Classification of Elements | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
- Element: It is the simplest form of matter that cannot split further into simpler substance by any kind of physical or chemical methods. It is divided into 3 types.
1. metals 2. non-metals 3. metalloids.
Currently, there are 114 elements known to us.
- Periodicity: Regular repetition of similar periodic properties at regular intervals is said to be periodicity.
- Metallic character : Metallic character increases as we go down the group & decreases as we move across left to right in the period
Reactivity : Reactivity increases as we go down the group.
Why we need to classify elements?
In 1800, only 31 elements were known.
By 1865, the number of identified elements had more than doubled to 63.
At present 114 elements are known.
Efforts to synthesise new elements are continuing. With such a large number of elements it is very difficult to study individually the chemistry of all these elements and their innumerable compounds individually.
To ease out this problem, scientists searched for a systematic way to organise their knowledge by classifying the elements.
History Of Periodic classification:
Dobereiner Triad rule:
J.W. Dorbereiner pointed out that within a group of three elements having similar chemical and physical properties,
the atomic weight of the middle element is the mean of the other two. Some examples of such triads are given
below. He also pointed out the triad - iron, cobalt and nickel in which the atomic weights of the elements are
almost the same.
Some representative triads of Dobereiner:
Triad Li N a K Ca Sr Ba S Se Te Cl Br I
Atomic weight 7 23 39 40 88 137 32 80 128 35.5 80 127
Mean value 23 88.5 80 81.25
Other example. (K, Rb, Cs), (P, As, Sb) (H, F, Cl) (Sc, Y, La).
Though it was the first successful attempt to rationalise the problem, it could not be generalised or extended.
Drawback or Limitation : All the known elements could not be arranged as triads.
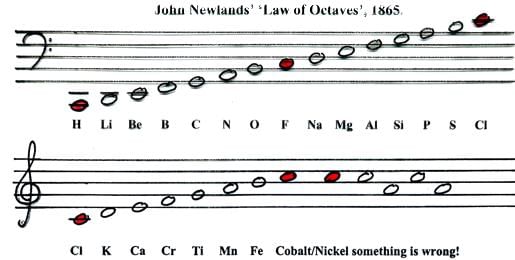
Newland's Octet rule:
- The English chemist, John Alexander Newlands in 1865 profounded the Law of Octaves. He arranged the elements in increasing order of their atomic weights and noted that every eighth element has properties similar to the first element. This relationship was just like every eighth note that resembles the first in octaves of music .
Mendeleev's Periodic Table:
(a) Mendeleef's periodic law : The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function
of their atomic weight
(b) Characteristic of Mendeleef's periodic table :
(i) It is based on atomic weight
(ii) 63 elements were known, noble gases were not discovered.
(iii) He was the first scientist to classify the elements in a systamatic manner i.e. in horizontal rows and in
vertical columns.
(iv) Horizontal rows are called periods and there were 7 periods in Mendeleev's Periodic table.
JEEMAIN.GURU
(v) Vertical columns are called groups and there were 8 groups in Mendeleev's Periodic table.
(vi) Each group upto VIIth is divided into A & B subgroups.'A' sub groups element are called normal elements
and 'B' sub groups elements are called transition elements.
(vii) The VIIIth group was consists of 9 elements in three rows (Transitional metals group).
(viii) The elements belonging to same group exhibit similar properties.
(c) Merits or advantages of Mendeleef's periodic table :
(i) Study of elements : First time all known elements were classified in groups according to their similar
properties. So study of the properties of elements become easier .
(ii) Prediction of new elements : It gave encouragement to the discovery of new elements as some gaps
were left in it.
Sc (Scandium) Ga (Gallium) Ge (Germanium) Tc (Technetium)
These were the elements for whom position and properties were well defined by Mendeleev even before
their discoveries and he left the blank spaces for them in his table.
Ex. Blank space at atomic weight 72 in silicon group was called Eka silicon (means properties like
silicon) and element discovered later was named Germanium .
Correction of doubtful atomic weights : Correction were done in atomic weight of some elements.
Atomic weight = Valency × Equivalent weight.
Initially, it was found that equivalent weight of Be is 4.5 and it is trivalent (V = 3), so the weight of Be was
13.5 and there is no space in Mendeleev's table for this element. So, after correction, it was found that
Be is actually divalent (V = 2). So, the weight of Be became 2 × 4.5 = 9 and there was a space between
Li and B for this element in Mendeleev's table.
