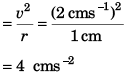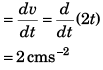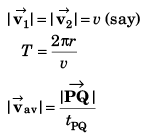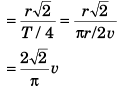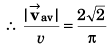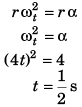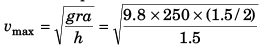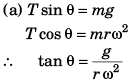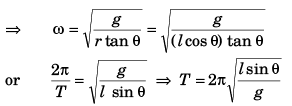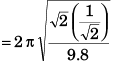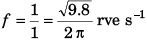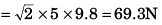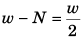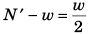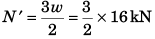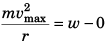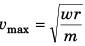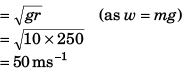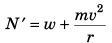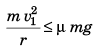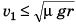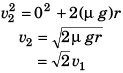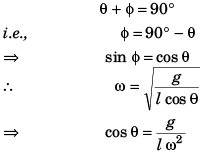DC Pandey Solutions: Circular Motion- 1 | DC Pandey Solutions for NEET Physics PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 7.1
Q.1. Is the acceleration of a particle in uniform circular motion constant or variable?
Ans. Variable
In uniform circular motion the magnitude of acceleration
does not changewhile its direction (being always towards the centre of the circular path) changes.
Q.2. Is it necessary to express all angles in radian while using the equation ω = ω0 + αt?
Ans. No
If ω0 and ω are in rad s-1 the value of a must be in rad s-2. But, if ω0 and ω are in degree s-1 the value of a must also be in degree s-2. Thus, it is not necessary to express all angles in radian. One way change rad into degree using π rad = 180°.
Q.3. Which of the following quantities may remain constant during the motion of an object along a curved path?
(i) Velocity
(ii) Speed
(iii) Acceleration
(iv ) Magnitude of acceleration
Ans. speed, acceleration, the magnitude of acceleration.
During motion of an object along a curved path the speed and magnitude of its radial acceleration may remain constant. Due to change in direction of motion the velocity of the object will change even if its speed is constant. Further, the acceleration will also change even if the speed is constant.
Q.4. A particle moves in a circle of radius 1.0 cm with a speed given by v = 2 t where v is in cm/s and t in seconds.
(a ) Find the radial acceleration of the particle at t = 1 s.
(b) Find the tangential acceleration at t = 1 s.
(c) Find the magnitude of net acceleration at t = 1 s.
Ans. (a) 4.0 cms-2 (b) 2.0 cms-2 (c) 2√5 cms-2
(i) Radial acceleration (αc)
(ii) Tangential acceleration (αT )
(iii) Magnitude of net acceleration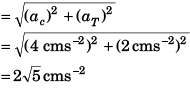
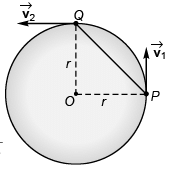
Q.5. A particle is moving with a constant speed in a circular path. Find the ratio of average velocity to its instantaneous velocity when the particle describes an angle 
Ans. 
Q.6. A particle is moving with a constant angular acceleration of 4 rad/s2 in a circular path. At time t =0, particle was at rest. Find the time at which the magnitudes of centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration are equal.
Ans: 1/2 s
ωt = 0 + 4t
Centripetal acceleration = tangential acceleration
Introductory Exercise 7.2
Q.1. Is a body in uniform circular motion in equilibrium?
Ans. In uniform circular motion of a body the body is never in equilibrium as only one force (centripetal) acts on the body which forces the perform circular motion.
Q.2. Find the maximum speed at which a truck can safely travel without toppling over, on a curve of radius 250 m. The height of the centre of gravity of the truck above the ground is 1.5 m and the distance between the wheels is 1.5 m, the truck being horizontal.
Ans.
= 35 ms-1
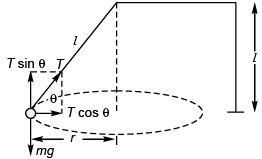
Q.3. (a) How many revolutions per minute must the apparatus shown in figure make about a vertical axis so that the cord makes an angle of 45° with the vertical?
(b) What is the tension in the cord then. Given, l = √2 m, a = 20 cm and m = 5.0 kg?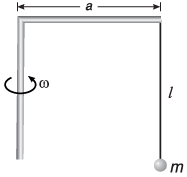
Ans.
∴
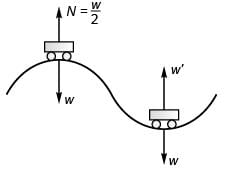
Q.4. A car moves at a constant speed on a straight but hilly road. One section has a crest and dip of the same 250 m radius.
(a) As the car passes over the crest the normal force on the car is one half the 16 kN weight of the car. What will be the normal force on the car as its passes through the bottom of the dip?
(b) What is the greatest speed at which the car can move without leaving the road at the top of the hill?
(c) Moving at a speed found in part (b) what will be the normal force on the car as it moves through the bottom of the dip? (Take g = 10 m/s2)
Ans.
(a) At rest :Required CPF =
⇒...(i)
At dip :
Required CPF = N' - w...(ii)
Comparing Eqs. (i) and (ii),
∴
= 24 kN
(b) At crest on increasing the speed (v), the value of N will decrease and for maximum value of v the of N will be just zero.
Thus,
⇒
(c) At dip :
= w + mg
= 2w = 32 kN
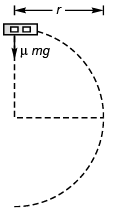
Q.5. A car driver going at speed v suddenly finds a wide wall at a distance r. Should he apply brakes or turn the car in a circle of radius r to avoid hitting the wall.
Ans. Case I. If the driver turns the vehicle
[where v1 = maximum speed of vehicle]
⇒
Case II. If the driver tries to stop the vehicle by applying breaks.
Maximum retardation = μg
As v2 > v1, driver should apply breaks to stop the vehicle rather than taking turn.
Q.6. Show that the angle made by the string with the vertical in a conical pendulum is given by cos θ = 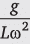 where L is the length of the string and ω is the angular speed.
where L is the length of the string and ω is the angular speed.
Ans. In the answer to question 3(a) if we replace θ by Φ
If θ is the angle made by the string with the vertical
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Circular Motion- 1 - DC Pandey Solutions for NEET Physics
| 1. What is circular motion? |  |
| 2. How is circular motion related to NEET exam? |  |
| 3. What is centripetal force and how is it related to circular motion? |  |
| 4. How can I calculate the centripetal force in circular motion? |  |
| 5. Are there any real-life examples of circular motion? |  |