Animal Life Class 5 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Types of Animals based on their Habitat |

|
| Body Coverings of Animals |

|
| Eating Habits of Animals |

|
| Breathing Methods of Animals |

|
| Some Important Questions |

|
Do You Know? 
The elephant is the largest land animal. It has a long trunk that can be used for various tasks, such as picking up food, drinking water, and even greeting other elephants. Elephants are highly intelligent and have a strong social structure within their herds.
Habitat: The place where an animal lives, feeds, and reproduces is called its habitat. Habitat provides food, water, and shelter to animals. Different animals live in different habitats.
Types of Animals based on their Habitat
1. Terrestrial Animals
- Animals that live on land are called terrestrial animals.
 Terrestrial Animals
Terrestrial Animals - Terrestrial animals have certain adaptations that help them to survive on land.
Adaptation
- Adaptation is the presence of specific features or habits that help a plant or animal to live in its surrounding.
Example of a Terrestrial Animal: Elephant
- Elephants are large animals that have long trunks and big ears.
Elephants live in:
- Elephants live in tropical conditions.
- They have certain adaptive features that help them to survive in a hot environment:
- Big ears of elephants help them to stay cool.
- Elephants are huge in size and produce lots of heat. Large ears of elephants help the elephant keep them cool.
- Elephants' ears help them to hear long distances and communicate.
2. Aquatic Animals
- Animals that live in water are called aquatic animals.
 Aquatic animals
Aquatic animals
3. Amphibians
- Animals that live both on land and in water are called amphibians.
- Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates (vertebrates have backbones) that don’t have scales.
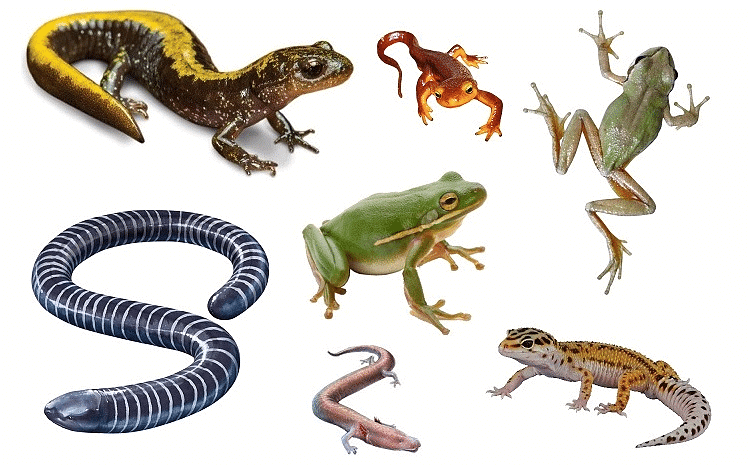 Amphibians
Amphibians
4. Arboreal Animals
- Some animals that mostly live in trees are known as arboreal animals.
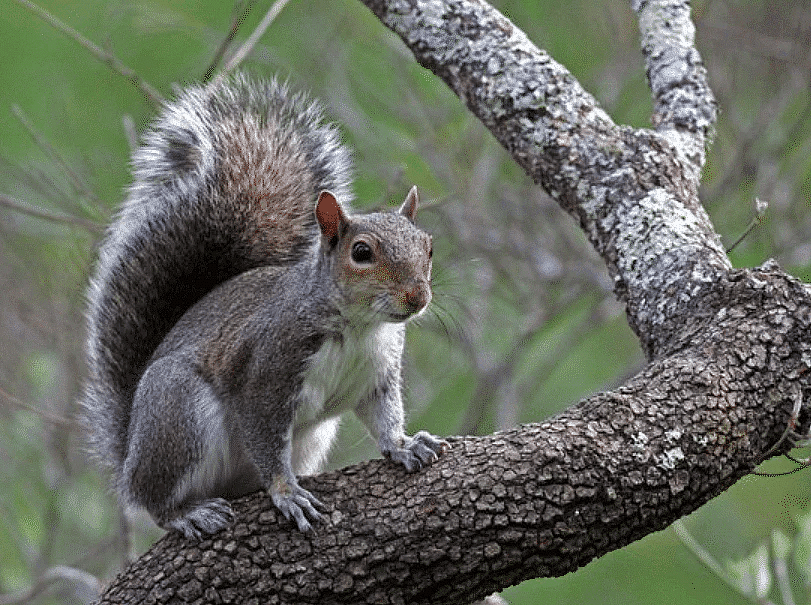 Squirrel
Squirrel
5. Aerial Animals
- Some animals can fly, they are called aerial animals.
