CBSE Paper Of Class 10 2017 Science Delhi (SET - 1) - Part 2 | Past Year Papers for Class 10 PDF Download
Ques 17: Soaps and detergents are both types of salts. State the difference between the two. Write the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps. Why do soaps not form lather (foam) with hard water? Mention any two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
Ans: Difference between soap and detergents
| Soap | Detergents |
| Soaps are sodium salts of long chain carboxylic acids. | Detergents are sodium salt of long chain benzene sulphonic acids. |
| The ionic group in soap is -COO-Na+ . | The ionic groups in detergents is SO3-Na+ or SO4-Na+ . |
| Soaps are not useful when water is hard. | Detergent can be used for washing purpose even when water is hard |
| Soaps are biodegradable | Some of the detergents are non-biodegradable. |
| Soaps have relatively weak cleansing action. | Detergents have strong cleansing action. |
The mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water. Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.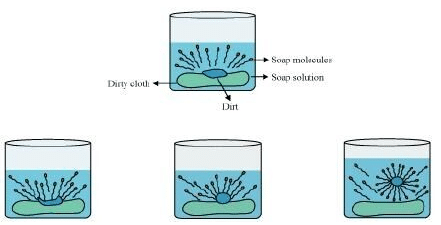 Soaps do not form lather (foam) with hard water
Soaps do not form lather (foam) with hard water
Soaps do not work properly when the water is hard. A soap is a sodium or potassium salt of long chain fatty acids. Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. When soap is added to hard water, calcium and magnesium ions present in water displace sodium or potassium ions from the soap molecules forming an insoluble substance called scum. A lot of soap is wasted in the process.
Problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soap
Detergents being non-biodegradable, they accumulate in the environment causing pollution.
In soil, the presence of detergents leads to pH changes making soil infertile.
The entry of detergents into food chain leads to bio-accumulation in living beings and tends toward serious health issues.
Ques 18: (a) Name the organ that produces sperms as well as secretes a hormone in human males. Name the hormone it secretes and write its functions.
(b) Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where fertilisation occurs.
(c) Explain how the developing embryo gets nourishment inside the mother's body.
Ans: (a) The organ that produces sperms as well as secretes male hormone is testis. The hormone secreted by it is testosterone.
Its important functions are as follows:
It stimulates sperm production.
It stimulates the development of secondary sexual characters in males like growth of facial hairs, low pitch voice, etc.
It involves in the development, maturation and functioning of the male accessory sex organs like vas deferens and seminal vesicles.
(b) In human female reproductive system, the process of fertilisation takes place in one of the fallopian tubes.
(c) The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called placenta. Placenta is a vascular membranous organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall of the mother. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. The placenta draws nourishment and oxygen, which it supplies to the fetus, from the maternal circulation. In turn, the placenta receives carbon dioxide and wastes of fetal metabolism and discharges them into the maternal circulation for disposal.
Ques 19: How do Mendel's experiments show that
(a) traits may be dominant or recessive?
(b) Inheritance of two traits is independent of each other?
Ans: (a) Mendel demonstrated that traits can be either dominant or recessive through his monohybrid cross. He crossed true-breeding tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plants. The seeds formed after fertilisation were grown and the plants that were formed represent the first filial or F1 generation. All the F1 plants obtained were tall.
Then, Mendel self-pollinated the F1 plants and observed that all plants obtained in the F2 generation were not tall. Instead, one-fourth of the F2 plants were short.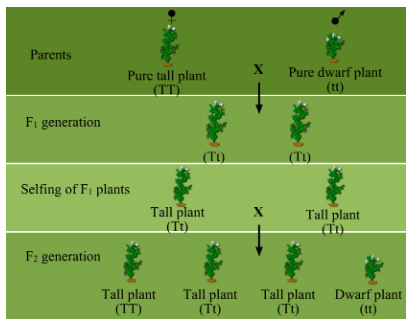 From this experiment, Mendel concluded that the F1 tall plants were not true breeding; they were carrying traits of both short height and tall height. They appeared tall only because the tall trait was dominant over the dwarf trait. This shows that traits may be dominant or recessive.
From this experiment, Mendel concluded that the F1 tall plants were not true breeding; they were carrying traits of both short height and tall height. They appeared tall only because the tall trait was dominant over the dwarf trait. This shows that traits may be dominant or recessive.
