Class 12 Economics Solved Paper (2011 Outside Delhi Set-II) | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Ques 1: Explain any three properties of Indifference Curves.
Ans: Indifference Curve (IC) is a curve that depicts various combinations of two goods that provides a consumer with the same level of satisfaction. The following are the three major properties of an IC.
(i) Indifference curve is downward sloping to the right: Downward slope of an IC to the right implies that a consumer cannot simultaneously have more of both the goods. An increase in the consumption of one good is possible only with the reduced consumption of another good.
(ii) Slope of IC: The slope of an IC is given by the Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS). It refers to the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for each additional unit of another good.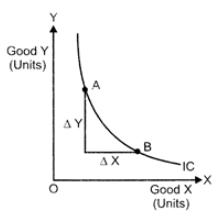
At point A:
Slope of IC (MRS) 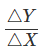
i.e., MRS shows the rate at which the consumer is willing to sacrifice good Y for an additional unit of good X.
(iii) Shape of indifference curve: An IC is convex to the origin. As we move down along th e IC to the right, the slope of IC (or MRS) decreases. This is because as the consumer consumes more and more of one good, the marginal utility of that good tails. On the other hand, the marginal utility of the (other) good which is sacrificed rises. In other words, the consumer is willing to sacrifice lesser and lesser for each additional unit of the other good consumed. Thus, as we move down the IC, MRS diminishes. This suggests the convex shape of indifference curve.
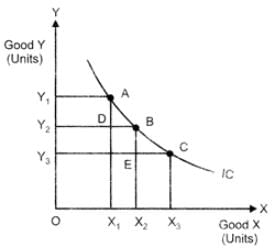
At point A, 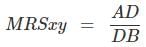
At point B,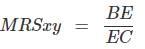
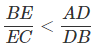
MRS at B < MRS at A, so MRS has fallen.
Ques 2: List the transactions of Current Account of the Balance of Payments Account.
Ans:
The following are the three main transactions of the Current Account of BOP.
(i) Export and Import of Goods: The transaction related to the export and import of goods are recorded in the Current Account of BOP. This record of exports and imports is also termed as 'Balance of Visible Traded?. The export of goods is recorded as positive items whereas, the import of goods are recorded as negative items in the Current Account of BOP.
(ii) Export and import of services: The second component of the Current Account is the export and import of services. The record of export and import of services is also termed the 'Balance of Invisible Trade\ Similar to the export of goods, export of services is recorded as positive items in the Current Account of BOP. Some of the major services that are included in the Current Account are shipping services, insurance and banking services, income from investment (i.e., income from profits and dividends), foreign travel, miscellaneous transactions such as royalties, consultancy services, telephone services, etc.
(iii) Unilateral transfer: Unilateral transfers refer to the one-sided transfer such as gifts, donations, grants from foreign governments, etc. A country makes such transfers to the rest of the world as well as receives transfers from the rest of the world. The receipts of unilateral transfers are recorded as positive items in the Current Account, whereas, the payments of unilateral transfers are recorded as negative items in the Current Account of BOP.
Ques 3: In an economy the marginal properity to save is 0.4. National income in the economy increases by Rs. 200 crore as a result of change in investment. Calculate the change in investment.
Ans:
Given, Marginal propensity to save (MPS) = 0.4
Increase in national income (AY) = Rs. 200 Crore
We know that,
Multiplier (K) = 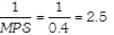
We also know that, K 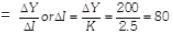
Change in investment = Rs. 80 crore.
Ques 4:
Giving reasons and explain the treatment assigned to the following while estimating national income:
(i) Social security contributions by employees.
(ii) Pension paid after retirement.
Ans:
(i) Social security contributions by employees should be included in the estimation of national income as it is part of compensation of an employee.
(ii) Pension paid after retirement should be included in the estimation of national income. This is because it is a part of compensation of employees.
Ques 5:
Calculate (a) 'Net National Product at Market Price' from the following: | ||
S. No. | Items | (Rs. in Crore) |
(i) | Net current transfers to abroad | 30 |
(ii) | Mixed income | 600 |
(iii) | Subsidies | 20 |
(iv) | Operating surplus | 200 |
(v) | National debt interest | 70 |
(vi) | Net factor income to abroad | 10 |
(vii) | Compensation of employees | 1400 |
(viii) | Indirect tax | 100 |
(ix) | Domestic product accruing to | 350 |
(x) | Current transfers by govern | 50 |
Ans:
MNPMP= Compensation of Employees + Operating Surplus + Mixed Income + (Indirect Tax - Subsides) - Net Factor Income to Abroad
= 1400+200+600+(100-20)-10
= Rs. 2,270 crore
|
4 videos|168 docs
|





