 Aerial animals
Aerial animals
Body Coverings of Animals
Body covering helps animals to adapt and live comfortably in their habitats.
- Feathers: Birds have feathers that keep them warm and help them to fly.
 Feathers of a Bird
Feathers of a Bird
- Scales: Fish have overlapping scales that do not let water enter their body. Reptiles such as crocodiles, snakes, and lizards also have scales for protection.
 Gills of Fish
Gills of Fish
- Shell: A very hard outer covering is called a shell. It protects the soft bodies of animals such as snails, tortoises, and oysters.
 Snail
Snail
Zebra has a striped body. It looks similar to the background where it lives. This is called camouflage. It prevents the animal from being seen by its predator.
- Wool: Some animals, such as sheep, have a hairy body covering called wool. It keeps their body warm.
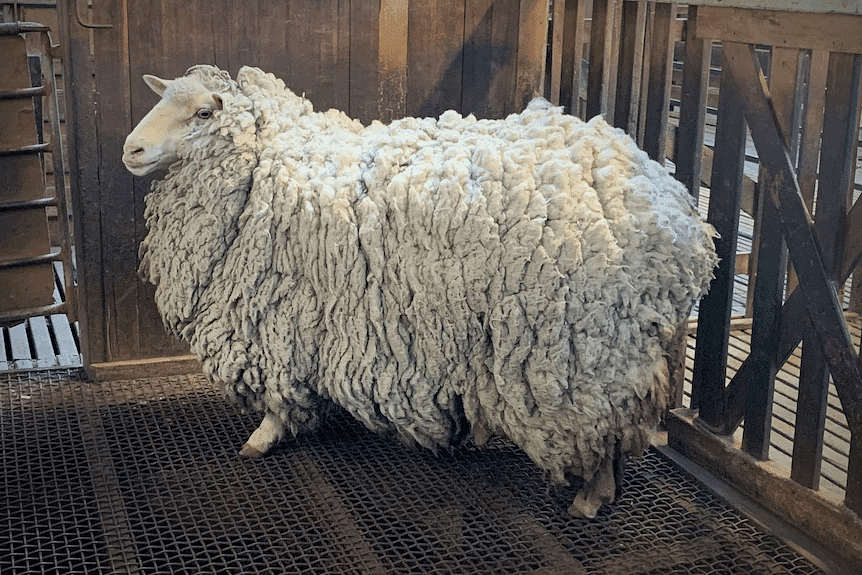 Wool of sheep
Wool of sheep
- Fur: The thick fur of a polar bear or an Arctic fox protects them from extreme cold.