(b) Mendel demonstrated that traits are inherited independently through his dihybrid cross. He considered two traits at a time, seed colour and seed shape in which yellow colour (YY) and round shape (RR) are dominant over green colour (yy) and wrinkled shape (rr), respectively.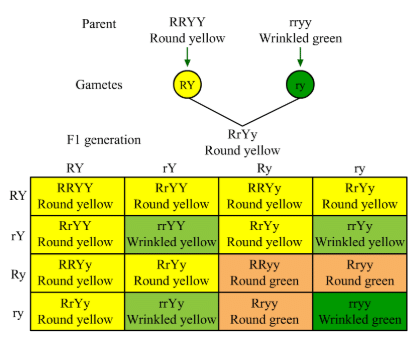 Mendel observed that the F2 progeny of dihybrid cross had a phenotypic ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 and produced nine plants with round yellow seeds, three plants with round green seeds, three plants with wrinkled yellow seeds and one plant with wrinkled green seeds.
Mendel observed that the F2 progeny of dihybrid cross had a phenotypic ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 and produced nine plants with round yellow seeds, three plants with round green seeds, three plants with wrinkled yellow seeds and one plant with wrinkled green seeds.
In this experiment, he found that round yellow and wrinkled green are parental combinations whereas round green and wrinkled yellow are new combinations. In a dihybrid cross between two plants having round yellow (RRYY) and wrinkled green seeds (rryy), four types of gametes (RY, Ry, rY, ry ) are produced. Each of these gametes segregate independently of each other and each has a frequency of 25% of the total gametes produced.
From this experiment, he concluded that when two pairs of traits are combined together in a hybrid, one pair of character segregates independent of the other pair of character. This is known as the law of independent assortment.
Ques 20: Analyze the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
Ans:
S. No. | Object distance u(cm) | Image distance v(cm) |
1 | −90 | +18 |
2 | −60 | +20 |
3 | −30 | +30 |
4 | −20 | +60 |
5 | −18 | +90 |
6 | −10 | +100 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Take an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
Ans: (a) from S.No 3 we can say that the radius of curvature of the lens is 30 cm because when an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a convex lens its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. And, we also know that focal length is half of the radius of curvature. Thus, focal length of the lens is + 15 cm.
(b) S.No: 6 is not correct as the object distance is between focus and pole so for such cases the image formed is always virtual but in this case a real image is forming as the image distance is positive.
(c) Approximate value magnification for object distance - 20 cm and image distance + 60 cm is 3.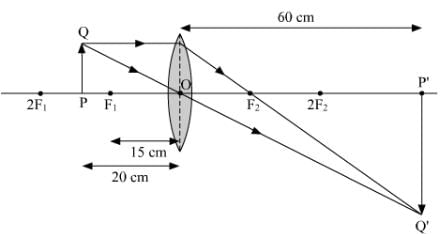
Ques 21: (a) To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
(b) A concave mirror produces three times magnified image on a screen. If the object is placed 20 cm in front of the mirror, how far is the screen from the object.
Ans:
(a) Two light rays whose path of refection are priorly know are:
(i) The incident ray passes through the centre of curvature: In this case, light after reflecting from the concave mirror moves back in the same path. This happens because light is incident perpendicularly on the mirror surface.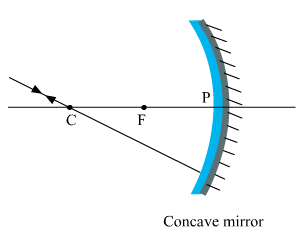 (ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.
(ii) The ray incident obliquely to the principal axis: In this case, the incident ray will be reflected back by the reflecting surface of the concave mirror obliquely and making equal angles with the principal axis.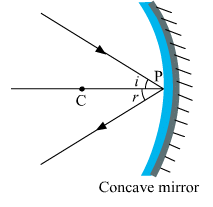 Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below:
Let an object "a candle" is placed between the focus and pole of the concave mirror. Then using above two rays, image of the candle can be located as shown below: 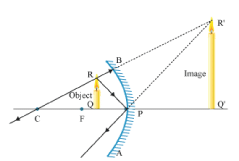 In this case, the image is formed behind the mirror. This image is virtual, erect and magnified.
In this case, the image is formed behind the mirror. This image is virtual, erect and magnified.
