Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Our Environment (complete notes)
Our Environment (complete notes) - Class 10 PDF Download
Topics in the Chapter
• Introduction• Ecosystem
→ Types of ecosystem
→ Natural ecosystem
→ Artificial ecosystem
→ Abiotic components
→ Biotic components
→ Producers
→ Consumers
• Division of consumers
→ Herbivores
→ Carnivores
→ Omnivores
→ Parasites
→ Decomposers
• Food Chain
→ Flow of energy between trophic levels
→ Biological magnification
• Food web
→ Environmental problems
• Ozone layer
→ Formation of ozone molecule
→ Depletion of ozone layer
• Garbage disposal
→ Types of materials in Garbage
→ Biodegradable
→ Non-biodegradable
• Methods of waste disposal
→ Biogas plant
→ Sewage treatment plant
→ Land fillings
→ Composting
→ Recycling
→ Reuse
Introduction
→ Everything that surrounds us is environment. It includes both living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components.
→ Interaction between these biotic and abiotic components form an ecosystem.
→ In an ecosystem living components depend on each other for their food which give rise to food chains and food webs in nature.
→ Human activities lead to environmental problems such as depletion of ozone layer and production of huge amount of garbage.
Ecosystem
→ All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. E.g., forest, pond etc.
Types of ecosystem
It is of two types
(i) Natural ecosystem: The ecosystem which exist in nature on its own.
Example: forest, lake, ocean.
(ii) Artifical ecosystem: Man-made ecosystems are called artificial ecosystem.
Example: crop field, aquarium, garden.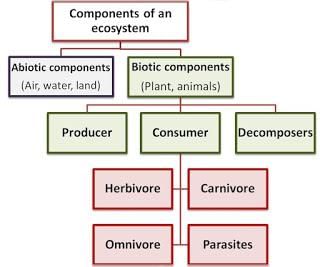
(i) Abiotic Components: All the non-living components such as air, water, land, light, temperature etc. form the abiotic components.
(ii) Biotic Components: All the living components such as plants, animals, bacteria, fungi etc. form the biotic components.
• On the basis of nutrition biotic components are further divided into:
→ Producers: All green plants and blue-green algae can produce their own food using abiotic components (photosynthesis), hence called producers.
→ Consumers: Include all animals which depend on producers directly or indirectly for their food.
Division of Consumers
(i) Herbivores: Plant eaters. Example: goat, deer.
(ii) Carnivores: Flash eaters. Example: tiger, crocodile.
(iii) Omnivores: Eats both plants and animals. Example: human.
(iv) Parasites: Live on the body of host and take food from it. Example: lice, cascuta.
Decomposers: Include organisms which decompose the dead plants and animals. Example: bacteria, fungi. These help in the replenishment of natural resources
→ Food chain is a series of organisms in which one organism eats another organism as food. For example:
• Grass → Deer → Lion
→ In a food chain various steps where transfer of energy takes place is called a trophic level.
Flow of energy between trophic levels.
→ Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
→ Green plants capture 1% of sunlight and convert it into food energy.
→ 10 percent law : Only 10% of energy is transferred to the next trophic level. The remaining 90% energy is used in life processes (digestion, growth, reproduction etc.) by present trophic level.
→ Due to this gradual decrease in energy, food chains contain 3-4 trophic levels.
Trophic levels
• Decrease in energy
1 kJ ↣ 10 kJ ↣ 100 kJ ↣ 1000 kJ
• Biological magnification: The concentration of harmful chemicals increases with every next trophic level in a food chain. This is called biological magnification.
→ Maximum concentration of such chemicals get accumulated in human bodies as human occupy the top level in any food chain.
Food web
→ In nature large numbers of food chains are interconnected forming a food web.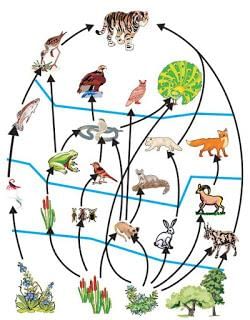
• Environmental problems: Changes in the environment affect us and our activities change the environment around us. Human activities leads to pollution, deforestation etc.
