Solved Examples - Linear Equations | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Section - 1
Ques 1: If x = 2, then x2 - 4x + 3 =
Ans: x2 — 4x + 3 =
(2)2 - 4(2) + 3 =
4 - 8 + 3 = -1
Ques 2: If x = 3, what is the value of x + 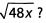
Ans: To evaluate the expression, replace x with (3).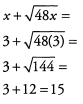
Ques 3: What is the value of 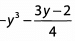 when y= -2 ?
when y= -2 ?
Ans: To evaluate the expression, replace/with (-2) everywhere in the equation. Be extra careful with the negative signs.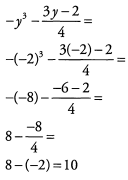
Ques 4: If p = 300c2 - c, what is the value of p when c = 100?
Ans: To find the value of p, we first need to replace c with 100.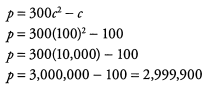
Ques 5: What is the value of y if 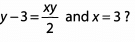
Ans: First we need to replace x with (3) in the equation.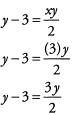
Now, to find the value of y, we need to isolate y on one side of the equation.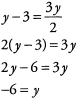
Section - 2
Solve for the variable in the following equations.
Ques 6: 14 - 3x = 2
Ans: 14 -3x = 2
Subtract 14
-3x = -12
Divide by -3
x= 4
Ques 7: 3 (7 -x ) = 4(1.5)
Ans: 3(7 - x ) = 4(1.5)
21 - 3x = 6
- 3x = -15
x= 5
Ques 8: .7x + 13 = 2x - 7
Ans: 7x + 13 = 2x — 7
5x+ 13 = -7
5x= -20
x = -4
Ques 9: 3t3 - 7 = 74
Ans: 3t3 - 7 = 74
3t3 = 81
t3 = 27
t= 3
Ques 10: 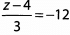
Ans:
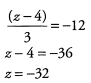
Ques 11: 1,200x + 6,000 =13,200
Ans: 1,200x + 6,000= 13,200
1,200x= 7,200
x = 6
Section - 3
Isolate x in the following equations.
Ques 12: 3x + 2(x + 2) = 2x + 16
Ans: 3x + 2(x+ 2) = 2x + 16
3x + 2x + 4 = 2x + 16
5x + 4 = 2x + 16
3x + 4 = 16
3x = 12
x = 4
Ques 13: 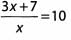
Ans: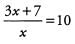
3x + 7 = 10x
7 = 7x
1 = x
Ques 14: 4(-3x - 8) = 8(-x + 9)
Ans: 4 (-3x -8 ) = 8 (-x + 9)
-12 x - 32 = - 8x + 72
-32 = 4 x+ 72
-104 = 4x
-26 = x
Ques 15: 3x+ 7 - 4x + 8 = 2 ( - 2 x - 6)
Ans: 3x + 7 - 4x + 8 = 2 (-2x - 6)
-x + 15 = -4x - 12
3x + 15 = -12
3x = -27
x = -9
Ques 16: 2x(4 - 6) = -2 x + 12
Ans: 2x(4 - 6) = -2x + 12
2x(-2) = -2x + 12
-4x= -2x + 12
- 2x = 12
x = -6
Section - 4
Solve for the values of both variables in each system of equations using substitution. The explanations will use substitution to solve.
Ques 17: 7x - 3y = 5
y= 10
Ans: 7x - 3y = 5,y= 10
7x - 3(10) = 5
7x - 30 = 5
7x = 35
x = 5
Answer: x= 5 ,y= 10
Ques 18: y = 4x+ 10
y = 7 x - 5
Ans: (4x+10) = 7x - 5
10 = 3x - 5
15 = 3x
5 = x
y = 4(5) + 10
y = 30
Answer:x = 5, y = 30
Ques 19: 2h-4k = 0,k = h - 3
Ans: 2 h - 4 ( h - 3 ) = 0
2h - 4h +12 =0
-2h = - 12
h = 6
k= (6) - 3
k = 3
Answer: h = 6, k = 3
Section - 5
Solve for the values of both variables in each system of equations using elimination. The explanations will use elimination to solve.
Ques 20: x -y = 4
2 x + y = 5
Ans: Notice that the first equation has the term -y while the second equation has the term +y . Because these terms will cancel, we do not need to do any manipulations before adding the equations together: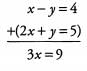
Therefore x = 3 and plugging this back in to the first equation yields: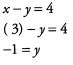
Answer: x = 3 and y = —1
Ques 21: a + b = 8,2a + b = 13
Ans: Both equations have the term +b, so we can eliminate the variable b by subtracting the second equation from the first: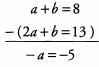
Hence a = 5. Then, we plug this value for a into the first equation to get (5) + b = 8, or b = 3.
Answer: a = 5, b = 3
Section - 6
Solve for the values of both variables in each system of equations. Decide whether to use substitution or elimination. Explanation will use one of the two methods and explain why that is the better solution method.
Ques 22: 5 x + 2 y = 12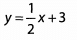
Ans: When one of the two equations is already solved for one of the variables, substitution is almost always the better method. In this particular problem, the second equation is solved for y, so we take the right-hand side of this equation and substitute it for y in the first equation: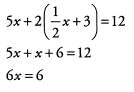
Therefore x = 1. We can now plug this value for x in to either of the original equations to solve for y, but it will be easiest to plug in to the equation that was used for the substitution (after all, it is already solved for y). Hence y = (1/2) x (1) + 3 = 3.5.
Answer: x = 1, y = 3.5
Ques 23: y -1 =x + 2
2y = x + 1
Ans: For this system of equations, either method would be appropriate. Both equations would require some manipulation before we could simply stack-and-add and neither equation is already solved for one of its variables. When neither method seems to have an advantage, pick whichever you like best.
If we use substitution, it is best to solve the first equation for y, giving us y = x + 3, and then substitute this into the second equation: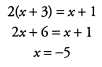
We then plug this into the equation used for the substitution step to get y = (-5) + 3 = -2.
Answer: x = -5 , y = -2
|
82 videos|273 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on Solved Examples - Linear Equations - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What is a linear equation? |  |
| 2. How do you solve a linear equation with one variable? |  |
| 3. What are some real-life applications of linear equations? |  |
| 4. Can a linear equation have more than one solution? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between a linear equation and a linear inequality? |  |
