(b) Here, Magnification, m = - 3 (As the image is real)
Object distance, u = - 20
cm Image distance, v = ?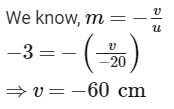 The screen is placed in front of the mirrors at a distance of 60 cm from the pole of the mirror.
The screen is placed in front of the mirrors at a distance of 60 cm from the pole of the mirror.
Thus, the screen is placed 40 cm (= 60 cm - 20 cm) away from the object.
Ques 22: You have four test tubes, A, B, C and D containing sodium carbonate, sodium chloride, lime water and blue litmus solutions respectively. Out of these the material of which test tube/ test tubes would be suitable for the correct test of acetic/ethanoic acid?
(a) only A
(b) A and B
(c) B and C
(d) A and D
Ans: Ethanoic (acetic) acid is an acid, and it will change blue litmus solution to red.
The chemical reaction between ethanoic (acetic) acid and sodium carbonate is:
2 CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2 CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
On passing CO2 gas through lime water, the lime water turn milky. The milky apprearance of lime water is due to the formation of solid calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
Therefore, out of four test tubes A, B, C and D, only A and D test tubes would be suitable for the correct test of acetic/ethanoic acid.
Acetic acid also reacts with lime water to give calcium acetate (CH3COO)2Ca) as a product. But here it is not consider as correct test of acetic/ethanoic acid. Reaction:
2 CH3COOH + Ca(OH)2 → (CH3COO)2Ca + 2 H2O
Hence, the correct answer is option (d).
Ques 23: For demonstrating the preparation of soap in the laboratory which of the following combinations of an oil and a base would be most suitable?
(a) Mustard oil and calcium hydroxide
(b) Castor oil and calcium hydroxide
(c) Turpentine oil and sodium hydroxide
(d) Mustard oil and sodium hydroxide
Ans: Soaps are sodium or potassium salt of long-chain fatty acids. They are prepared by the reaction of a long-chain fatty acid with either NaOH or KOH. This reaction is known as the saponification reaction. Among the given sets of materials, as soap can be prepared by the reaction between sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and turpentine oil (long-chain fatty acid).
Hence, the correct answer is option (c).
Ques 24: A student took four test tubes P, Q, R and S and filled about 8 mL of distilled water in each. After that he dissolved an equal amount of Na2SO4 in P, K2SO4 in Q, CaSO4 in R and MgSO4 in S. On adding an equal amount of soap solution and shaking each test tube well, a good amount of lather will be obtained in the test tubes:
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) P, Q and S
(d) Q, R and S
Ans: Soaps do not form lather with hard water (water containing calcium and magnesium ions). Among the given test tubes, test tubes R and S contain calcium and magnesium ions, respectively. So the addition of soap solution in these will not produce lather.
On the other hand, water present in test tubes P and Q are soft water (containing sodium and potassium ions), so the addition of soap solution in these will produce a good amount of lather.
Hence, the correct answer is option (a).
Ques 25: A student while observing an embryo of a gram seed listed various parts of the embryo as listed below : Testa, Micropyle, Cotyledon, Tegmen, Plumule, Radicle. On examining the list the teacher commented that only three parts are correct. Select these three correct parts :
(a) Cotyledon, Testa, Plumule
(b) Cotyledon, Plumule, Radicle
(c) Cotyledon, Tegmen, Radicle
(d) Cotyledon, Micropyle, Plumule
Ans: The three correct parts are cotyledon, plumule and radicle. Among the given options, testa and tegmen are parts of the seed coat and micropyle is found in ovule. The parts of dicot embryo include radicle, plumule and a pair of cotyledons.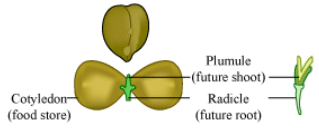 Hence, the correct answer is option (b).
Hence, the correct answer is option (b).
Ques 26: Select the set of homologous organs from the following :
(a) Wings of pigeon and a butterfly
(b) Wings of bat and a pigeon
(c) Forelimbs of cow, a duck and a lizard
(d) Wings of butterfly and a bat
Ans: The wings of pigeon and a butterfly are analogous as they perform similar function, i.e. flying, but they are structurally different from each other. The wings of pigeon are formed of limb bones covered with flesh, skin and feathers, whereas the wings of butterfly are extensions of integuments which is supported with few muscles.
