be charged using both friction and conduction methods simultaneously? |  |
| 5. Is it possible to charge a body by induction without a charged object? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|