Ozone layer
→ Ozone layer is a protective blanket around the earth which absorbs most of the harmful UV (ultraviolet) radiations of the sunlight, thus protecting living beings from many health hazards such as skin cancer, cataract, destruction of plants etc.
→ Ozone (O3) layer is present at higher levels of atmosphere (i.e. stratosphere). It is a deadly poison at ground level.
Formation of ozone molecule
(i) The high energy UV radiations break down the O2 molecules into free oxygen (O) atoms.
O →(UV) O + O (atoms)
(ii) These oxygen atoms then combine with oxygen (O2) molecule to form the ozone molecule.
O2 + O → O3 (ozone)
Depletion of ozone layer
→ The decrease in the thickness of ozone layer over Antarctica was first observed in 1985 and was termed as ozone hole.
→ This decrease was linked to excessive use of synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used in refrigerators, ACs, fire-extinguishers, aerosols sprays etc.
→ United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) succeeded in forging an agreement to stop CFC production at 1986 levels (KYOTO PROTOCOL) by all countries.
Garbage disposal
→ Improvements in lifestyle have resulted in accumulation of large amounts of waste materials.
Types of materials in Garbage
(i) Biodegradable: Substances which can be decomposed by the action of micro-organisms are called biodegradable wastes.
Example: fruit and vegetable peels, cotton, jute, dung, paper, etc.
(ii) Non-biodegradable wastes:Substances which cannot be decomposed by the action of micro-organisms are called non-biodegradable wastes.
Example: plastic, polythenes, metals, synthetic fibres, radioactive wastes, pesticides etc.
→ Micro-organisms release enzymes which decompose the materials but these enzymes are specific in their action that’s why enzymes cannot decompose all the materials.
Methods of waste disposal
(i) Biogas plant: Biodegradable waste can be used in biogas plant to produce biogas and manure.
(ii) Sewage treatment plant: The drain water can be cleaned in sewage treatment plant before adding it to rivers.
(iii) Land fillings: The wastes are buried in low lying areas and are compacted by rolling with bulldozers.
(iv) Composting: Organic wastes are filled in a compost pit and covered with a layer of soil, after about three months garbage changes to manure.
(v) Recycling: Non-biodegradable wastes are recycled to make new items.
(vi) Reuse: It is a conventional technique to use an item again. Example: newspaper for making envelops.
Thanks for visiting here !
Follow me to get all the notification of my uploads !
FAQs on Our Environment (complete notes) - Class 10
| 1. What are the major environmental issues addressed in Class 10's "Our Environment" article? |  |
Ans. The major environmental issues addressed in the article "Our Environment" for Class 10 are air pollution, water pollution, deforestation, climate change, and waste management.
| 2. How does air pollution impact the environment and human health? |  |
Ans. Air pollution can have severe consequences on both the environment and human health. It can lead to the deterioration of air quality, causing respiratory problems, allergies, and even long-term health issues like lung cancer. Additionally, air pollution contributes to the formation of smog and acid rain, which can harm ecosystems and damage buildings and infrastructure.
| 3. What are the causes of water pollution discussed in the article? |  |
Ans. The article highlights several causes of water pollution, including industrial waste discharge, agricultural runoff, improper sewage disposal, oil spills, and dumping of chemicals and plastics into water bodies. These human activities introduce harmful substances into water sources, leading to contamination and the degradation of aquatic ecosystems.
| 4. How does deforestation contribute to environmental degradation? |  |
Ans. Deforestation, the clearing of forests for various purposes, has detrimental effects on the environment. It leads to habitat loss for countless plant and animal species, disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, and contributes to climate change. Trees play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide, and their removal increases greenhouse gas emissions, leading to global warming.
| 5. What are the measures suggested for waste management in the article? |  |
Ans. The article suggests several measures for effective waste management, such as reducing, reusing, and recycling waste materials. It emphasizes the importance of segregating waste into different categories to facilitate recycling and composting. Additionally, the article promotes the adoption of sustainable practices like using eco-friendly products and promoting awareness about waste management among communities.
Related Searches















