Ideal & Non-Ideal Solutions | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is an Ideal Solution? |

|
| What is a Non-Ideal Solution? |

|
| Types of Non-Ideal Solution |

|
| What are Azeotropes? |

|
Raoult’s Law states that the mole fraction of the solute component is directly proportional to its partial pressure.
On the basis of Raoult’s Law, liquid-liquid solutions are classified into two types of solutions, they are:
• Ideal Solutions
• Non-ideal Solutions
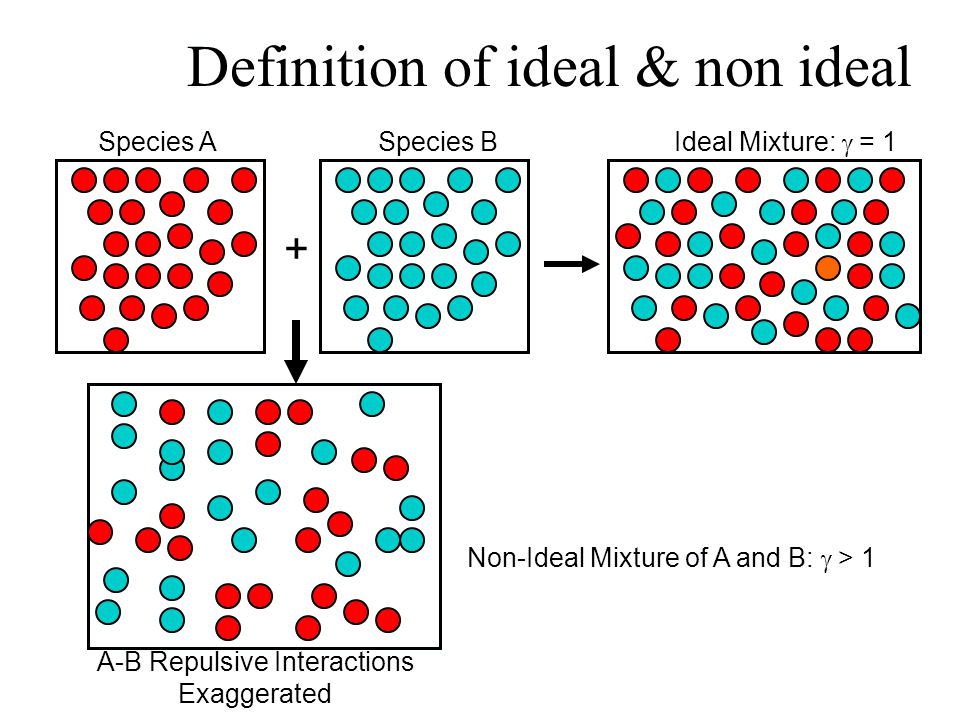
What is an Ideal Solution?
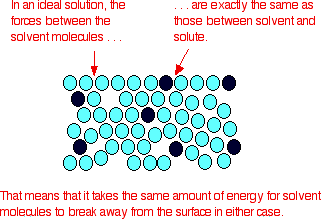
An ideal solution is a mixture in which the molecules of different species are distinguishable, however, unlike the ideal gas, the molecules in ideal solution exert forces on one another. When those forces are the same for all molecules independent of species then a solution is said to be ideal.
