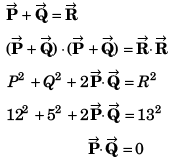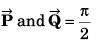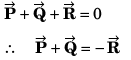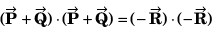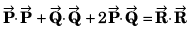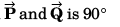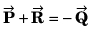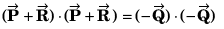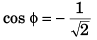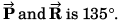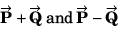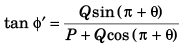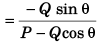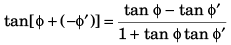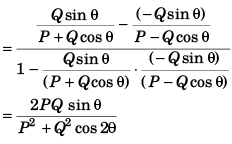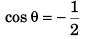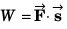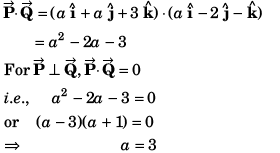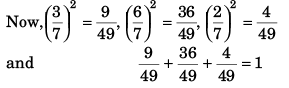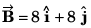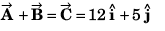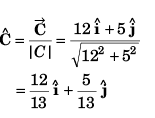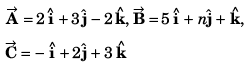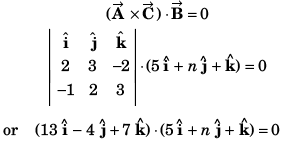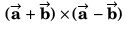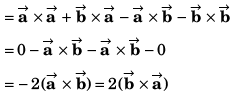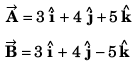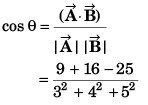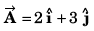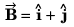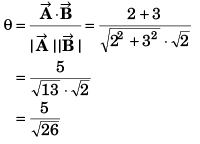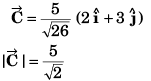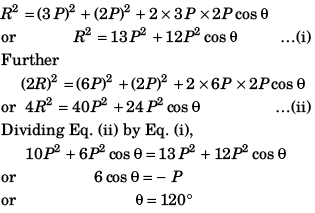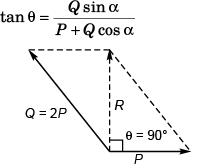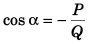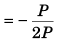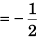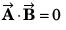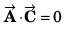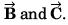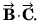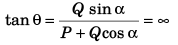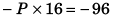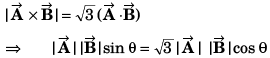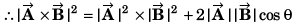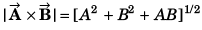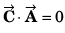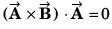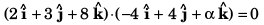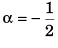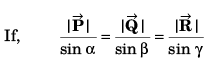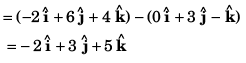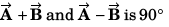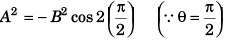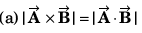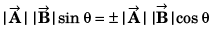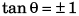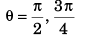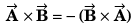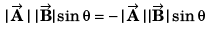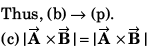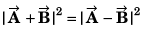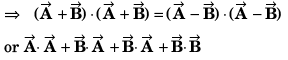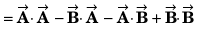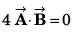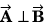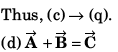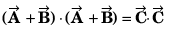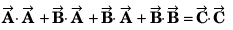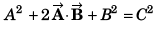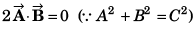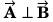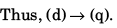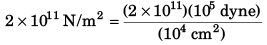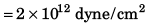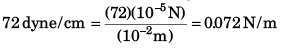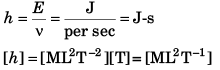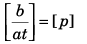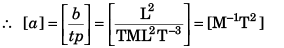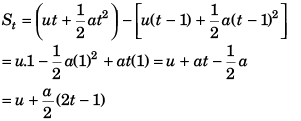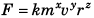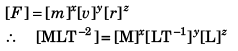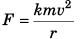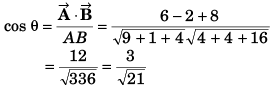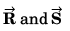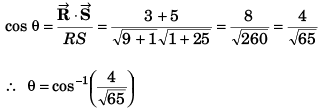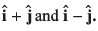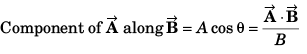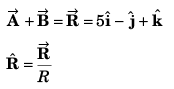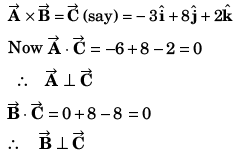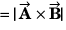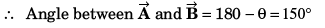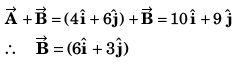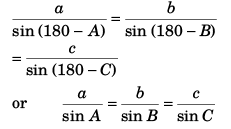DC Pandey Solutions: Units, Dimensions & Vectors - 2 | DC Pandey Solutions for NEET Physics PDF Download
Q31. Which one is a vector quantity?
