Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper Term I - 11 (With Solutions) | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
Ques 1: When did Louis XVI ascend the throne of France?
Ans: In 1774, Louis XVI ascended the throne of France.
Ques 2: Which river is known as Meghan in Bangladesh?
Ans: The Ganga is known as Meghna in Bangladesh.
Ques 3: What had taken place in Chile on 11th September, 1973?
Ans: In Chile, on 11th September, 1973, a military coup had taken place under the leadership of General Augusto Pinochet, in which the President Salvador Attende was killed.
Ques 4: When did Estonia restore its independence from the Soviet Union?
Ans: Estonia, a state in the Baltic region at Northern Europe got independence from the Soviet Union on 20th August, 1991.
Ques 5: Which variety of rock is used for manufacture of talcum powder?
Ans: A form of talc known as 'soapstone' is used for manufacture of talcum power.
Ques 6: What is fixed capital?
Ans: Tools, machines and buildings, which can be used in production over many years, are called fixed capital.
Ques 7: Name a country which did not have natural resources, but by investing in human resource, has become developed and rich.
Ans: Japan did not have natural resources, but by investing on people especially in the field of education and health, has become developed and rich.
Ques 8: Name the propounded of the theory 'Survival of the Fittest'.
Ans: Herbert Spencer propounded the theory 'Survival of the Fittest'.
Ques 9: What was the guillotine? How was it used?
Ans: The guillotine was a device consisting of two poles and a blade with which a person was beheaded. It was used by Robespierre, who followed a policy of 'Reign to Terror' i.e., of severe control and punishment. Those who did not agree with his methods were arrested, imprisoned and then tried by a revolutionary tribunal. If the court found them 'guilty', they were guillotined. It was named after Dr Guillotin who invented it. Finally Robespierre himself was guillotined.
Ques 10: State any three factors which made the Weimar Republic Politically Fragile.
Or
Explain the New Economic Policy of Lenin.
Ans: The Weimar Constitution had three inherent defects
(i) It was based on proportional representation, which made achieving a majority by one party virtually impossible. Only coalition governments ruled.
(ii) Existence of Article 48 in the Constitution, which gave the President the power to impose emergency, suspend civil rights and rule by decree.
(iii) Due to 20 different coalition governments being formed, people lost confidence in the democratic parliamentary system, as it offered no solutions to their problems.
Or
Lenin's New Economic Policy, promulgated by decree on 21st March, 1921, was a temporary retreat from full socialism to partial capitalism for the purpose of rebuilding Russia's economy. It permitted small businesses to make personal profits, while the state continued to control banks, foreign trade and large industries. Elements of capitalism such as individual profit and private ownership of land were permitted in order to revitalize the Russian economy.
Ques 11: Describe the condition of Russian workers on the eve of Russian Revolution in 1917. Or When and between whom was the treaty of Versailles signed? Mention two most important clauses of the treaty of Versailles.
Ans: In Russia, most of the industry was the private property of industrialists. Government supervised large factories to ensure minimum wages and limited hours of work. But factory inspectors could not prevent rules being broken. The working day was sometimes 15 hours. Workers in Russia were divided on the basis of skill. The metal workers considered themselves aristocrats among workers, as their occupation demanded more training and skill. They were better organized, quick to form associations and undertake strikes for better work conditions and rein statement of co-workers. Women formed 31% of the work force, but were paid less than men.
Ques 12: How were the great plains of Northern India formed?
Ans: The Northern plain has been formed by the interplay of the Indus, the Ganges and the Brahmaputra along with their tributaries. In due course of time, this depression gradually got filled with deposition of sediments by the rivers flowing from the lofty mountains and the peninsular plateau. A flat land of extensive alluvial deposits resulted in the formation of the Northern plains of India. It spreads over an area of 7 lakh sq. km. The plain being about 2400 km long and 240 to 320 km broad and is a densely populated area.
Ques 13: What is a river pattern? What factors control a river pattern?