The wings of bat and a pigeon are also analogous. Both are used for flying, but wings of bat are actually skin folds stretched between elongated fingers. The wings of pigeon, on the other hand, are formed of limb bones covered with flesh, skin and feathers.
The forelimbs of cow, a duck and a lizard are homologous organs. Though they perform different functions, yet they are similar in anatomical structure. The wings of butterfly and a bat are also analogous organs. Wings of butterfly are extensions of integuments which is supported with few muscle, whereas wings of bat are actually skin folds stretched between elongated fingers.
Ques 27: Three students A, B and C focused a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine the focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below: Student A : From mirror to the screen Student B : From building to the screen Student C : From building to the mirror Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Ans: A concave mirror always forms the image of a distant object at its focus.
In the given case the distance between the mirror and the screen is equal to the focal length of the mirror. Thus, student A measures the focal length correctly. Hence, the correct answer is the option (a).
Ques 28: In the following diagram the correctly marked angles are :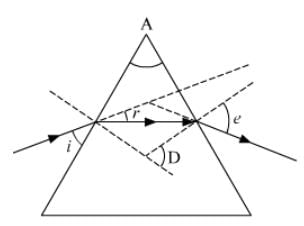 (a)∠A and ∠e
(a)∠A and ∠e
(b) ∠i, ∠A and ∠D
(c) ∠A ∠r and ∠e
(b) ∠A ∠r and ∠D
Ans: The correctly marked angles here are the angle of the prism (A) and the angle of emergent (e). Hence, the correct answer is option (a).
Ques 29: The correct sequencing of angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of refraction and lateral displacement shown in the following diagram by digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 is: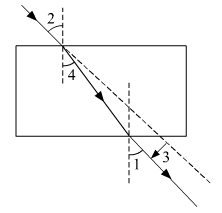 (a) 2, 4, 1, 3
(a) 2, 4, 1, 3
(b) 2, 1, 4, 3
(c) 1, 2, 4, 3
(d) 2, 1, 3, 4
Ans: Angle 2 is the angle of incidence. As, it is formed between the incident ray and the normal.
Angle 1 is the angle of emergence. As, it is formed between the emergent ray with normal.
Angle 4 is the angle of refraction. As, it is formed between the refracted ray and the normal.
3 shows the lateral displacement.
Hence, the correct answer is option (b).
Ques 30: A gas is liberated immediately with a brisk effervescence, when you add acetic acid to sodium hydrogen carbonate powder in a test tube. Name the gas and describe the test that confirms the identity of the gas.
Ans: When acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to the sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) powder in a test tube, then the products obtained are sodium acetate, carbon dioxide and water.
Observations in this reaction are: Brisk effervescence is seen because of CO2 gas escaping out from the reaction mixture. The gas turns lime water milky that confirms the identity of CO2 gas.
Chemical reactions involved: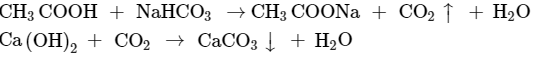
Ques 31: Name the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost. Write the first step from where such a type of reproduction begins. Draw first two stages of this reproduction.
Ans: Binary fission is the type of asexual reproduction in which two individuals are formed from a single parent and the parental identity is lost. This reproduction starts with karyokinesis (division of nucleus).
The first and second stages of this type of reproduction can be depicted as follows: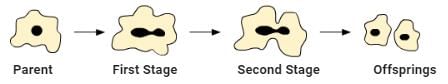
Ques 32: A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
Ans: (a) He move the screen away from the lens to focus the image.
(b) Size of the image increases.
(c) The intensity of image decreases as the flame moves towards the lens.
(d) At approximately 20 cm from the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size.
FAQs on CBSE Paper Of Class 10 2017 Science Delhi (SET - 1) - Part 2 - Past Year Papers for Class 10
| 1. What was the difficulty level of CBSE Class 10 Science Delhi 2017 (SET - 1) exam? |  |
| 2. How many marks were allotted to the CBSE Class 10 Science Delhi 2017 (SET - 1) exam? |  |
| 3. Can you provide an overview of the topics covered in the CBSE Class 10 Science Delhi 2017 (SET - 1) exam? |  |
| 4. How can I prepare effectively for the CBSE Class 10 Science Delhi 2017 (SET - 1) exam? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific tips to score well in the CBSE Class 10 Science Delhi 2017 (SET - 1) exam? |  |
