(a) Time
(b) Temperature
(c) Flux density
(d) Magnetic field intensity
Magnetic field intensity.
Option (d) is correct.Vector Quantity has both Magnitude and Direction
Q32. Given that P = 12,Q = 5 and R =13 also  then the angle between
then the angle between  will be
will be
(a) π
(b) π/2
(c) zero
(d) π/4
∴ Angle between
Option (b) is correct.
Q33. The forces, which meet at one point but their lines of action do not lie in one plane, are called
(a) non-coplanar non-concurrent forces
(b) non-coplanar concurrent forces
(c) coplanar concurrent forces
(d) coplanar non-concurrent forces
non-coplanar concurrent forces
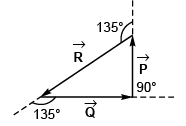
Q34. Given that 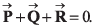 Two out of the three vectors are equal in magnitude. The magnitude of the third vector is √2 times that of the other two. Which of the following can be the angles between these vectors?
Two out of the three vectors are equal in magnitude. The magnitude of the third vector is √2 times that of the other two. Which of the following can be the angles between these vectors?
(a) 90°, 135°, 135°
(b) 45°, 45°, 90°
(c) 30°, 60°, 90°
(d) 45°, 90°, 135°
or
or
or…(i)
Let Q2 = P2 and R = P√2
Thus, Eq. (i) takes the form
P2 + P2 + 2PQcos θ = 2P2
or 2PQcos θ = 0
or cosθ = 0
or θ = 90°
∴ Angle between
∴
or
or P2 + R2 + 2PR cos φ = Q2
or 2PR cos φ = Q2 - P2 - R2
or 2PR cos φ = - R2
or 2P cos φ = - R
or 2P cos φ = - P√2
or
∴ φ = 135°∴ Angle between
Option (a) is correct.
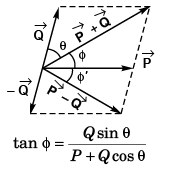
Q35. The angle between 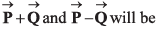
(a) 90°
(b) between 0° and 180°
(c) 180° only
(d) None of these
Angle (φ) between
Angle φ between
This implies that angle betweenand
will vary from 0 to π.
Option (b) is correct.
Q36. Two vectors of equal magnitude have a resultant equal to either of them, then the angle between them will be
(a) 30°
(b) 120°
(c) 60°
(d) 45°
R2 = P2 + Q2 + 2PQcosθ
for R = P = Q
P2 = P2 + P2 + 2PPcos θ
or
or θ = 120°
Option (b) is correct.
Q37. A force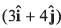 newton acts on a body and displaces it by
newton acts on a body and displaces it by 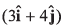 metre. The work done by the force is
metre. The work done by the force is
(a) 5 J
(b) 25 J
(c) 10 J
(d) 30 J
= 25 J
Option (b) is correct.
Q38. If the vectors 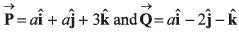 are perpendicular to each other then the positive value of a is
are perpendicular to each other then the positive value of a is
(a) zero
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Other value is - ive.
Option (d) is correct.
Q39. The angles which the vector 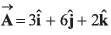 makes with the co-ordinate axes are
makes with the co-ordinate axes are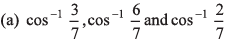
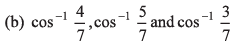
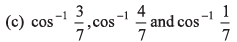
(d) none of the above
If a vector makes angles α, β and γ with the co-ordinate axes, then
cos2 α + cos2 β + cos2 γ = 1
∴ Option (a) is correct.