Ans: A river along with its tributaries is known as river pattern. Different river patterns have been identified such as dendritic, radial and trellis and rectangular patterns. The stream with its tributaries resembles the branches of a tree, thus it is known as dendritic. The radial pattern develops when streams flow in different directions from a central peak. A river joined by its tributaries, at approximately right angles, develops a trellis pattern. A rectangular drainage pattern develops on a strongly jointed rocky terrain. The following factors control them
(i) Slope of the land
(ii) Geological structure i.e., underlying rock structure
(iii) Climatic conditions of the area.
Ques 14: Name the major tectonic plates. What are the three types of tectonic plate movements?
Answer: Major Tectonic plates are
(i) Pacific plate
(ii) North American plate
(iii) South American plate
(iv) African plate
(v) Indo-Australian plate
(vi) Eurasian plate
(vii) Antarctic plate
Three types of Tectonic plate movements are
(i) Converging
(ii) Diverging
(iii) Transformational
Ques 15: What was the condition of the blacks under the apartheid system in South Africa?
Ans: The blacks in South Africa were discriminated against on racial grounds and faced the following problems
(i) They were forbidden from living in white areas.
(ii) They could work in white areas only if they had a permit.
(iii) Trains, buses, taxies, hotels, schools and hospitals, etc were all separate for the whites and the blacks.
(iv) They could not even visit the churches where the whites worshipped.
(v) Blacks could not form associations nor protest against the terrible treatment.
Ques 16: We blame politicians for all wrong doings and excuse ourselves by saying that we have the right to elect, not to recall. Can this problem be solved by us?
Ans: Of course, this problem can be solved by us only if
(i) We choose honest, dedicated and hard working social workers as our leaders.
(ii) We are not biased on the basis of caste and religion before choosing our candidates.
(iii) We do not accept cash and any kind of object distributed by candidates before any election.
Ques 17: Compare two non-democratic governments, that is Pinochet's in Chile and Communists in Poland.
Ans: The differences between the two governments were
(i) Chile was ruled by a dictator, while Poland was ruled by a political party i.e., Polish United Workers Party.
(ii) The Government of Poland claimed that it was ruling on behalf of the working classes. The Government of Chile made on such claim.
The common features between the two Governments were
(i) The people could not choose or change their rulers.
(ii) There was no real freedom to express views, to form political associations and organize protests and political action.
Ques 18: Which major changes indicate improvement in public health in India?
Ans: The social obligation for the government is to ensure highest possible heath status to its population. The following factors indicate improvement in public health in India.
(i) Life expectancy of Indians has increased upto 65 years in 2011.
(ii) Infant Morality Rate (IMR) has come down from 147 in 1951 to 47 in 2010. Crude birth rates have dropped to 22.1and death rates to 7 within the same time.
(iii) While life expectancy has increased, death rates has dropped to 7 with in the same duration of time. Increase in longevity of life, reduction in infant mortality, all these indicate improvement in public health.
Ques 19: Explain the changes that took place in the field of agriculture in India due to the Green Revolution in the late 1960s.
Ans: The changes that occurred due to the Green Revolution in India were
(i) The use of advanced technology in agriculture implying use of HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers and pesticides and a well developed system of irrigation led to a substantial increase in the production of food grains, mainly wheat and rice.
(ii) It resulted in higher income growth. Even poor farmers who practiced modern farming with advanced technology started becoming rich.
(iii) It led to commercialization of agriculture as farmers started cultivating flowers, cotton, tobacco, etc.
Ques 20: What can done so that non-farm production activities can be started in villages?
Ans: To encourage non-farm activities in villages some measures can be taken
(i) Banks should provide loans at low interest rates so that the poor villagers can start some business to help them earn a living.
(ii) Government should be more active and start effective employment generating schemes.
(iii) Government should provide training to the villagers in different small crafts.
(iv) Government should provide facilities for transportation and selling of locally manufactured goods of the villagers in the cities.
(v) Industries can be setup in rural areas.
Ques 21: (a) On the given physical map of India, identify, the points marked as (1) and (2) and write their correct names.
1. An area receiving more than 400 cm rainfall.
2. An area receiving less than 20 cm rainfall.
(b) Also mark and label the following on the same map.
