Class 12 Economics Solved Paper (2012 Delhi Set-II) | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Ques 1: What is 'Marginal Rate of Transformation'? Explain with the help of an example.
Ans: Marginal Rate of Transformation (MRT) refers to the amount of good Y that must be sacrificed in order to gain an additional unit of X, with full and efficient utilization of available resources. It is also known as marginal opportunity cost. MAT indicates the slope of PPC.
Production Possibility Curve | ||
Production Possibilities | Consumer Goods (units) | Capital Goods (units) |
A | 50 | 0 |
B | 48 | 1 |
C | 44 | 2 |
D | 35 | 3 |
E | 0 | 4 |
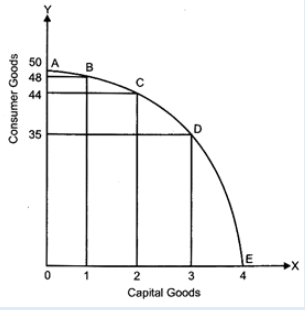
In the above figure, AE represents the PPC for good X and good Y. Suppose, the initial production point in B, where 1 unit of good X and 48 units of good Fare produced. To produce one additional unit of good X, 4 units of good Y must be sacrificed (point C). Thus, at point C, the MRT is 4 units of good Y.
Similarly, at point D, the MRT is 9 units of good Y.
Thus, as we move down the PPC, MRT (or the opportunity cost) increases. This increasing MRT indicates the concave shape of PPC.
Ques 2: A producer borrows money and opens a shop. The shop premises is owned by him. Identify the implicit and explicit costs from this information. Explain.
Ans:
In this case the implicit cost will consist of
(i) Imputed rent of the shop and
(ii) Imputed value of his own services
The explicit cost will consist of interest payment made on the borrowed money. Implicit cost (Imputed cost) refers to cost of the factor that a firm neither hires nor purchases. It is not actually paid by the producers but is included in the cost of production. It is estimated as the difference between the economic profit and accounting profit. On the other hand, explicit costs are those costs that are borne directly by the firm and paid to the factors of production.
Ques 3: Define Marginal Rate of Substitution. Explain why is an indifference curve convex?
Ans: The Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) is defined as the amount of good that a consumer is ready to forego or substitute for an additional unit of good 1. In other words, it represents the cost of good 1 that the consumer is ready to pay in terms of the other good. The MRS between two goods is given by the absolute value of the ratio of change in the consumption of good 2 to the change in the consumption of good 1. That is,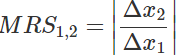
The IC is convex to the origin because of the diminishing MRS. As the consumer consumes more and more of one good, the marginal utility of the good falls. On the other hand, the marginal utility of the good which is sacrificed rises. In other words, the consumer is willing to sacrifice less and less for each additional unit of the other good consumed. Thus, as we move down the IC, MRS diminishes. This suggests the convex shape of indifference curve.
Ques 4:
Calculate Net Value Added at Factor Costs: | ||
S. No. | Items | Amount (in Rs) |
(i) | Consumption of fixed capital (Rs) | 600 |
(ii) | Import duty (Rs) | 400 |
(iii) | Output sold (units) | 2,000 |
(iv) | Price per unit of output (Rs) | 10 |
(v) | Net change in stock (Rs) | (-) 50 |
(vi) | Intermediate cost (Rs) | 10,000 |
(vii) | Subsidy (Rs) | 500 |
Ans:
NVAFC = Sales + Change in Stock - Intermediate Cost - Consumption of Fixed Capital - Net Indirect Taxes Sales = Quantity × Price
=2,000× 10=Rs. 20,000
Net Indirect taxes = Taxes - subsidy
= Import duty - subsidy
=Rs. 400−500=−100
∴NVAFC=20,000+(−50)−10,000−600(−100)
= Rs. 9,450 crore
Ques 5:
Find investment from the following; | |
Items | Amount (Rs.) |
National Income | Rs. 500 |
Autonomous Consumption | Rs. 100 |
Marginal propensity to Consume | 0.75 |
Ans:
At equilibrium
Y=C+I
or, Y=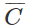 +bY+I where, b = MFC
+bY+I where, b = MFC
500=100+(0.75× 500)+I
500−100−375=I
∴ Investment = Rs. 25
Ques 6: Giving reason explain how should the following be treated in estimating national income:
(i) Payment of bonus by a firm
(ii) Payment of interest on a loan taken by an employee from the employer.
Ans: (i) Payment of bonus by a firm:
Payment of bonus by a firm should be included in the national income because it is a part of the compensation of employees (while estimating National Income by Income Method).
(ii) Payment of interest on loan taken by employee from the employer:
Payment of interest on loan taken by employee from the employer should be included in the national income because it is a part of operating surplus (while estimating National Income by Income Method).
Ques 7:
Find out (a) Net National Product at Market Price: | ||
(Rs. in crore) | ||
(i) | Net current transfers from abroad | (-) 10 |
(ii) | Wages and Salaries | 1,000 |
(iii) | Net factor income to abroad | (-) 20 |
(iv) | Social security contributions by employers | 100 |
(v) | Net Indirect Tax | 80 |
(vi) | Rent | 300 |
(vii) | Consumption of fixed capital | 120 |
(viii) | Corporation Tax | 50 |
(ix) | Dividend | 200 |
(x) | Undistributed profits | 60 |
(xi) | Interest | 400 |
Ans:
(a) Net National Product at Market Price
= Wages and salaries + social security contributions by employers + Rent + Interest + Corporation tax + Dividend + Undistributed profits + Net indirect tax - Net factor income to abroad
= (ii) + (iv) + (vi) + (xi) + (viii) + (ix) + (x) + (v) - (iii)
=1,000+100+300+400+50+200+60+80−(−20)
= Rs. 2,210 crore
|
4 videos|168 docs
|





