Q40. Unit vector parallel to the resultant of vectors 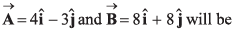
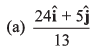
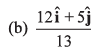
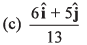
(d) None of these
and
∴
Option (b) is correct.
Q41. The value of n so that vectors 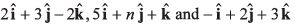 may be coplanar, will be
may be coplanar, will be
(a) 18
(b) 28
(c) 9
(d) 36
∴ Vectorswill be coplanar if their scalar triple product is zero i.e.,
or 65 - 4n + 7 = 0
or n = 18
Option (a) is correct.
Q42. Which one of the following statement is false?
(a) A vector has only magnitude, whereas a scalar has both magnitude and direction
(b) Distance is a scalar quantity but displacement is a vector quantity
(c) Momentum, force, torque are vector quantities
(d) Mass, speed and energy are scalar quantities
A vector has only magnitude, whereas a scalar has both magnitude and direction
Q43. are two vectors then the value of
are two vectors then the value of 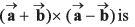
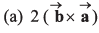
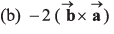
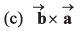
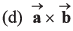
Option (a) is correct.
Q44. The angle between the two vectors 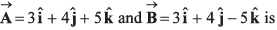
(a) 60°
(b) 0°
(c) 90°
(d) None of these
= 0
⇒ θ = 90°
Option (c) is correct.
Q45. Maximum and minimum values of the resultant of two forces acting at a point are 7 N and 3 N respectively. The smaller force will be equal to
(a) 5 N
(b) 4 N
(c) 2 N
(d) 1 N
A + B = 7
A - B = 3
∴ B = 2 N
Option (c) is correct.
Q46. The component of vector 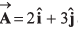 along the vector
along the vector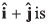
(a) 5/√2
(b) 10/√2
(c) 5 √2
(d) 5
Angle between
and
Component of
Option (a) is correct.
Q47. The resultant of two forces 3P and 2P is R. If the first force is doubled then the resultant is also doubled. The angle between the two forces is
(a) 60°
(b) 120°
(c) 70°
(d) 180°
Option (b) is correct.
Q48. The resultant of two forces, one double the other in magnitude, is perpendicular to the smaller of the two forces. The angle between the two forces is
(a) 120°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 150°
As θ = 90°, tan α = ∞
∴ P + Q cos α = 0
i.e.,
∴ α = 120°
Option (a) is correct.
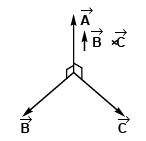
Q49. Three vectors satisfy the relation 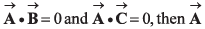 is parallel to
is parallel to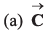
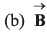
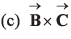
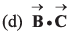
⇒…(i)
⇒…(ii)
From Eq. (i) and Eq. (ii), we conclude thatis perpendicular to the plane containing
This implies thatis perpendicular to
Option (c) is correct.
Q50. The sum of two forces at a point is 16 N. If their resultant is normal to the smaller force and has a magnitude of 8 N. Then two forces are
(a) 6N, 10N
(b) 8 N, 8 N
(c) 4 N, 12N
(d) 2 N, 14N
P2 + Q2 + 2PQ cos α = R2
or P2 + Q2 + 2PQ cos α = 82
or P2 + Q2 + 2PQ + 2PQ cos α - 2PQ = 64
or (P + Q)2 + 2 PQ (cos α - 1) = 64
or (16)2 + 2 PQ (cos α - 1) = 64
or 2 PQ (cos α - 1) = - 192
or PQ cos α - PQ = - 96 …(i)
(as θ = 90°)
∴ P + Q cos α = 0
Qcos α = -P …(ii)
Using Eq. (ii) and Eq. (i),
P (- P) - PQ = - 96or - P (P + Q) = - 96
or
P = + 6 N
∴ Q = 10 N
Option (a) is correct.
Q51.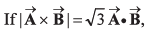 then the value of
then the value of 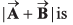
(a) (A2 + B2 + AB)1/2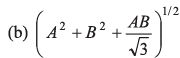
(c) (A + B)
⇒ tan θ = √3
⇒ θ = 60°
= A2 + B2 + 2AB cos 60°
= A2 + B2 + AB
Q52. If the angle between the vectors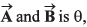 the value of the product
the value of the product 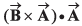 is equal to
is equal to
(a) BA2 cos θ
(b) BA2 sin θ
(c) BA2 sin θ cos θ
(d) zero
is perpendicular to both
∴
or
Option (d) is correct.
