Class 12 Economics Solved Paper (2011 Delhi Set-III) | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Ques 1: What is normative economics?
Ans: A perspective on economics that incorporates subjectivity within its analyses. It is the study or presentation of what ought to be rather than what actually is. Normative economics deals heavily in value judgments and theoretical scenario. For example, the statement what should an ideal rate of inflation be is a normative economic statement.
Ques 2: What are monotonic preferences? Explain why is an indifference curve (i) Downward sloping from left to right and (ii) Convex.
Ans:
Monotonic preferences refer to those consumer preferences where the consumer prefers those consumption bundles which have at least more of one good and no less of the other good than other consumption bundles.
Suppose, there are two consumption bundles, bundle A (7, 5) and bundle B (3, 5). In this case, consumer preferences would be called monotonic if he prefers bundle A over bundle B. This is because bundled has more units of good 2 (i.e. 7 unit are compared to only 3 units in bundle B) and less of good 1.
(i) An indifference curve is downward sloping from left to right because a consumer cannot simultaneously have more of both the goods. An increase in the quantity of one good is associated with the decrease in the quantity of the other good. This is in accordance with the assumption of monotonic preferences.
(ii) An indifference curve is convex to the origin because of diminishing MRS. As the consumer consumes more and more of one good, the marginal utility of the good falls. On the other hand, the marginal utility of the good which is sacrificed rises. In other words, as the consumer consumes more of one good he is willing to sacrifice less and less of other good for each additional unit of the good. Thus, as we move down the 1C, MRS diminishes. This confirms the convex shape of the indifference curve.
Ques 3: What does balance of payments account show? Name the two parts of the balance of payments account.
Ans: Balance of payment account shows the record of economic transactions of a country with the rest of the world. In other words, it reflects the inflow of foreign exchange into the country and the outflow of foreign exchange from the country.
The two parts of the BOP account are as follows:
(i) Current account: The Current account of BOP is that account which maintains the records of imports of goods and services as well as the record of unilateral transfers.
(ii) Capital account: Capital account of BOP is that account which records all the transactions that cause a change in the status of assets and liabilities of the government or any of the residents of a country.
Ques 4: If national income is Rs. 90crore and consumption expenditure Rs. 81 crore, find out average propensity to save. When income rises to Rs. 100 crore and consumption expenditure to Rs. 88 crore, what will be the marginal propensity to consume and marginal propensity to save.
Ans: Given:
National Income, Y = 90
Consumption Expenditure, C = 81
We know,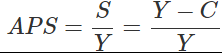
Substituting the values, 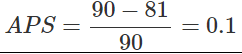
Now given,
Y = 100
C = 88
We know,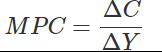
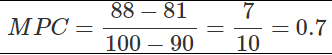
Now,
MPS = 1 - MPC
or, MRS =1−0.7
or, MPS = 0.3
Ques 5:
Giving reasons identify whether the following are final expenditure or intermediate expenditure:
(i) Expenditure on maintenance of an office building.
(ii) Expenditure on improvement of a machine in a factory.
Ans: (i) Expenditure on maintenance of an office building is a final expenditure as it is used for final consumption purposes.
(ii) Expenditure on improvement of a machine in a factory is also a final expenditure as it increases the capital formation.
Ques 6:
| Calculate Net National Product at market Price and Gross National Disposable Income: | ||
| S. No. | Items | (Rs. Arab) |
| (i) | Consumption of fixed capital | 40 |
| (ii) | Change in stocks | (-) 10 |
| (iii) | Net imports | 20 |
| (iv) | Gross domestic fixed capital formation | 100 |
| (v) | Private final consumption expenditure | 800 |
| (vi) | Net current transfer to rest of the world | 5 |
| (vii) | Government final consumption expenditure | 250 |
| (viii) | Net factor income to abroad | 40 |
| (ix) | Net indirect tax | 130 |
Ans:
Expenditure Imports
GDP=P+G+I+(X−M)
=800+250+(100−10)−20
=1050+90−20
=1140−20
= Rs. 1120 Arab
NNPmp = GDPmp - Dep + NFIA
=1120−40−40
=1120−80
= Rs. 1040 Araba
|
4 videos|168 docs
|

