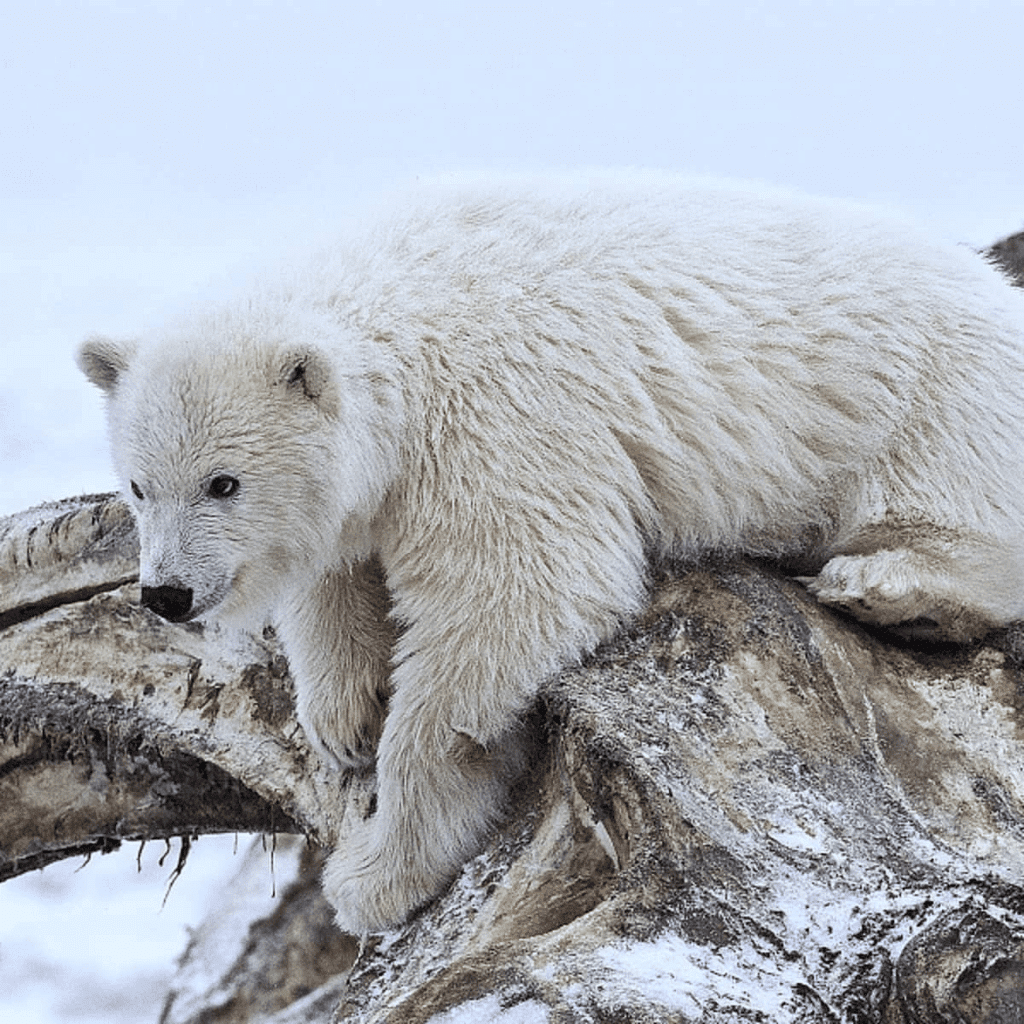 Fur of Polar Bear
Fur of Polar Bear
- Cuticle: Insects such as bees and ants have a waxy and water-resistant outer covering called a cuticle.
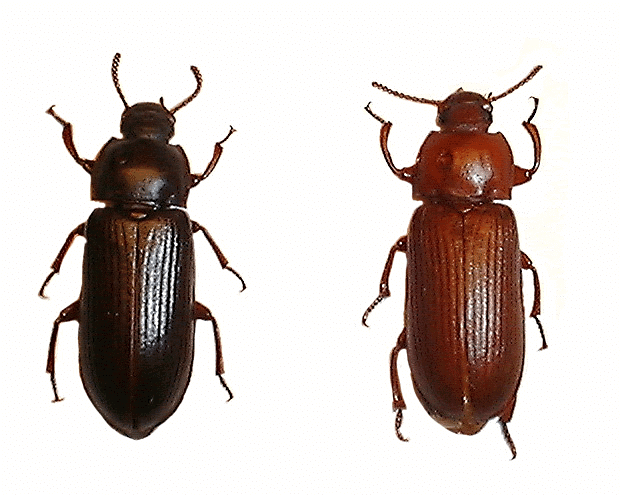 Cuticle of insects
Cuticle of insects
- Hard plates: Animals such as armadillos have hard, armor-like plates that provide protection from enemies.
