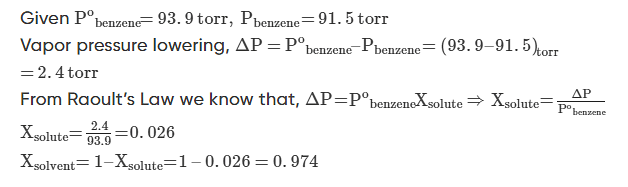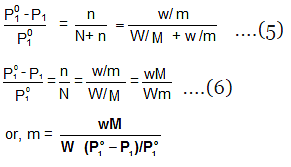Colligative Properties: Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Colligative Properties? |

|
| Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure |

|
| Vapour Presure Lowering as a Colligative Property |

|
| Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure - Formula |

|
What are Colligative Properties?
The colligative properties of the solution, are the properties that are bound by the number of solute and solvent particle present in the solution. Colligative properties are features of a solution that change based on how much solute is dissolved in it, rather than what the solute or solvent are. These properties, like boiling point elevation or freezing point depression, depend on the number of solute particles, not their type. And generally, the larger the solute molecules, the less effect they have on these properties.

There are four main colligative properties
- Elevation of Boiling point
- Depression Freezing point
- Lowering of Vapour Pressure
- Osmotic Pressure
 Colligative Properties and Its Types
Colligative Properties and Its Types
Applications of Colligative Properties
Colligative properties are important in various practical applications, including in the pharmaceutical industry, food science, and chemical engineering They are also used in analytical techniques, such as osmometry, to determine the molecular weight of substances.
Note: It's important to note that colligative properties are only applicable to ideal solutions, which means that the solute-solvent interactions are relatively weak, and the solute particles do not associate or dissociate significantly in the solution. In real-world situations, deviations from ideal behaviour can occur, especially at high solute concentrations or when solute-solvent interactions are strong.
Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure
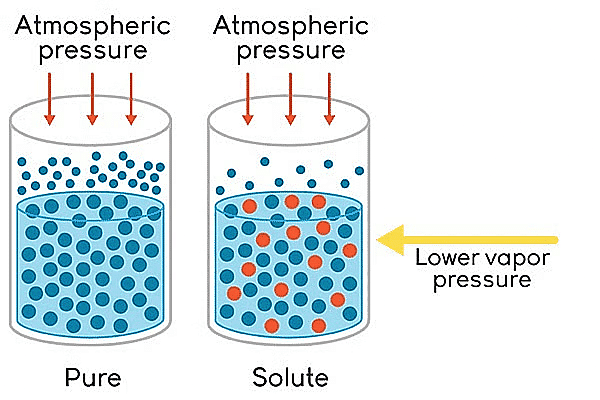
The relative lowering of vapour pressure is one of the colligative properties in chemistry. On adding a nonvolatile solute to a solvent, the vapour pressure of the solution (solute + solvent) becomes lower than the vapour pressure above the pure solvent.
 Lowering of Vapour Pressure
Lowering of Vapour Pressure
- The vapour pressure of a volatile solvent gets lowered when a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it.
- If p∘ represents then the vapour pressure of a pure solvent and p represents the vapour pressure of the solution, we have-
- Lowering of pressure: po - p
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure = po - p/ p
- The relative lowering of pressure and lowering of pressure are colligative properties.
- A relation between the pressure of the solution, the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, and the mole fraction of the solute were discovered by a French chemist Raoult.
- Raoult’s law, states that the lowering in vapour pressure of a dilute solution is equal to the mole fraction of the solute in the solution.
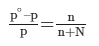
Here, n is the moles of the solute dissolved in N moles of the solvent.
Vapour Presure Lowering as a Colligative Property
Vapour pressure is not a colligative property. This is because vapour pressure does not depend on the number of solute particles but depends on the nature of the solute.
- Relative vapour pressure is a colligative property, i.e. it depends on the number of solute particles. The dissociation of ionic compounds will affect the vapour pressure of the solution. With an increase in the number of dissociated solute ions, the vapour pressure of the solution decreases.
- For example, it was found that the lowering of vapour pressure of a solution consisting of 1M NaCl is more than that of a solution having 1M glucose. The concentration of both solutions at standard temperature and pressure is the same. The reason behind this difference can be accounted for by the following reactions.
NaCl(s)→Na+(aq)+Cl–(aq) ⇒ 2 dissolved particles
C6H12O6(s)→C6H12O6(aq) ⇒1dissolved particles
Sodium chloride is an ionic compound that dissociates into two ions, whereas glucose being an organic compound does not dissociate. Therefore, equal concentrations of sodium chloride and glucose solution will result in twice as many dissolved particles in the case of sodium chloride. The vapour pressure of the sodium chloride solution will be lowered to twice the amount of the glucose solution.
Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure - Formula
Experimentally, we know that the vapour pressure of the solvent above a solution containing a nonvolatile solute (i.e., a solute that does not have a vapour pressure of its own) is directly proportional to the mole fraction of solvent in the solution. This behaviour is summed up in Raoult’s Law:
Psolution = Xsolvent × Posolvent
In a binary solution, if a volatile solute is added to the volatile solvent, each solute’s and solvent’s component is added to the total pressure
According to Raoult’s Law, the partial vapour pressure of two components, solvent (A) and solute (B), of a solution may be given as:
Vapour Pressure Lowering Example Problems With Solutions
Q.1: At 25oC the vapor pressure of pure benzene is 93.9 torr. When a nonvolatile solute is added to benzene, the vapour pressure of benzene is lowered to 91.5 torr. Calculate the mole fraction of the solute and the solvent.
Solution.
Q.2: The vapour pressure of a pure liquid at 298K is 4×104Nm2. On adding a nonvolatile solute, the vapour pressure of the solution becomes 3.65×104Nm2. Calculate the relative vapour pressure, lowering of vapour pressure, and relative lowering of vapour pressure.
