Class 12 Economics Solved Paper (2011 Delhi Set-II) | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Ques 1 : What is positive economics?
Ans: The study of economics based on objective analysis. Most economics today focuses on positive economic. For example, the statement 'rate of inflation at present is 4%? is a positive economic statement.
Ques 2: Explain the conditions determining how many units of a good the consumer will buy at a given price.
Ans:Given the price of a good a consumer decides how many units of the good to buy based on the marginal utility derived from the good and the marginal utility of money for him.
A consumer purchases those many units of good where the marginal utility of a rupee spent on the good becomes equal to the marginal utility of money.
That is where,
Marginal Utility of a Rupee spent on the commodity = Marginal Utility of Money
Marginal Utility of rupee spent on the commodity refers to the utility derived from each additional unit of the rupee spent on the purchase of the good. Algebraically,
Marginal Utility of Rupee = 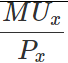
Marginal Utility of money refers to the valuation of a unit of a rupee for a consumer. It is assumed to constant.
Thus, the consumer purchases those many units of the good where,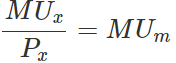
However, if the marginal utility of the rupee spent on the commodity is greater than the marginal utility of money, 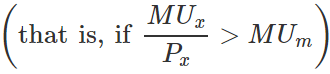 then, the consumer would continue to consume more and more units of the good until the equality is again reached.
then, the consumer would continue to consume more and more units of the good until the equality is again reached.
On the other hand, if the marginal utility of the rupee spent on the good is less than the marginal utility of money, 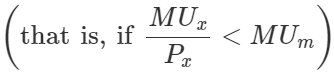
then, the consumer would reduce the consumption of the good until marginal utility becomes equal to the price paid by him.
Ques 3: Explain the concept of Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) by giving an example. What happens to MRS when consumer moves downwards along the indifference curve? Give reasons for your answer.
Ans: Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) refers to the rate at which a consumer is willing to substitute one good for each additional unit of the other good. Algebraically,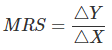
It shows how many units of good Y the consumer is willing to sacrifice to gain one additional unit of good X.
The following schedule explains the concept of MRS
Consumption Combination | Units of good X | Units of good Y | MRSXY |
| P | 2 | 10 | - |
| Q | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| R | 4 | 2 | 3 |
| S | 5 | 1 | 1 |
As the consumer moves from consumption combination P to consumption combination Q, consumption of good X increases from 2 units to 3 units while, the consumption of good Y falls from 10 units to 5 units. That is to gain one additional unit of good X, the consumer sacrifices 5 units of good the consumer sacrifices 5 units of good K Thus, the MRS is 5.
The Indifference Curve depicting the above consumption combination is drawn as follows.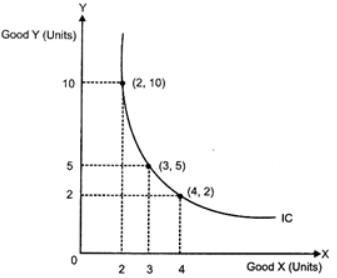
As we move down along the Indifference curve to the rights the Marginal Rate of Substitution falls. This is because as the consumer consumes more and more of one good, the marginal utility of the good falls. On the other hand, the marginal utility of the good which is sacrificed rises. In other words, as we move down along the Indifference Curve, the consumer is willing to sacrifice less and less for each additional unit of the other good consumed. Initially, at point Q the consumer has 2 units of good X and 10 units of good Y. As the consumer moves from point P to point Q, he is willing to sacrifice 5 units of good Y for one additional unit of good X. As compared to this, at point R the consumer has 4 units of good X and only 2 units of good Y. Now, as the consumer has 4 units of good X and only 2 units of good Y. Now, as the consumer moves from R to 5, he is willing to sacrifice only one unit of good Y for one additional unit of good X Thus, as the consumer moves down along the IC, he has more of good X and to consume one additional unit of good X he is willing to sacrifice lesser and lesser units of good Y.
Ques 4: State the components of capital account of balance of payments.
Ans:
Capital Account of Balance of payment (BOP) refers to that account of BOP, which records all the transactions that cause a change in the status of assets and liabilities of the government or any of the residents of a country. The following are the components of capital account of BOP.
(i) Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Portfolio Investment: Foreign Direct Investment refers to the investment in the assets of a foreign country that follows control over the asset. On the contrary, Portfolio Investment refers to the investment in the assets of a foreign country without any control over that asset. Both FDI and portfolio are non-debt creating capital transactions. They cause an inflow of foreign exchange into the country. Thus, they are recorded as positive items in the capital account of BOP.
(ii) Loans and Borrowings: A country takes loans and borrowings from the foreign countries and from the international monetary transactions. Loans and borrowings are debt-increasing capital transactions. They result in inflow of foreign exchange into the country. Hence, they are recorded as positive items in the Capital Account of BOP.
(iii) Banking Capital Transactions: Banking capital transactions refer to the transactions of external financial assets and liabilities of the commercial banks and cooperative banks that operate as authorized dealers in the foreign exchange market.
Ques 5: If National Income is Rs. 50 crore and Saving Rs. 5 crore, find out average propensity to consume. When income rises to Rs. 60 crore and saving to Rs. 9 crore, what will be the average propensity to consume and the marginal propensity to save?
Ans:
Given:
National Income, Y=50
Saving, S=5
We know,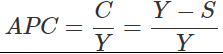
Substituting the values, 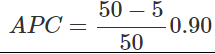
Now given,
Y = 60
S = 9 we know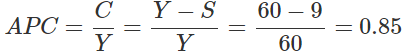
Now,
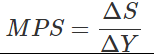
or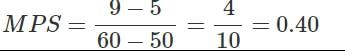
Ques 6: Giving reasons classify the following into intermediate products and final products:
(i) Computers installed in an office.
(ii) Mobile sets purchased by a mobile dealer.
Ans:
(i) Computers installed in an office is a final product as they are used by the office for final consumption purposes and does not undergo any further processing.
(ii) Mobile sets purchased by a mobile dealer are intermediate products as they are purchased by the dealer for resale in the market.
Ques 7:
| Find the gross National Product at market price from the following: | ||
| S. No. | Items | (Rs. Arab) |
| (i) | Opening stock | 50 |
| (ii) | Private final consumption expenditure | 1000 |
| (iii) | Net current transfers to abroad | 5 |
| (iv) | Closing stock | 40 |
| (v) | Net factor income to abroad | (-) 10 |
| (vi) | Government final consumption expenditure | 300 |
| (vii) | Consumption of fixed capital | 30 |
| (viii) | Net imports | 20 |
| (ix) | Net domestic fixed capital forma | 150 |
Ans:
GDPMP=P+G+I+(X−M)
=1000+300+(150+30+40−50)+(−20)
=1300+170−20
= 1450
GDPMP = GDPMP + NFIA
=1450−(−10)
= Rs. 1460
|
4 videos|168 docs
|
