Characteristics of Ideal Solution
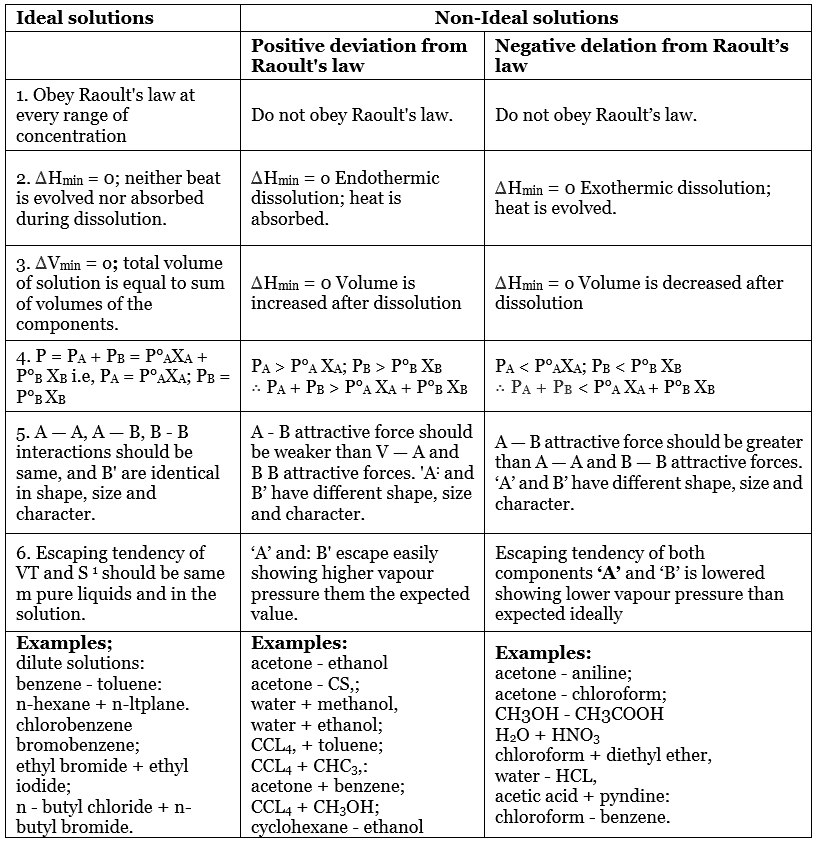
- The solutions which obey Raoult’s Law at every range of concentration and at all temperatures are called Ideal Solutions.
- We can obtain ideal solutions by mixing two ideal components that are, a solute and a solvent having similar molecular size and structure.
Example: consider two liquids A and B, and mix them. The formed solution will experience several intermolecular forces of attractions inside it, which will be:
• A – A intermolecular forces of attraction
• B – B intermolecular forces of attraction
• A – B intermolecular forces of attraction
- The solution is said to be an ideal solution, only when the intermolecular forces of attraction between A – A, B – B and A – B are nearly equal.
- They follow Raoult’s Law, which means partial pressure of components A and B in a solution will be PA = PA0 xA and PB = PB0 xB where PA0 and PB0 are respective vapour pressure in pure form and xA and xB are respective mole fractions of components A and B.
- The enthalpy of mixing of two components should be zero, that is, Δmix H = 0. This signifies that no heat is released or absorbed during mixing of two pure components to form ideal solution.
- The volume of mixing of two components should be zero that is, Δmix V = 0. This means that the total volume of solution is equal to the sum of the volume of solute and solution. Adding further, it also signifies that there is no occurrence of contraction or expansion of volume while mixing of two components.
- The solute-solute interaction and solvent-solvent interaction is nearly equal to solute-solvent interaction
Note: Perfectly ideal solutions are rare in nature, only some solutions show some ideal behaviour.
Examples of Ideal Solutions
- n-hexane and n-heptane
- Bromoethane and Chloroethane
- Benzene and Toluene
- CCl4 and SiCl4
- Chlorobenzene and Bromobenzene
- Ethyl Bromide and Ethyl Iodide
- n-Butyl Chloride and n-Butyl Bromide
What is a Non-Ideal Solution?
The solutions which don’t obey Raoult’s law at every range of concentration and at all temperatures are called Non-Ideal Solutions. Non-ideal solutions deviate from ideal solutions and are also known as Non-Ideal Solutions.
Types of Non-Ideal Solutions
Characteristics of Non-Ideal Solution
- The solute-solute and solvent-solvent interaction is different from that of solute-solvent interaction
- The enthalpy of mixing that is, Δmix H ≠ 0, which means that heat might have released if the enthalpy of mixing is negative (Δmix H < 0) or the heat might have observed if the enthalpy of mixing is positive (Δmix H > 0).
- The volume of mixing that is, Δmix V ≠ 0, which depicts that there will be some expansion or contraction in dissolution of liquids
Types of Non-Ideal Solution
- Non-ideal solutions showing positive deviation from Raoult’s Law
- Non-ideal solutions showing negative deviation from Raoult’s Law
Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law
Example: consider two components A and B to form non-ideal solutions.
Let the vapour pressure, pure vapour pressure and mole fraction of component A be PA , PA0 and xA respectively and that of component B be PB , PB0 and xB respectively.
These liquids will show positive deviation when Raoult’s Law when
- PA > PA0 xA and PB > P0B xB, as the total vapour pressure (PA0 xA + P0B xB) is greater than what it should be according to Raoult’s Law.