Q53. If a vector 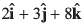 is perpendicular to the vector
is perpendicular to the vector 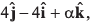 then the value of α is
then the value of α is
(a) -1
(b) 1/2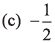
(d) 1
⇒ - 8 + 12 + 8a = 0
∴
Option (c) is correct.
Q54. Minimum number of vectors of unequal magnitudes which can give zero resultant are
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) more than four
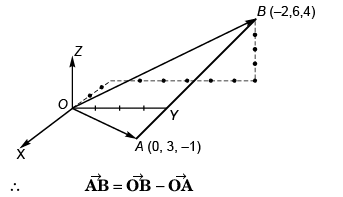
Q55. The (x, y, z) coordinates of two points A and B are given respectively as (0, 3, - 1) and (- 2, 6, 4). The displacement vector from A to B is given by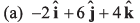
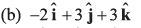
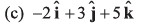
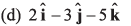
Option (c) is correct.
Q56. The sum of two vectors 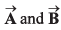 is at right angles to their difference. Then
is at right angles to their difference. Then
(a) A = B
(b) A = 2B
(c) B = 2A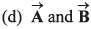 have the same direction
have the same direction
Using answer to questions no. 35, as angle between
A2 + B2 cos 2θ = 0
or A2 = - B2 cos 2θ
or
or A2 = - B2 cos π
or A2 = B2
⇒ A = B
Option (a) is correct.
Match the Columns
Q1. Column-I shows some vector equations. Match column I with the value of the angle between A and B given in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
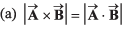 | (p) zero |
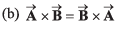 | (q) π/2 |
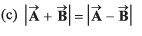 | (r) π/4 |
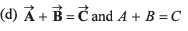 | (s) 3π/4 |
or
or
⇒
Thus, (a) → (r) (s).
(given)
or
or
or sin θ = - sin θ
or 2 sin θ = 0
⇒ θ = 0 rad
or
or
⇒
or
or
or
or
⇒
Section-II
Subjective Questions
Q1. Young’s modulus of steel is 2.0 x 1011 N / m2. Express it in dyne/cm2.
Q2. Surface tension of water in the CGS system is 72 dynes/cm . What is its value in SI units
Q3. In the expression y = a sin (ωt + θ), y is the displacement and t is the time. Write the dim ensions of a, ω and θ.
[a] = [y] = [L]
Sol: [wt] = [M0L0 T0] ∴ [ω] = [T-1][θ] = [M0L0 T0]
Q4. The relation between the energy E and the frequency v of a photon is expressed by the equation E = hv, where h is Planck’s constant. Write down the SI units of h and its dimensions.
Q5. Write the dimensions of a and b in the relation.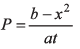
where P is power, x is distance and t is time.
[b] = [x2] = [L2]
Q6. Check the correctness of the relation 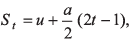 where u is initial velocity, a is acceleration and St is the displacement of by the body in tth second.
where u is initial velocity, a is acceleration and St is the displacement of by the body in tth second.
Here t in second. Hence the given equation seems to be dimensionally incorrect. But it is correct because 1 is hidden.
Q7. Let x and a stand for distance. 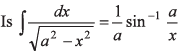 dim ensionally correct?
dim ensionally correct?
LHS is dimensionless. While RHS has the dimensions [L-1].
Q8. In the equation 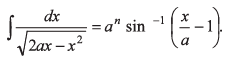
Find the value of n.
LHS is dimensionless. Hence n = 0.
Q9. Show dimensionally that the expression, 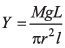 is dimensionally correct, where Y is Young’s modulus of the material of wire, L is length of wire, Mg is the weight applied on the wire and l is the increase in the length of the wire.
is dimensionally correct, where Y is Young’s modulus of the material of wire, L is length of wire, Mg is the weight applied on the wire and l is the increase in the length of the wire.
Just write the dimension of different physical quantities.
Q10. The energy E of an oscillating body in simple harmonic motion depends on its mass m, frequency n and amplitude a. Using the method of dimensional analysis find the relation between E, m, n and a.
E = kmxnyaz.
