Reproduction in Plants | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 4 PDF Download
Introduction
Plants are very useful to us. They are the only living beings which make their own food and provide food for all other living beings. Plants also give out oxygen which all human beings and animals need for breathing. Plants also check soil erosion. They are, therefore, called our green friends. Hence, it is necessary to grow more and more plants on earth.
Reproduction in Plants
Living things do not live forever. They all die but life continues due to the process of reproduction. Like animals, plants also reproduce. Plants produce new plants like themselves. This process of production of new plants is called reproduction.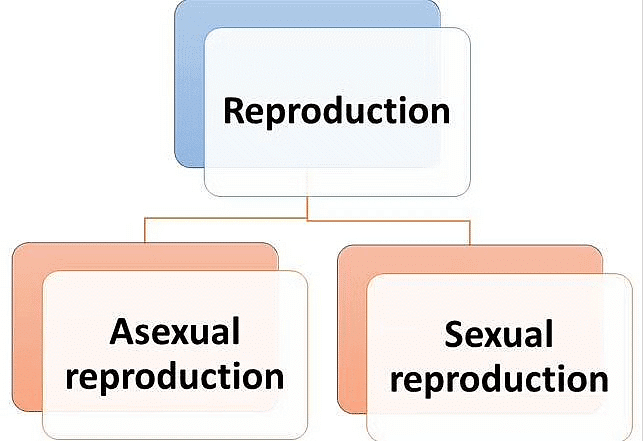
1. Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent and inherit the character of that parent only. These off-springs are the exact copies of the parent plant.
Vegetative Propagation: The kind of reproduction in which a new plant grows from the body parts of a plant such as the stem, roots and leaves is called vegetative propagation.
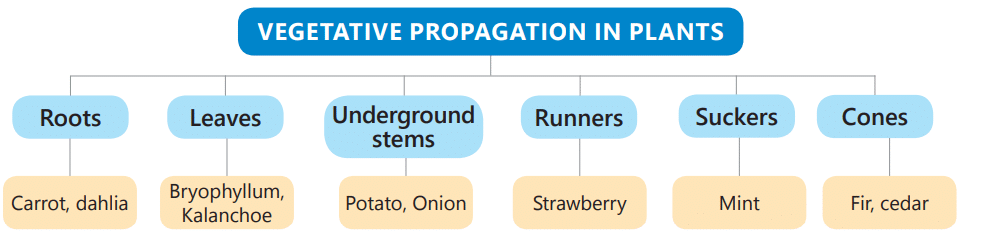
1. Vegetative propagation by Roots
A new plant can also grow from the roots of the mother plant. Sweet potato, carrot, radish, turnip and dahlia are some examples of plants whose roots can grow into new plants.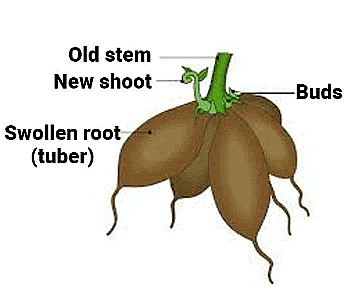 Vegetative Propagation by Roots in Sweet PotatoSome plants like gladioli, lilies and tuberoses grow from the bulbs of the mother plants. The bulbs are underground buds. These are called bulbs because these are shaped like bulbs.
Vegetative Propagation by Roots in Sweet PotatoSome plants like gladioli, lilies and tuberoses grow from the bulbs of the mother plants. The bulbs are underground buds. These are called bulbs because these are shaped like bulbs.
2. Vegetative propagation by Stem
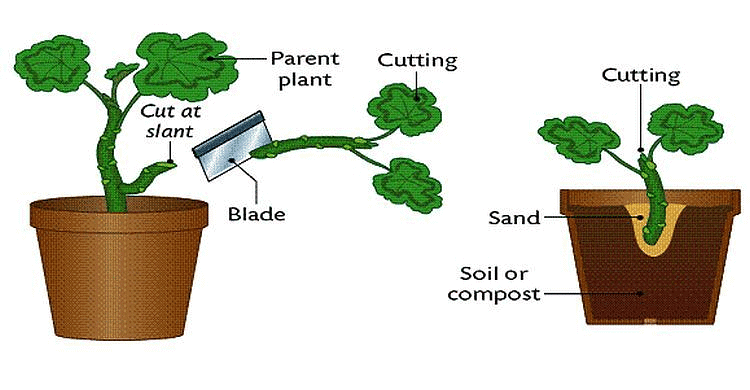
Some plants like rose, hibiscus, money plant and sugarcane can grow from the stems of old plants. A piece of stem having buds is taken from the mother plant and is planted in the soil. After a few days, new plants grow out from the buds. This method is called stem cutting.
- The potato is a stem that grows underground and has buds called ‘eyes’. Any part of a potato that has buds, when planted in the soil, can grow into a new plant.
- Onion and ginger are also underground stems from which new plants grow.