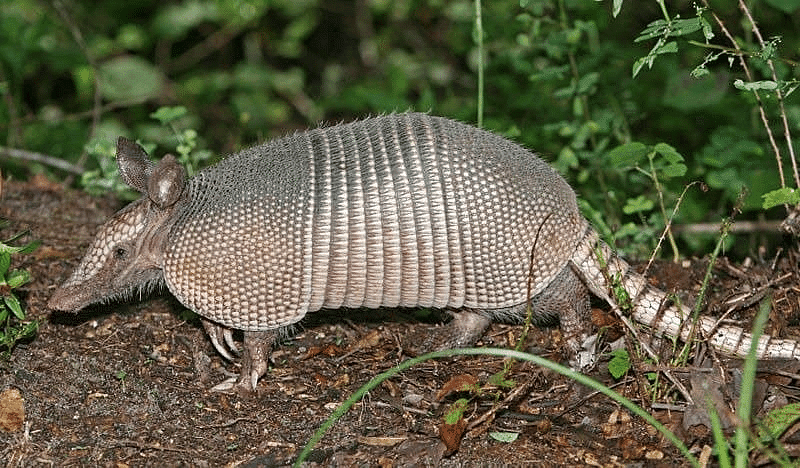 Plates of Armadillos
Plates of Armadillos
The deer is not easily visible in the forest due to its body covering. A porcupine has sharp, needle-like spines called quills on its body for protection against enemies.
Eating Habits of Animals
- Herbivores: Zebra, giraffe, cow, goats, and deer have sharp front teeth to cut the grass and broad back teeth to chew and grind them, such animals are called herbivores.
They eat plants such as herbs and shrubs, and leaves of trees.
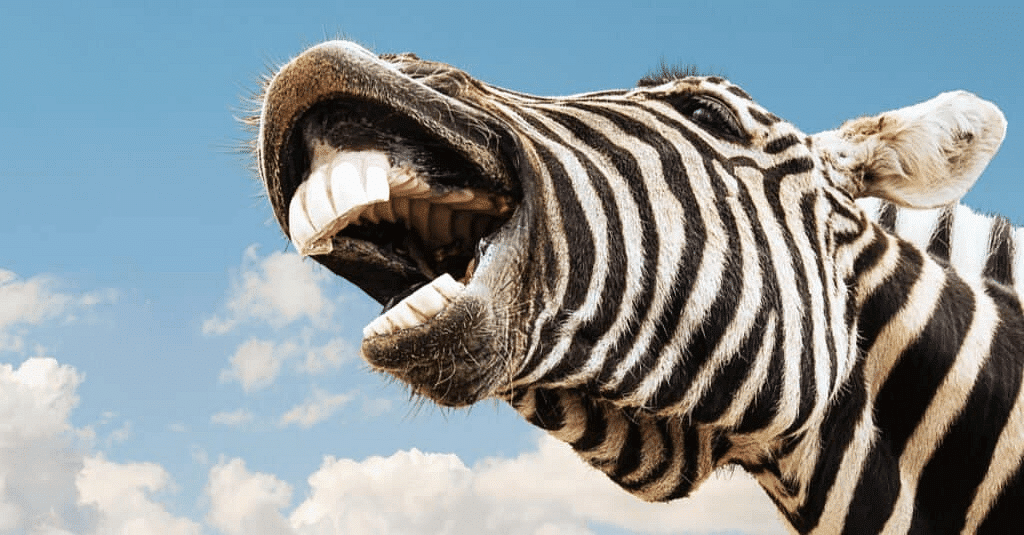 Sharp front teeth of Zebra
Sharp front teeth of Zebra
- Carnivores: Animals such as cats, tigers, and lions eat the flesh of other animals. They are called carnivores.
They have sharp and pointed front teeth for tearing flesh.
 Pointed teeth of Tiger
Pointed teeth of Tiger
Birds such as eagles and vultures too are carnivores. The hooked beak of these birds helps them to tear the flesh.
- Rodents: Small animals such as rats and squirrels have sharp front teeth. They use these teeth to gnaw on their food. These animals are called rodents.