Here k = a dimensionless constant
∴ [E] = [m]x [n]y [a]z
∴ [ML2 T–2] = [M]x[T–1]y[L]z
∴ x = 1, y = 2 and z = 2
Q11. The centripetal force F acting on a particle moving uniformly in a circle may depend upon mass (m), velocity (v) and radius r of the circle. Derive the formula for F using the method of dimensions.
(k = a dimensionless constant)
Solving we get,
x = 1, y = 2 and z = - 1
∴
Q12. Taking force F, length L and time T to be the fundamental quantities, find the dimensions of (a) density, (b) pressure, (c) momentum and (d) energy.
[d] = [F]x [L]y [T]z
∴ [ML–3] = [MLT–2]x[L]y[T]z
Equating the powers we get,
x = 1, y = - 4, z = 2
∴ [ d] = [FL–4 T2]
Similarly other parts can be solved.
Vectors
Q13. Find the cosine of the angle between the vectors 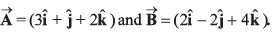
Q14. Obtain the angle between 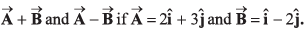
Angle between
Q15. Under what conditions will the vectors 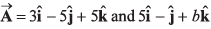 be perpendicular to each other ?
be perpendicular to each other ?
Their dot product should be zero.
Q16. Deduce the condition for the vectors 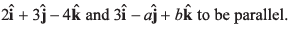
Ratio of coefficients of
should be same.
Q17. Three vectors which are coplanar with respect to a certain rectangular co-ordinate system are given by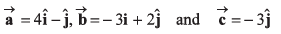
Find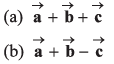
(c) Find the angle between 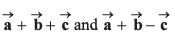
No solution is required.
Q18. Find the components of a vector 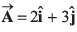 along the directions of
along the directions of
Q19. If vectors 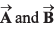 be respectively equal to
be respectively equal to 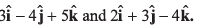 Find the unit vector parallel to
Find the unit vector parallel to 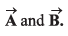
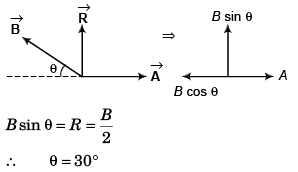
Q20. If two vectors are 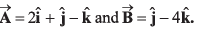 By calculation, prove that
By calculation, prove that
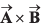 is perpendicular to both
is perpendicular to both 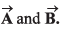
Q21. Find the area of the parallelogram whose sides are represented by
Area of parallelogram
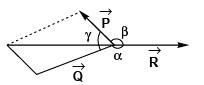
Q22. The resultant of two vectors 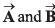 is at right angles to
is at right angles to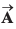 and its magnitude is half of
and its magnitude is half of 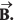 Find the angle between
Find the angle between 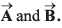
Q23. The x and y-components of vector 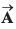 are 4 m and 6 m respectively. The x and y-components of vector
are 4 m and 6 m respectively. The x and y-components of vector 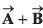 are 10 m and 9 m respectively. Calculate for the vector
are 10 m and 9 m respectively. Calculate for the vector 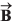 the following
the following
(a) its x andy-components
(b) its length
(c) the angle it makes with x-axis
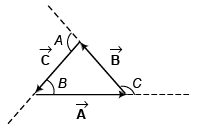
Q24. Prove by the method of vectors that in a triangle 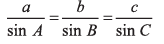
Applying sine law, we have
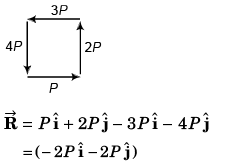
Q25. Four forces of magnitude P, 2P, 3P and AP act along the four sides of a square ABCDm cyclic order. Use the vector method to find the resultant force.
Q26. 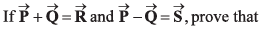
R2 + S2 = 2(P2 + Q2)
R2 = P2 + Q2 + 2PQ cos θ
S2 = P2 + Q2 - 2PQ cos θ
∴ R2 + S2 = 2 (P2 + Q2)
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Units, Dimensions & Vectors - 2 - DC Pandey Solutions for NEET Physics
| 1. What are the units and dimensions of physical quantities? |  |
| 2. How do you convert between units of physical quantities? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of vectors in physics? |  |
| 4. How do you add and subtract vectors? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of vector products? |  |