- The solute-solvent forces of attraction is weaker than solute-solute and solvent-solvent interaction that is, A – B < A – A or B – B
- The enthalpy of mixing is positive that is, Δmix H > 0 because the heat absorbed to form new molecular interaction is less than the heat released on breaking of original molecular interaction
- The volume of mixing is positive that is, Δmix V > 0 as the volume expands on dissolution of components A and B
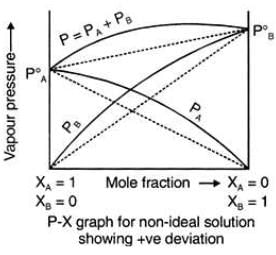
Examples: Following are examples of solutions showing positive deviation from Raoult’s Law
- Acetone and Carbon disulphide
- Acetone and Benzene
- Carbon Tetrachloride and Toluene or Chloroform
- Methyl Alcohol and Water
- Acetone and Ethanol
- Ethanol and Water
Negative Deviation from Raoult's Law
Negative Deviation occurs when the total vapour pressure is less than what it should be according to Raoult’s Law. Considering the same A and B components to form a non-ideal solution, it will show negative deviation from Raoult’s Law only when:- PA < PA0 xA and PB < P0B xB as the total vapour pressure (PA0 xA + P0B xB) is less than what it should be with respect to Raoult’s Law
- The solute-solvent interaction is stronger than solute-solute and solvent-solvent interaction that is, A – B > A – A or B – B
- The enthalpy of mixing is negative that is, Δmix H < 0 because more heat is released when new molecular interactions are formed
- The volume of mixing is negative that is, Δmix V < 0 as the volume decreases on dissolution of components A and B
Examples: Following are examples of solutions showing negative deviation from Raoult’s Law
- Chloroform and Benzene
- Chloroform and Diether
- Acetone and Aniline
- Nitric Acid ( HNO3) and water
- Acetic Acid and pyridine
- Hydrochloric Acid ( HCl) and water
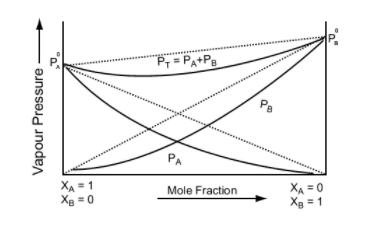 Image 5: Graph between vapour pressure and mole fraction
Image 5: Graph between vapour pressure and mole fraction
What are Azeotropes?
Azeotropes are defined as a mixture of two liquids which has a constant composition in the liquid and vapour phase at all temperatures.
- Azeotropes can’t be separated by fractional distillation, as the composition of the vapour phase remains the same after boiling.
- Because of uniform composition azeotropes are also known as Constant Boiling Mixtures.
Each azeotrope has a characteristic boiling point.
The boiling point of an azeotrope is either less than the boiling point temperatures of any of its constituents (a positive azeotrope), or greater than the boiling point of any of its constituents (a negative azeotrope).
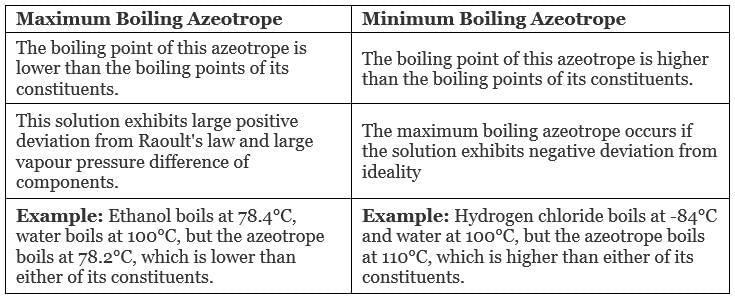
Types of Azeotropes
- Maximum Boiling Azeotrope
- Minimum Boiling Azeotrope
Maximum Boiling Azeotrope is formed when we mix two non-ideal solutions at some specific composition, showing a large negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
Examples:
- Nitric Acid (HNO3) (68%) and water (32%) form maximum boiling azeotrope at a boiling temperature of 393.5 K
- Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) (20.24%) and water form maximum boiling azeotrope at a boiling temperature of 373 K
Minimum Boiling Azeotrope is formed when we mix two non-ideal solutions at some specific composition, which shows a large positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
Example: Ethanol ( 95.5%) and water (4.5%) form minimum boiling azeotrope at a boiling temperature of 351.5 K
|
78 videos|351 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Ideal & Non-Ideal Solutions - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is an Ideal Solution? |  |
| 2. What is a Non-Ideal Solution? |  |
| 3. What are the types of Non-Ideal Solutions? |  |
| 4. What are Azeotropes? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between an ideal and non-ideal solution? |  |
