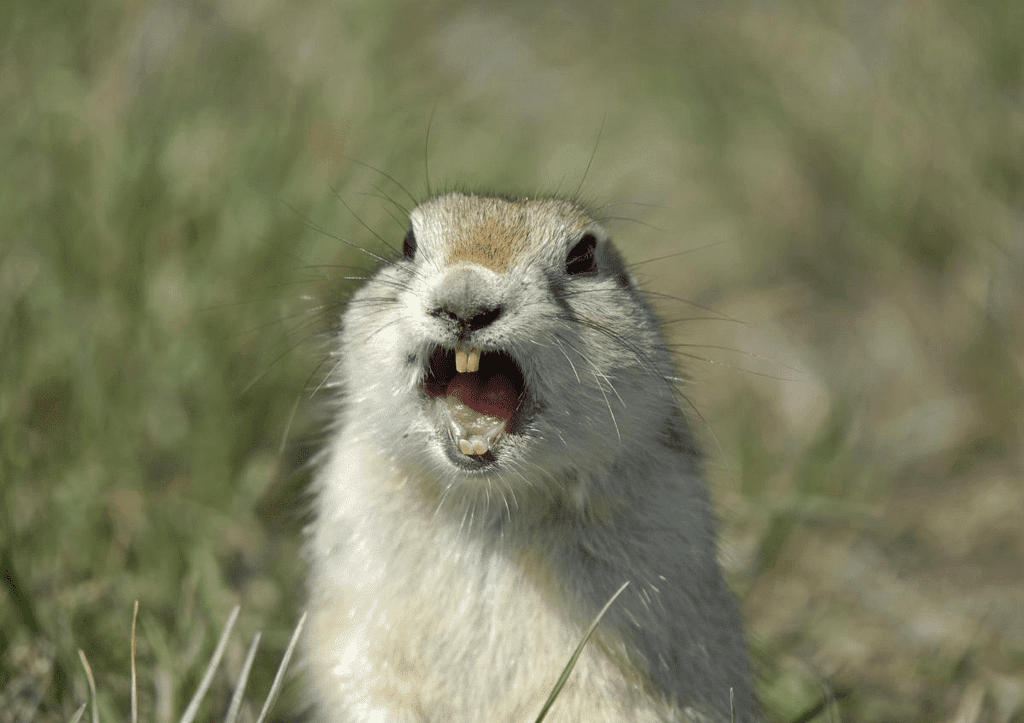 Sharp front teeth of Squirrel
Sharp front teeth of Squirrel
Proboscis: Butterflies have a long, thin tube-like mouth called a proboscis. They use it to suck nectar from flowers. Mosquitoes have a needle-like tube that helps them to suck blood.
_2.jpg)
Breathing Methods of Animals
Breathing is a process by which animals take in and give out air. The air they breathe in supplies oxygen to their bodies.
Aquatic animals get oxygen from the air dissolved in water.
Different animals have different organs for breathing.
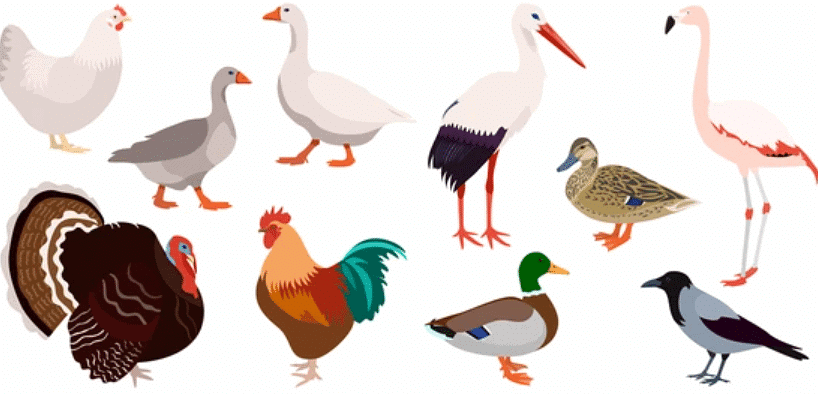
- Birds, reptiles, and mammals: They breathe through their lungs.
- Insects: They have small holes called spiracles on their body which lead into a network of tubes present all through the body, called the trachea.
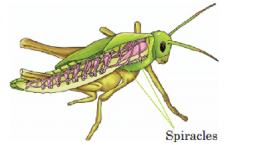
- Fish, tadpoles, and other aquatic animals: They breathe through gills. Gills are thin, flat structures that have many blood vessels.
