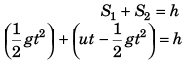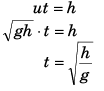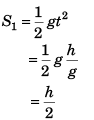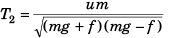JEE Corner
Assertion and Reason
Ques 1: Assertion: Velocity and acceleration of a particle are given as,
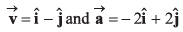
This is a two dimensional motion with constant acceleration.
Reason: Velocity and acceleration are two constant vectors.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Sol: As acceleration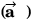 is just opposite to velocity
is just opposite to velocity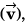 the particle will move along a straight line.
the particle will move along a straight line.
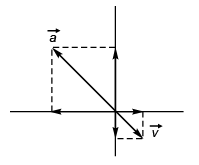
∴ Assertion is false (motion being one dimensional).
Reason is true as do not depend upon time.
do not depend upon time.
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 2: Assertion: Displacement-time graph is a parabola corresponding to straight line velocity-time graph.
Reason : If v = u + at, then 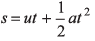
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Sol: Displacement-time graph is parabolic only when the slope of the straight line velocity-time graph is not zero i.e., acceleration is not zero.
If acceleration is zero.
s = ut
i.e., the displacement-time graph will be a straight line.
∴ Assertion is wrong.
Reason: v = u + at
i.e., 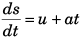
or ∫ ds = ∫ (u + at) dt
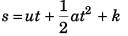
If at t = 0, s = 0
The value of k will be zero.
∴ 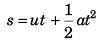
Thus, reason is true.
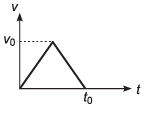
Ques 3: Assertion: In v-t graph shown is figure, average velocity in time interval from 0 t0 to depends only on v0. It is independent of t0.
Reason: In the given time interval average velocity is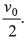
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion
Sol: Displacement in time t0 = Area under v-t graph
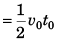
∴ average velocity in time interval t0
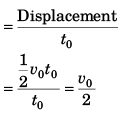
∴ Assertion is true.
Reason is also true as proved.
Ques 4: Assertion: We know the relation 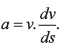 Therefore, if velocity of a particle is zero, then acceleration is also zero.
Therefore, if velocity of a particle is zero, then acceleration is also zero.
Reason: In the above equation, a is the instantaneous acceleration.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true
Sol: Acceleration (a) will be zero only when velocity does not change with time
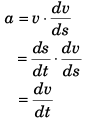
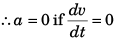
or v is constant with time.
Thus, Assertion is wrong.
Reason is correct as a is equal to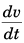 which is instantaneous acceleration.
which is instantaneous acceleration.
Ques 5: Assertion: Speed of a particle may decrease, even if acceleration is increasing.
Reason: This will happen if acceleration is positive.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
Sol: If acceleration is in the opposite direction to the velocity of the particle the speed will decrease.
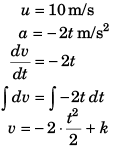
At t = 0 s, velocity = + 10 m/s
∴ k = + 10 m/s
∴ v = - t2 + 10
Time (t)
| v m/s
| speed (m/s)
|
| 15 | 9 | 9 |
| 25 | 6 | 6 |
| 35 | 1 | 1 |
∴ Assertion is true.
Reason is false as when acceleration is positive the speed will increase.
Ques 6: Assertion: Starting from rest with zero acceleration if acceleration of particle increases at a constant rate of 2 ms-3 then velocity should increase at constant rate of 1 ms-2.
Reason: For the given condition.
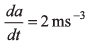 ∴ a = 2t.
∴ a = 2t.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Sol: 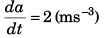 (given)
(given)
[This implies that reason is true]
∫ da = ∫ 2 dt
a = 2t + C
If at t = 0, a = 0
we have C = 0
∴ a = 2t
or 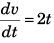
∴ Assertion is false.
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 7: Assertion: Average velocity can’t be zero in case of uniform acceleration.
Reason: For average velocity to be zero, velocity should not remain constant.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true
Sol: If initially particle velocity is - ive and acceleration is uniform and + ive, the particle will return to its initial position after a certain time interval. In this time interval the average velocity will be zero as net displacement will be zero.
∴ Assertion is false.
For average velocity to zero, the particle must return to its initial position (as discussed above) and for this velocity can’t remain constant.
∴ Reason is true.