Solution.
Q.3: The density of a 0.438 M solution of potassium chromate at 298 K is 1.063 g cm-3. Calculate the vapour pressure of water above this solution. Given: Po (water) = 23.79 mm Hg.
Solution.
A solution of 0.438 M means 0.438 mol of K2CrO4 is present in 1L of the solution. Now,
Mass of K2CrO4 dissolved per litre of the solution = 0.438 × 194 = 84.972 g
Mass of 1L of solution = 1000 × 1.063 = 1063 g
Amount of water in 1L of solution = 978.028/18 = 54.255 mol
Assuming K2CrO4 to be completely dissociated in the solution, we will have;
Amount of total solute species in the solution = 3 × 0.438 = 1.314 mol.
Mole fraction of water solution = 54.335/(54.335 + 1.314) = 0.976
Finally, Vapour pressure of water above solution = 0.976 × 23.79 = 23.22 mm Hg
Determination of Molar Masses from Lowering of Vapour Pressure
- It is possible to calculate molar masses of non-volatile non-electrolytic solutes by measuring the vapour pressures of their dilute solutions.
- Suppose, a given mass, w gram, of a solute of molar mass m, dissolved in
W gram of solvent of molar mass M lowers the vapour pressure from Po1 to P1. - We know that the relative lowering of the vapour pressure of a solution containing a non-volatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of the solute present in the solution.
- This implies
Some Important Questions
Q.1. What are the properties arising due to varying concentrations of solute in a given solvent, irrespective of the nature of the solute concerning the solvent?
a) Colligative properties
b) Intensive properties
c) Extensive properties
d) Solute properties
Ans: a
Colligative properties are a set of four properties. This set of properties purely depends on the number of solute particles present in the solution/solvent, independent of the nature of the particles concerning the solution/solvent.
The properties are
1.) Relative lowering of vapor pressure,
2.) Elevation in boiling point,
3.) Depression in freezing point and
4.) Osmotic pressure.
Q.2. Which law specifically governs the relative lowering of vapor pressures in solutions?
a) Van’t Hoff law
b) Boyle’s law
c) Raoult’s law
d) Amagat’s law
Ans: c
Raoult’s law quantifies the relative lowering in vapor pressure. From the law, it follows that p1 = X1 x po1. If p01 was the original pressure before the X2 mole fraction of solute was added to the solvent then a reduction in vapor pressure is given as:
Δp1 = po1 – p
= po1 – po1 X1
= po1(1 – X1)
= po1X2
Therefore, the relative reduction in vapor pressure (∆p1/po1) = X2 i.e. mole fraction of solute in the solution.
Q.3. On addition of non-volatile potassium iodide in water at 298K it is noticed that vapor pressure reduces from 23.8 mm Hg to 2.0 cm Hg. What is the mole fraction of solute in the solution?
a) 0.916
b) 0.160
c) 0.084
d) 0.092
Ans: b
Given,
P0water =23.8 mm Hg
Pwater= 2.0 cm Hg = 20.0 mm Hg (after addition of solute)
From the law of relative lowering of vapor pressure, ∆p1 = X2 x po1 (where X2 is the mole fraction of solute)
On rearranging, Δp1/po1 =X2
Δp1 = 23.8 – 20.0 = 3.8 mm Hg
X2 = 3.8/23.8 = 0.160
Q.4. Which of the following is Raoult’s law applicable to, to determine molar masses correctly?
a) Ionic solute in liquid
b) Non-ionic solute in dilute solution
c) Non-ionic solute in concentrated solution
d) Ionic solid in insoluble form in solvent
Ans: b
To determine molar masses correctly, the solute must be non-volatile, non-ionic, and present in dilute form only. If it is ionic one has to account for its van’t Hoff factor, i, for association in concentrated solution and dissociation in dilute solution. Molar masses can only be calculated from dilute solutions containing non-dissociable non-ionic solutes.
Q.5. Which of the following is a colligative property?
a) Relative lowering of fluid pressure
b) Decrease in boiling point
c) Decrease in freezing point
d) Change in volume after mixing
Ans: c
A decrease in freezing point is the correct colligative property, known as ‘Depression in freezing point’. This is caused by solute particles present on the surface which lowers the equilibrium solid-vapor pressure. Therefore, a lower freezing temperature is required to match the pressure outside. The other correct colligative properties are
1.) Relative lowering of vapor pressure,
2.) Elevation in boiling point,
3.) Depression in freezing point and
4.) Osmotic pressure.
Q.6. Mass of Urea (NH2CONH2) required to be dissolved in 1000 g of water in order to reduce the vapour pressure of water by 25% is _________ g. (Nearest integer)
Given: Molar mass of N, C, O and H are 14,12,16 and 1 g mol−1 respectively
Ans: 1111
Given: Vapor pressure reduction: 25% (0.75 times the vapor pressure of pure water)
Molar mass of water (H2O): 18g/mol
Mass of solvent (water): 1000g
Using Raoult's law: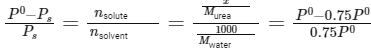
Solving for (x):
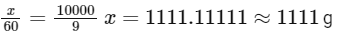
So, the mass of urea required to be dissolved in 1000g of water is 1111g.
|
117 videos|226 docs|237 tests
|
FAQs on Colligative Properties: Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What is the concept of relative lowering of vapour pressure in colligative properties? |  |
| 2. How is vapour pressure lowering considered as a colligative property? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for calculating the relative lowering of vapour pressure? |  |
| 4. How can the measurement of the lowering of vapour pressure be done experimentally? |  |
| 5. How is the concept of relative lowering of vapour pressure relevant in NEET exams? |  |