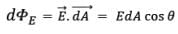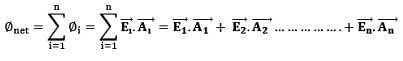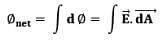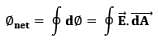Electric Flux | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
What is Electric Flux?
- Electric flux is a characteristic of an electric field, representing the number of field lines that pass through a specific area. These lines typically originate from positive charges and terminate at negative charges.
- When these lines enter a closed surface, they are seen as negative, whereas those exiting a closed surface are seen as positive.
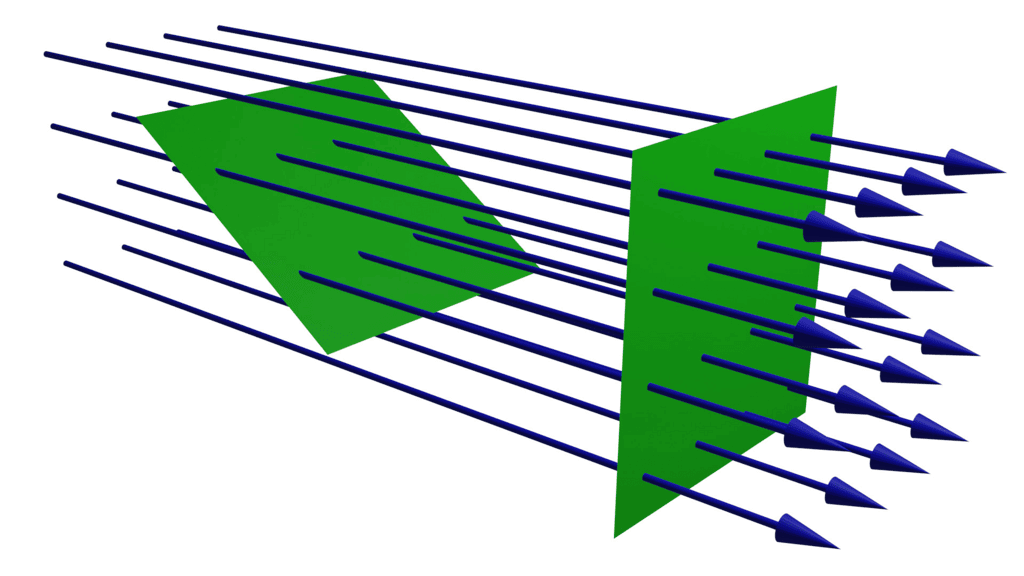 Electric Flux
Electric Flux
Analogy of Electric Flux with Flow of Water
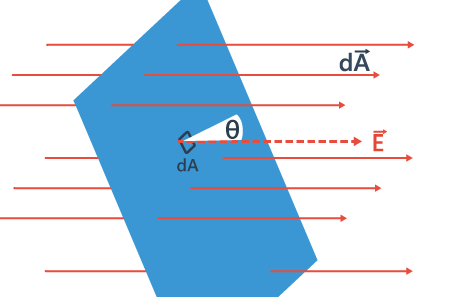
- Consider flow of a liquid with velocity v, through small flat surface dA, in a direction normal to the surface. The rate of flow of liquid is given by the volume crossing the area per unit time vdA and represents the flux of liquid flowing across the plane.
- If the normal to the surface is not parallel to the direction of flow of liquid, i.e., to v, but makes an angle θ with it, the projected area in a plane perpendicular to v is vdA cosθ. Therefore the flux going out of the surface d A isV. ñ dA.
- For the case of the electric field, we define an analogous quantity and call it electric flux.
- We should however note that there is no flow of a physically observable quantity unlike the case of liquid flow. In the picture of electric field lines described above, we saw that the number of field lines crossing a unit area, placed normal to the field at a point is a measure of the strength of electric field at that point.
- This means that if we place a small planar element of area ΔA normal to E at a point, the number of field lines crossing it is proportional to E ΔA. Now suppose we tilt the area element by angle θ. Clearly, the number of field lines crossing the area element will be smaller. The projection of the area element normal to E is ΔA cos θ.
- Thus, the number of field lines crossing ΔA is proportional to E.ΔA.cosθ. When θ = 90° , field lines will be parallel to ΔA and will not cross it at all (Figure).
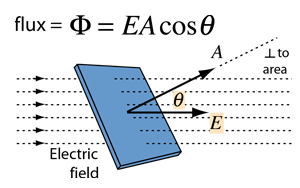
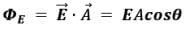
where E is the magnitude of the electric field (having units of V/m), A is the area of the surface, and θ is the angle between the electric field lines and the normal (perpendicular) to A.
Note: That that an area element should be treated as a vector. It has a magnitude and also a direction. How to specify the direction of a planar area? Clearly, the normal to the plane specifies the orientation of the plane. Thus, the direction of a planar area vector is along its normal.
But a normal can point in two directions. Which direction do we choose as the direction of the vector associated with the area element?
Conventionally, the vector associated with every area element of a closed surface is taken to be in the direction of the outward normal.
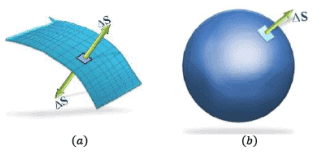
In above diagram, note that:
- Represents an open surface, thus, it is irrelevant to define ‘outward’ normal. You can choose any of the two normal at the surface.
- The surface in b is a closed one, it is important to define ‘ outward normal’ as the direction of area vector (as shown in the figure), conventionally.
- For infinitely small area element 𝑑𝐴

And if the Electric field holds different value on different points on the surface, then, we must add up the electric flux from all of them individually, - For finite number of surfaces (let’ s assume n),

- For infinite addition of infinitesimal surfaces i.e. integration,

- For closed surfaces,

Solved Examples
Q.1. An electric field of 500 V/m makes an angle of 30.00 with the surface vector. It has a magnitude of 0.500 m2. Find the electric flux that passes through the surface.
Ans. The electric flux which is passing through the surface is given by the equation as:
ΦE = E.A = EA cos θ
ΦE = (500 V/m) (0.500 m2) cos 30°
ΦE = 217 Vm
Notice: That the unit of electric flux is a volt-times meter.
Q.2. Consider a uniform electric field E = 3 × 103 î N/C. What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane?
(a) 30 Nm2/C
(b) 40 Nm2/C
(c) 50 Nm2/C
(d) 60 Nm2/C
Ans. (a)
Solution.
The flux of an electric field is given by,
ϕ = EA ⇒ ϕ = 3 × 103 × 0.1 × 0.1 ⇒ ϕ
= 30 Nm2/C
Therefore, the flux of the field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane is 30 Nm2/C
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
FAQs on Electric Flux - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is electric flux? |  |
| 2. Can you provide an analogy of electric flux with the flow of water? |  |
| 3. How is electric flux calculated? |  |
| 4. What are the units of electric flux? |  |
| 5. How does the electric flux change with respect to the orientation of the surface? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|