Class 12 Economics Solved Paper (2012 Outside Delhi Set-III) | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Ques 1: What is Opportunity Cost? Explain with the help of an example.
Ans: The cost of enjoying more of one good in terms of sacrificing the benefit of another good is termed as opportunity cost of the additional unit of the good.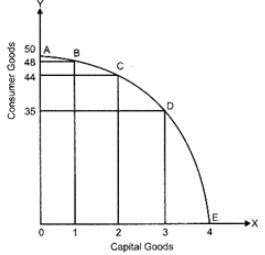
Production Possibility Curve | ||
Production Possibilities | Consumer Goods (units) | Capital Goods (units) |
A | 50 | 0 |
B | 48 | 1 |
C | 44 | 2 |
D | 35 | 3 |
E | 0 | 4 |
In the above figure, as we move downwards along the PPC from left to right (i.e. from A to E), we observe that in order to produce more units of capital goods, the economy must sacrifice some amount of consumer goods. In other words, it reflects the opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of another good. For example, a movement from point B to point C implies that the economy is diverting resources from the production of consumer goods to the production of goods.
In order to produce one additional unit of capital good, the economy is sacrificing four units (i.e. 48−44 units) of consumer goods. Thus, the opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of capital goods is 4 units of consumer goods.
Opporunity Cost from B to C = Amount of Consumer Goods Sacrificed/ Amount of Capital Goods Gained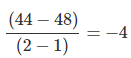
Ques 2: A producer borrows money and starts a business. He himself looks after the business. Identify implicit and explicit costs from this information. Explain.
Ans:
(i) In the given example, the producer is borrowing money to start his business, So the expenses incurred (interest) on money borrowed is explicit cost.
(ii) The producer looks after the business himself, therefore the imputed cost of the efforts of the businessman is implicit cost because of he had worked somewhere else, he would have earned some money.
Ques 3: What is budget set? Explain what can lead to change in budget set.
Ans:
Budget set is the set of all consumption bundles of two goods that a consumer can afford at the same prices of goods which is given. It also shows the income level of consumers. The budget set changes because of changes in the price of the goods and changes in the income of consumer.
Using M as income, P1 as price of good X. P2 as price of good Y. A consumer can buy any bundle which he can get by spending M on good X and good Y in the following manner:
P1X+P2Y ≤M
This means money spent on good X and good Y should not exceed income. If there is any change in the budget set it takes place due to change in money variables fulfilling the basic condition stated above.
Ques 4: A consumer buys 8 units of a good at a price of Rs. 7 per unit. When price rises to Rs. 8 per unit he buys 7 units. Calculate price elasticity of demand through the expenditure approach. Comment upon the shape of demand curve based on this information.**
Ans:
Price (Rs.) | Q (Units) | Total Expenditure (Rs.) |
7 | 8 | 56 |
8 | 7 | 56 |
According to expenditure method, since the total expenditure does not change, the elasticity of demand will be equal −1 . In this case, the demand curve will be a rectangular hyperbola. | ||
Ques 5:
Find out Net Value Added at Factor Cost: | ||
(i) | Price per unit of output (Rs.) | 25 |
(ii) | Output sold (units) | 1,000 |
(iii) | Excise duty (Rs.) | 5,000 |
(iv) | Depreciation (Rs.) | 1,000 |
(v) | Change in stocks (Rs.) | (-) 500 |
(vi) | Intermediate costs (Rs.) | 7,000 |
Ans:
NVA at Factor Cost
= [Price per unit of output × Output sold (units)] + Change in stocks - Intermediate costs - Depreciation - Excise duty
= [(i) + (ii) + (v) - (vi) - (iv) - (iii)
=(25× 1,000)+(−500)−7,000−1,000−5,000
=25,000−13,500=Rs. 11,500
Ques 6: Find Investment from the following:
National Income = Rs. 600
Autonomous Consumption = Rs. 150
Marginal propensity to consume = 0.70
Ans:
Given, National Income (Y) = Rs. 600
Autonomous Consumption (a) = Rs. 150
MPC (b) = 0.70
∴ Y=a+bY+I
or 600=150+0.7×600+I
or 600=150+420+I
or 600−570=I
or I = 30
Ques 7: How should the following be treated while estimating National Income? Give reasons.
(i) Expenditure on education of children by a family.
(ii) Payment of electricity bill by a school.
Ans:
(i) Expenditure on education of children by a family is a final consumption expenditure of households because it is a payment for the services rendered by the school. It will be included.
(ii) Payment of electricity by a school is intermediate cost of the school and therefore is used for finding out value added and not directly included in the estimation of national income.
Ques 8:
Find out (a) Net National Product at Market Price form the following: | ||
(Rs. crore) | ||
(i) | Undistributed profits | 20 |
(ii) | Compensation of employees | 800 |
(iii) | Rent | 300 |
(iv) | Dividend | 100 |
(v) | Royalty | 40 |
(vi) | Net current transfers to abroad | (-) 30 |
(vii) | Corporation tax | 50 |
(viii) | Interest | 400 |
(ix) | Depreciation | 70 |
(x) | Net factor income from abroad | (-) 10 |
(xi) | Net indirect tax | 60 |
Ans:
(a) NNPMP
= Compensation of employees + Rent + Royalty + Undistributed profits + Dividend + Corporation tax + Net factor income earned from abroad + Interest + Net indirect tax
= (ii) + [(iii) + (v)] + [(i) + (iv) + (vii)] + (x) + (viii) + (xi)
=800+(300+40)+(20+100+50)+(−10)+400+60=800+340+170−10+460
= Rs. 1,760 crores
|
4 videos|168 docs
|
