 Gills of Fish
Gills of Fish
- Whales and dolphins: Both whales and dolphins also live in the water. They have lungs that can take in oxygen only from the air. So, they cannot breathe underwater and have to come to the surface of the water to breathe. They have blowholes on the head for breathing.
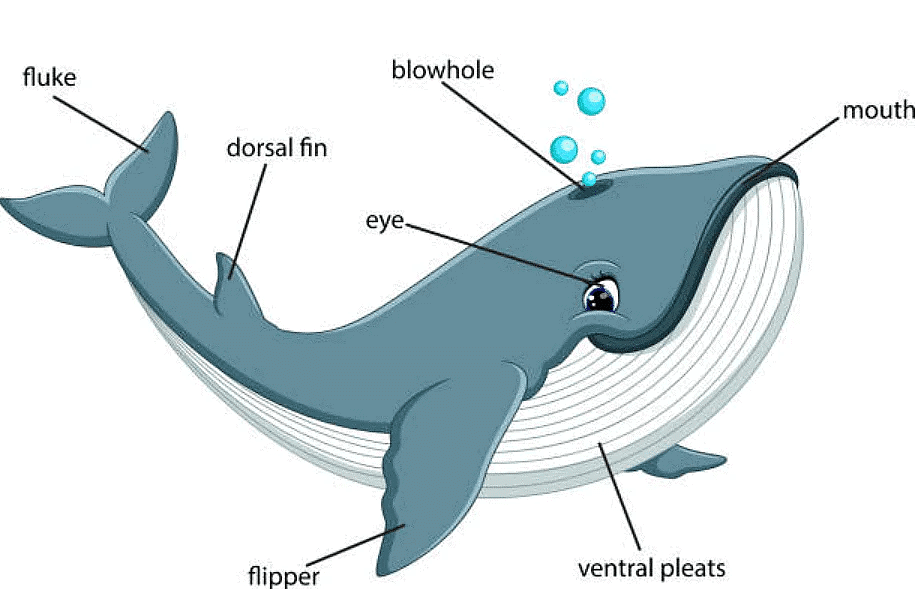 Parts of a whale
Parts of a whale
- Earthworm: It breathes through its skin.
- Frogs: They breathe through their skin when they are in the water. On land, frogs breathe through their lungs. Baby frogs or tadpoles breathe through gills.
Some Important Questions
1. What are the different types of animals based on their habitat?
Ans: The different types of animals based on their habitat include terrestrial animals (live on land), aquatic animals (live in water), amphibians (live both on land and in water), arboreal animals (live on trees), and aerial animals (can fly).
2. How do the body coverings of animals help them to adapt to their habitats?
Ans: Body coverings help animals to adapt and live comfortably in their habitats by providing protection, warmth, and camouflage. For example, feathers in birds help them stay warm and fly, scales in fish protect their bodies from water, and fur in polar bears keeps them warm in extreme cold.
3. What are the different eating habits of animals?
Ans: Animals can have different eating habits depending on their diet. Herbivores eat plants, such as grass, shrubs, and leaves; carnivores eat the flesh of other animals; and rodents have sharp front teeth to gnaw on their food. Some animals, like butterflies, have a proboscis for sucking nectar from flowers.
4. How do different animals breathe?
Ans: Different animals have different organs for breathing. Birds, reptiles, and mammals breathe through their lungs; insects have small holes called spiracles on their body connected to a network of tubes called the trachea; fish and other aquatic animals breathe through gills; and earthworms and frogs breathe through their skin.
5. What is camouflage?
Ans: Camouflage is a natural adaptation in which animals have body patterns, colors, or textures that help them blend in with their surroundings, making them less visible to predators or prey.
|
43 videos|371 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Animal Life Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What are the different types of animals based on their habitat? |  |
| 2. How do animals differ in their body coverings? |  |
| 3. What are the different eating habits of animals? |  |
| 4. How do animals breathe, and what are the different methods of respiration? |  |
| 5. What is animal migration, and why do animals migrate? |  |





















