Electroplating | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Electroplating is the process through which one metal is plated to another metal through hydrolysis. It is usually done for decorative purposes along with prevention of corrosion of metals. Fig: ElectroplatingElectroplating is the process through which one metal is plated to another metal through hydrolysis. It is usually done for decorative purposes along with prevention of corrosion of metals. There are certain specific types of electroplating like copper plating, chromium plating and silver plating.
Fig: ElectroplatingElectroplating is the process through which one metal is plated to another metal through hydrolysis. It is usually done for decorative purposes along with prevention of corrosion of metals. There are certain specific types of electroplating like copper plating, chromium plating and silver plating.
The manufacturers get the benefit of electroplating since they can easily use inexpensive metals like zinc and steel for the majority of the product and then electroplate different metals on outside for appearance, protection and achieving the other desired properties for the product. The surface can be plastic or even a metal.
The process of electroplating includes using an electrolytic cell which consists of applying a negative charge to the metal and dipping it in a solution containing metal salt i.e. electrolytes which is full of positively charged metal ions.
Attraction between the two metals occurs owing to the positive and the negative charges.
The process of electroplating was first discovered by Luigi Brugnatelli in 1805. He electroplated the gold by using the electrode position process.
CHOOSING THE ELECTROLYTES AND PREPARING THE SURFACE:
Determining the right electrolyte for electroplating is important to maintain the quality of plating. Some of the electrolytes used are acids, metal salts, bases or molten salts. While choosing the correct type of electrolyte, it is important to keep certain things in the mind. They are corrosion, brightness, reflectivity, resistance, hardness, ductility, mechanical strength and wear resistance.
The surface is prepared before starting to plate another metal on it is to make sure that the surface is clean and free from the contaminants which can interfere in the bonding. Due to contamination, lack of adhesion happens along with no deposition. The surface is prepared in three steps by cleaning it with solvents, treatment (surface modification where there is hardening of parts and application of metal layers) and rinsing.
USES OF ELECTROPLATING: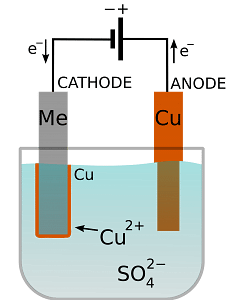 Fig: Process of electroplating
Fig: Process of electroplating
• It can make a relatively cheap metal like copper look expensive by coating copper with a thin layer of gold or silver.
• Electroplating can be used to make things rust resistant.
• Chromium plating improves the wear and appearance of the objects.
• Zinc or the tin coatings are used for making anything corrosion resistant.
• Electroplating can also be done for increasing the thickness of any item.
• Electroplating is mostly used in automobile industries, electronics, airplanes, toys and jewellery.
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|
FAQs on Electroplating - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is electroplating? |  |
| 2. How does electroplating work? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of electroplating? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of electroplating? |  |
| 5. Are there any environmental concerns associated with electroplating? |  |
|
352 videos|596 docs|309 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