A. Jog falls
B. Cardamom hills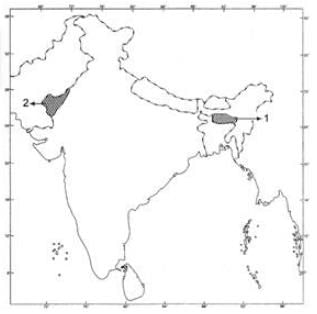
Ans: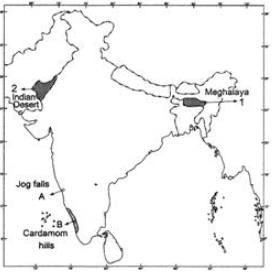
Ques 22: Locate and label the following on the map of India
(a) Western Ghats
(b) Nilgiri Hills
(c) Garo Hills
Ans: 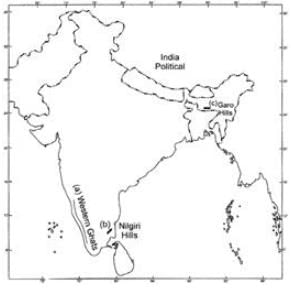
Ques 23: What is the role of philosophers in the French Revolution?
Ans: The revolutionary ideas of philosophers encouraged people to fight for their rights.
(i) Voltaire believed that man's destiny was in his own hands.
(ii) John Locke criticized the divine and absolute rights of the rulers.
(iii) Rousseau put forward the idea of formation of a government based on a social contract between people and their representatives. Men had the right to change their government, if they were not satisfied with it.
(iv) Montesquieu believed that all powers should not be concentrated in one person's hand. They should be divided between the Legislature, the Executive and the Judiciary. The ideas of these philosophers were discussed by common people in salons and coffee houses and inspired them to fight for their rights.
Ques 24: Describe the manner in which the Constituent Assembly worked.
Ans: The Constituent Assembly worked in a systematic open and consensual manner as given below
(i) Initially, some basic principles were decided and agreed upon.
(ii) Then a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr BR Ambedkar prepared a Draft Constitution for discussion.
(iii) Several rounds of thorough discussions were held on the Draft Constitution clause by clause.
(iv) Amendments were proposed. More than two thousand amendments were considered.
(v) Every document presented and every word spoken in the Constituent Assembly has been recorded. It is known as Constituent Assembly Debates. (These debates provide the rationale behind every provision of the Constitution.)
Ques 25: What is land? Suggest any three ways to sustain land.
Ans: Land is the basic natural resource that is required in as a factor or an input in many production activities. Land is a fixed asset it cannot be expanded or produced. Many of human activities depend on land. It is very necessary to be careful in its use. Three ways to sustain land are
(i) Soil is the vital part of land, chemical fertilisers and pesticides reduce its fertility and pollute soil in many ways. So, there should be emphasis on use of bio-compost and eco-friendly methods.
(ii) Some farming practices helps in making land sustainable. These practices includes intensity of cropping, rotation of crops, multiple cropping, etc.
(iii) The modern farming methods should be used carefully and rationally according to scientific standards so that natural resource base that soil provides is saved from further damage.
Ques 26: What is the Mid-day Meal Scheme? Explain its purpose.
Ans: The Mid-day Meal Scheme was started to provide a cooked mid-day meal on every school day with nutritional content of 450 calories, 12 gm proteins and other micro nutrients to all children studying in classes I to VIII in government, local body and government aided schools, etc. The basic purpose of this scheme was to improve enrollment, retention and attendance of the children in school and simultaneously improving nutritional levels among them. This encouraged poor children, belonging to disadvantaged sections, to attend school more regularly and help them concentrate on classroom activities. An additional purpose was to provide nutritional support to children of primary classes in drought affected areas during summer vacation It is the largest school feeding programme in the world covering 10.44 crore children in 12.2 lakh elementary schools across the country. The MDM is one the most successful schemes of Government of India.
