Introduction of Biological Classification | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Biological Classification of Living Organisms
- Biological classification of plants and animals was first proposed by Aristotle on the basis of simple morphological characters.
- Linnaeus later classified all living organisms into two kingdoms: Plantae and Animalia.
- Whittaker proposed an elaborate five-kingdom classification: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
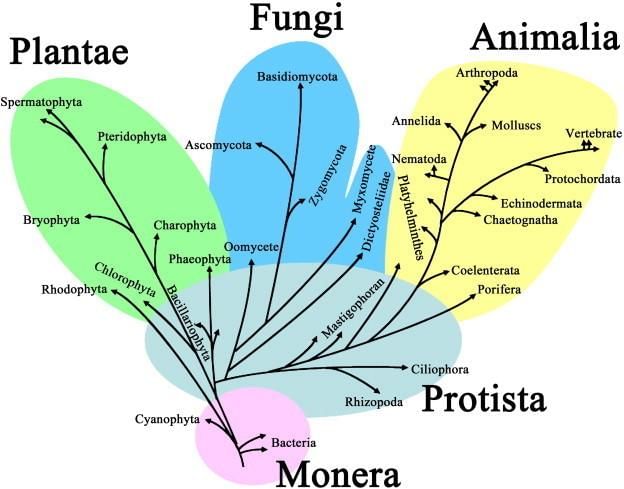 Whittaker Five - Kingdom Classification
Whittaker Five - Kingdom Classification - The five-kingdom classification's main criteria were cell structure, body organisation, mode of nutrition and reproduction, and phylogenetic relationships [evolutionary development and diversification of a species].
Table: Two Kingdom Classification
➢ Five Kingdom Classification
At present, the biological classification includes:
- Kingdom Monera
- Kingdom Protista
- Kingdom Fungi
- Kingdom Plantae
- Kingdom Animalia
Viruses, Viroids and Lichens are not included in the above classifcation.
➢ Criteria For the Classification of Organisms Into Five-Kingdom
- Cell structure (if the organisms are prokaryotic or eukaryotic).
- If the organisms are unicellular or multicellular.
- Presence or absence of a cell wall.
- Mode of nutrition (autotrophic or heterotrophic) and reproduction.
- Phylogenetic relationship.
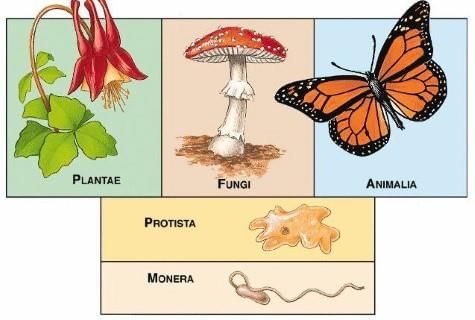 Five Kingdom
Five Kingdom
- In the five-kingdom classification, bacteria are included in Kingdom Monera.
- Kingdom Protista includes all single-celled eukaryotes such as Chrysophytes, Dinoflagellates, Euglenoids, Slime-moulds and Protozoans.
- Members of Kingdom Fungi show a great diversity in structures and habitat. Most fungi are saprophytic in their mode of nutrition.
- The Plantae includes all eukaryotic chlorophyll-containing organisms. Algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms are included in this group.
- The heterotrophic eukaryotic, multicellular organisms lacking a cell wall are included in the Kingdom Animalia.
- Some acellular organisms like viruses and viroids as well as the lichens are not included in the five-kingdom system of classification.
Solved Examples
Ques 1: Which one of the following is not a eukaryotic organism?
(A) Paramecium caudatum
(B) E. coli
(C) Euglena viridis
(D) Amoeba proteus
Ans: (B)
Sol: E. coli is a prokaryotic celled gram-negative bacterium.
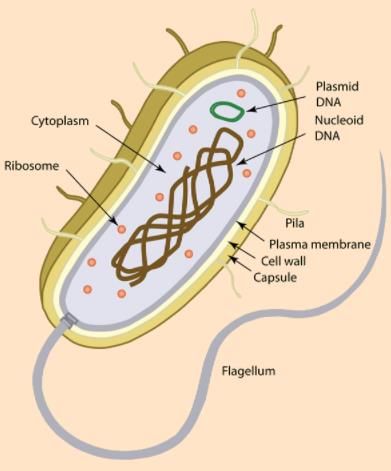 E. coli
E. coli
Ques 2: In Eubacteria, a cellular component that resembles eukaryotic cells is:
(A) Plasma membrane
(B) Nucleus
(C) Ribosome
(D) Cell wall
Ans: (A)
Sol: Eubacteria are prokaryotic, but they are enclosed by plasma membrane like eukaryotic cells.
Ques 3: Organisms called Methanogens are most abundant in a:
(A) Sulphur rock
(B) Cattle yard
(C) Polluted stream
(D) Hot spring
Ans: (B)
Sol: Methanogens are archaebacteria abundant in cattle yard and paddy fields.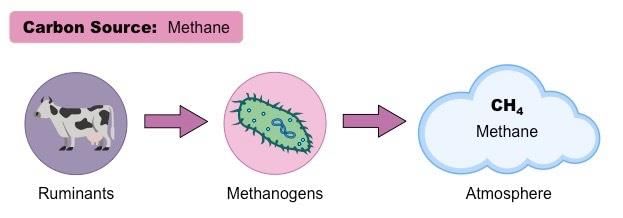
Ques 4: Trinomial nomenclature of classification was proposed by:
(A) Linneaus
(B) Huxley and Strickland
(C) John-Ray
(D) Theophrastus
Ans: (B)
Sol:
- Linnaeus is considered the father of taxonomy and was first to use the binomial nomenclature for organisms.
- The scientific name of an organism having three words is referred to as trinomial.
- It usually mentions intraspecific/subspecific epithets after the generic name and specific epithet.
- The names of intraspecific epithets are guided by the same rules, like that of specific epithets. For example, the trinomial name of mustard is Brassica oleracea capitata.
- Here Brassica is the generic name followed by specific epithet (oleracea) and the name of the variety (capitata).
- The trinomial nomenclature was proposed by Huxley and Strickland.
Ques 5: Most of the Botanical Names are drawn from the following language:
(A) German
(B) Greek
(C) Latin
(D) Spanish
Ans: (C)
Sol: In Europe, before the middle of the 18th century, the lingua franca was Latin. In the universities, the education was in Latin. All the scientific publications were in Latin.
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction of Biological Classification - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is biological classification and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How are living organisms classified into different groups? |  |
| 3. What are the main criteria used for biological classification? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of binomial nomenclature in biological classification? |  |
| 5. How does biological classification help in studying the evolutionary history of organisms? |  |






