3. Some plants grow by layering
Some plants can also be grown by layering. In this method, the side branches are bent towards the ground and covered with moist soil, keeping the tip free. After a few days, new roots develop. Jasmine plant and lemon plant reproduce by the process of layering.
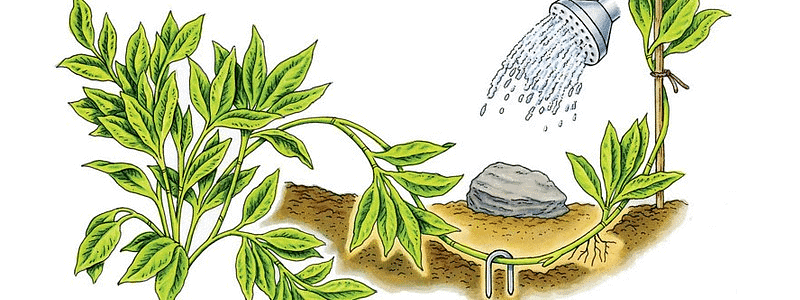 Layering
Layering
4. Growing of grass
We know that grass plants creep along the ground like a green carpet. Side branches grow out of creeping stems. They separate and grow into new plants. These are called runners. Mango, grapes, rose and many other fruit plants are grown by stem cutting and budding.
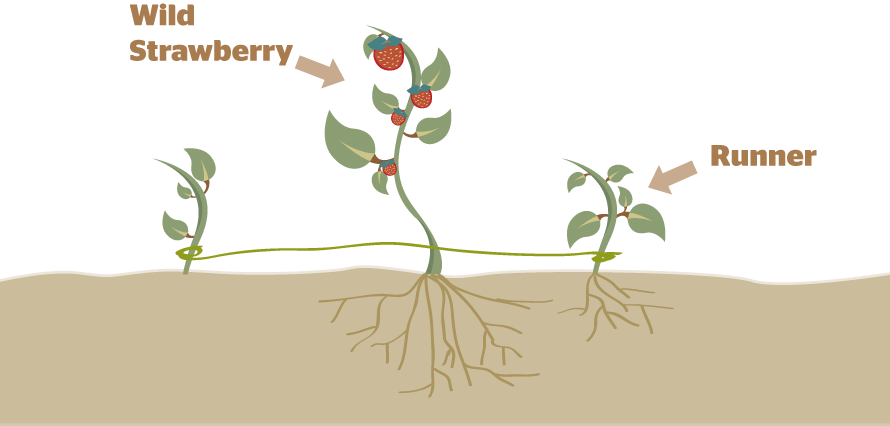
5. Vegetative Reproduction by Leaf
Leaves of certain plants produce buds along their margins. New plants grow from these buds if the leaves are placed in moist soil. For example, Bryophyllum leaves.
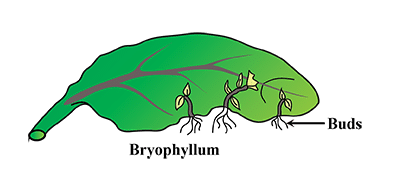 Vegetative Propagation by Leaf in Bryophyllum
Vegetative Propagation by Leaf in Bryophyllum
6. Vegetative propagation by spores
Certain plants do not bear flowers and seeds. They have special structures called spores which help in reproduction. For example, mushrooms, ferns and mosses. If you rub many dark coloured dots lying underside of a fern plant between your thumb and forefinger, the powdery substance you can feel between your fingers are the spores.
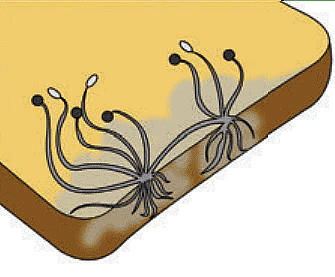 Spores of Fungi
Spores of Fungi
Advantages of Vegetative Reproduction:
1. Vegetative propagation is a faster method to produce a new plant.
2. It is a very useful method for production of seedless plants such as grapes and banana.
3. The plants produced by vegetative propagation bear flowers and fruits earlier than the new plants produced by seeds.
Sexual reproduction:
Sexual reproduction is the method of reproduction in plants by which offsprings produce from a male and a female parent. The offspring will inherit the traits of both the parents. Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants. They turn into fruits, which have seeds inside them. New plants grow from seeds.
Interesting Facts:
- Venus fly trap, pitcher plant and bladder worth etc. derive their nitrogen requirement from the insects.
- Bamboo is not a tree but a grass
- The flower of Raffles is the largest known flower
- Edible mushroom grows completely within 7 days.
- Amount of carbon dioxide produced by plants are less than that of oxygen produced by them.
|
11 videos|15 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Reproduction in Plants - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 4
| 1. Why is reproduction important for plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants reproduce? |  |
| 3. What are the different modes of asexual reproduction in plants? |  |
| 4. What is pollination in plants? |  |
| 5. How are seeds formed in plants? |  |

