Ques 27: Describe any three events that were responsible for the Revolution of 1905. Mention two important effects of the revolution. Or In what ways did the Nazi state seek to establish total control over its people?
Ans: The three events responsible for the Revolution of 1905 were
(i) Russia's defeat in the Russo-Japanese War in 1905 brought all the simmering discontent of the Russian people to the forefront. High prices, scarcity of essential commodities and the national humiliation due to defeat in the war against Japan added to the already existing adverse conditions.
(ii) On a Sunday in 1905, strikes took place all over the country and student walk-outs forced universities to close down. Professionals and middle class workers demand for a Constituent Assembly led to the creation of the Duma. A new form of organization called 'Soviets' developed. All these were the outcome of the incident of 'bloody Sunday'.
(iii) The incident provoked disturbances in practically every part of the country and among every social class. Sections of the army and navy revolted and sympathized with the
Two important effects of the revolution were
(i) In this revolution, a new form of organization called the 'Soviets' developed. These 'Soviets' which began as committees to conduct strikes, later became the instruments of political power.
(ii) The Tsar yielded to political pressure and introduced the October manifesto which granted freedom of speech, press and association and conferred the power to make laws upon an elected body, called the 'Duma.'
Or
After becoming the Chancellor of Germany (1933), Hitler captured all powers. In the following ways the Nazi state seek to establish total control over its people
(i) All political parties and trade unions were banned except the Nazi Party and its affiliates.
(ii) The state established total control over the economy, media, army and judiciary.
(iii) Germany became almost a police state. Special surveillance, security forces, secret state police (Gestapo) were created to control the society.
(iv) The Nazi rule glorified war and chose the path of war as a way out of the economic crisis.
(v) The Nazi rule targeted the Jews as the cause of all miseries and undertook genocidal war against the Jews.
(vi) Hitler introduced a massive programme of militarization to enhance the military power of Germany and to restore her international honour and glory.
Ques 28: Why do you think there is more importance of a Constitution to a democratic country?
Ans: The Constitution of a country is a set of written rules that are accepted by all people of a country. The Constitution has more importance in a democratic form of government because
(i) In a democracy, the government is formed according to the Constitution and also works according to it.
(ii) The Constitution delimits the scope of activity of the various organs of the government. The Constitution specifies who will have the power to take which decisions.
(iii) In a democracy, the Constitution safeguards the rights of the citizens.
(iv) The constitution expresses the aspirations of the people about creating a good society. It constantly goes on growing and evolving according to the needs and aspirations of the people.
Ques 29: How can you say that Palampur is a well-developed village?
Ans: Palampur is well-connected with neighboring villages and towns. Raiganj is a big village, is 3 km from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further to nearest town of Shahpur. Many kind of transport are visible on the road starting from bullock carts, tongas, bogeys loaded with jaggery, wheat and other commodities to vehicles like motorcycles, jeeps, tractors and trucks. It is possible that the opportunities for non-farm activities in the village will increase in the future. It is quite a large village with 450 families. The 80 upper caste families have their houses made of bricks and cement plastering. Most of the house have electric connection. Electricity powers all the tubewells in the fields and is use din various types of small business. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school. There is a primary health, centre run by government an done private dispensary where the sick are treated. The description above shows that Palampur has fairly well-developed system of road, transport, electricity, irrigation, schools and health centres. So, we can say that Palampur is a well-developed village.
Ques 30: Compare the actions of converging and diverging tectonic plates.
Ans: Convergent boundaries occur when two plate slide toward each other to form either a subduction zone or a continental collision. When two tectonic plates converge, the crust is destroyed and recycled back into the interior of the Earth as one plate dives under another. Mountains and volcanoes area often found where plates converge. The Himalayas were formed due to the converging of the Eurasian plate with the Indo-Australian plate. As divergent boundaries, new crust is created as two plates pull away from each other. Oceans are born and grow wider where plates diverge or pull apart. When a diverging boundary occurs on land, a 'rift' will arise and the mass of land will break apart into distinct land masses. A divergent boundary between the North American and Eurasian plates has caused a ridge in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
