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 8: Assertion: In displacement-time graph of a particle as shown in figure. Velocity of particle changes its direction at point A.
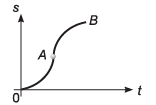
Reason: Sign of slope of s-t graph decides the direction of velocity.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Sol: From O to A velocity of the particle is increasing while from A to B it is decreasing without change in direction as for the velocity to change its direction the slope of s-t graph must be negative.
∴ Assertion is false.
If the slope of s-t graph is + ive the velocity of the particle will be + ive while if it is - ive the velocity of the particle will also be - ive.
∴ Reason is true.
Ques 9: Assertion: Displacement-time equation of two particles moving in a straight line are, S1 = 2t - 4t2 and s2 = - 2t + At2. Relative velocity between the two will go on increasing.
Reason: If velocity and acceleration are of same sign then speed will increase.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true
Sol: S1 = 2t - 4t2
and S2 = - 2t + 4t2
⇒ displacement of particle 2 w.r.t. 1.
S21 = S2 - S1
= (- 2t + 4t2) - (2t - 4t2)
= - 4t + 8t2
Time t
| Relative Displacement
|
0 s
| 0 m
|
1 s
| 4 m
|
2 s
| 24 m
|
3 s
| 60 m
|
As relative displacement is increasing the relative velocity would also be increasing.
∴ Assertion is false.
Reason is true.
Ques 10: Assertion: Acceleration of a moving particle can change its direction without any change in direction of velocity.
Reason: If the direction of change in velocity vector changes, the direction of acceleration vector also changes.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Sol: If v = u + (- a) t [acceleration being made - ive]
Velocity (v) of the particle will be zero
at t = u/a.
Thus, for 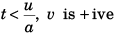
i.e., the acceleration can change its direction without change in direction of velocity.
∴ Assertion is true.
If ΔV changes sign say from + ive to - ive, the acceleration which equals ΔV/Δt
will also change sign from + ive to - ive.
∴ Reason is true but it is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Ques 11: Assertion: A body is dropped from height h and another body is thrown vertically upwards with a speed 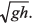 They meet at height h/2.
They meet at height h/2.
Reason: The time taken by both the blocks in reaching the height h/2 is same.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion
Sol: At time t when the two are at the same height.
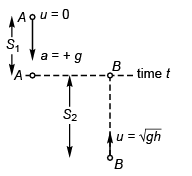
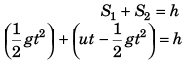
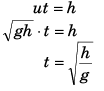
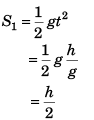
∴ Assertion is true.
Reason is also true as assertion is based on this.
Ques 12: Assertion: Two bodies of unequal masses m1 and m2 are dropped from the same height. If the resistance offered by air to the motion of both bodies is the same, the bodies will reach the earth at the same time.
Reason: For equal air resistance, acceleration of fall of masses m1 and m2 will be different.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) If Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
(d) If Assertion is false but the Reason is true.
Ans: If Assertion is false but the Reason is true
Sol:
While going up:
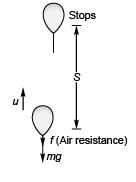
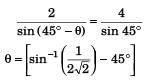
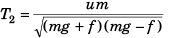
Now, if masses of the bodies are different, the value of T2 (time to reach earth) will be different if f (air resistance) is same.
Thus, Assertion is false further Reason is correct as explained above.
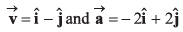
 is just opposite to velocity
is just opposite to velocity the particle will move along a straight line.
the particle will move along a straight line.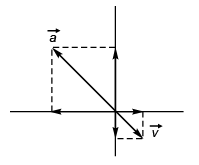
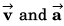 do not depend upon time.
do not depend upon time.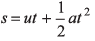
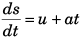
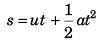
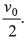

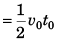

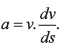 Therefore, if velocity of a particle is zero, then acceleration is also zero.
Therefore, if velocity of a particle is zero, then acceleration is also zero.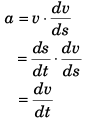
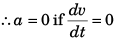
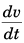 which is instantaneous acceleration.
which is instantaneous acceleration.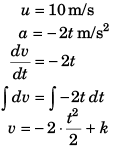
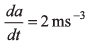 ∴ a = 2t.
∴ a = 2t.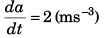 (given)
(given)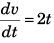

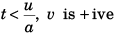
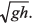 They meet at height h/2.
They meet at height h/2.