– Corrections were done in atomic weight of elements are – U, Be, In, Au, Pt.
(d) Defects of Mendeleef's Periodic Table:
(i) Position of hydrogen is uncertain. It has been placed in lA and VII A groups because of its resemblance
with both the groups.
(ii) No separate positions were given to isotopes.
(iii) It is not clear whether the lanthanides and actinides are related to IIA or IIB group.
(iv) Although there is no resemblance except valency of subgroups A and B, they have been put in the same
group.
(v) Order of increasing atomic weights is not strictly followed in the arrangement of elements in the periodic
table. For e.g. – Co (At. wt. 58.9) is placed before I (127) and Ar (39.9) before K (39).
MODERN PERIODIC TABLE (MODIFIED MENDELEEF PERIODIC TABLE) :
(a) It was proposed by Moseley.
(b) Modern periodic table is based on atomic number.
(c) Moseley did an experiment in which he bombarded high speed electron on different metal surfaces and
obtained X-rays.
He found out that Z where = frequency of X-rays, Z = atomic number.
(d) Modern periodic law : The physical & chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of
their atomic number.
Characteristics of modern periodic table
(a) 9 vertical columns called groups.
(b) I
st to VIII group + 0 group of inert gases.
(c) Inert gases were introduced in periodic table by Ramsay.
(d) 7 horizontal series called periods.
Important Points :
(a) 2nd period elements (Li, Be, B) Shows diagonal relationship with 3rd period elements (Mg, Al, Si) so (Li,
Be, B) are called Bridge elements. Because of same ionic potential value they shows similarity in properties.
(Ionic potential = Charge/Radius)
Li Be B
↘ ↘ ↘
Na Mg Al Si
(b) 3rd period elements (Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl) are called typical elements because they represent the
properties of other element of their respective group.
(c) Atomic number of last inert gas element is 86.
(d) Number of Gaseous elements – 11 (H, N, O, F, Cl + Noble gases)
Number of Liquid elements – 6 (Cs, Fr, Ga, Hg, Br, Uub)
Bromine is the only non-metal which exists in liquid form.
Number of Solid elements – 95 (if discovered elements are 112)
(e) 2nd period contains maximum number of gaseous elements. They are 4 (N, O, F, Ne)
NOMENCLATURE OF ELEMENTS WITH ATOMIC NUMBERS > 100
The roots are put together in order of digits, which make up the atomic number and “ium” is added at the end.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
nil un bi tri quad pent hex sept oct enn
- Notation (Roots) for IUPAC Nomenclature of Elements
Atomic No. IUPAC Name Symbol IUPAC Official Name
101 Un nil unium Unu Mendelevium 102 Un nil bium Unb Nobelium
103 Un nil trium Unt Lawrencium
104 Un nil quadium Unq Rutherfordium
105 Un nil pentium Unp Dubnium
106 Un nil hexium Unh Seaborgium
107 Un nil septium Uns Bohrium
108 Un nil octium Uno Hassnium
109 Un nil ennium Une Meitnerium
110 Un un nilium Uun Darmstadtium
CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
s-BLOCK ELEMENTS
(a) The elements of the periodic table in which the last electron enters in s-orbital, are called s-block elements.
(b) s-orbital can accommodate a maximum of two electrons.
(c) Their general formulae are ns1
and ns2
respectively, where n = (1 to 7)
(d) IA group elements are known as alkali metals because they react with water to form alkali. II A group
elements are known as alkaline earth metals because their oxides react with water to form alkali and
these are found in the soil or earth.
(e) Total number of s-block elements are 14.
(f) Fr57 and Ra88 are radioactive elements while H and He are gaseous elements.
(g) Cs and Fr are liquid elements belonging to s-block.
p-BLOCK ELEMENTS
The p-Block Elements comprise those belonging to Group 13 to 18
- s-Block & p-block Elements are called the Representative Elements or Main Group Elements.
- The outermost electronic configuration varies from ns2np1 to ns2np6 in each period. At the end of each period is a noble gas element with a closed valence shell ns2np6 configuration.
- All the orbitals in the valence shell of the noble gases are completely filled by electrons and it is very difficult to alter this stable arrangement by the addition or removal of electrons.
- The noble gases thus exhibit very low chemical reactivity.
- Preceding the noble gas family are two chemically important groups of non-metals. They are the halogens (Group 17) and the chalcogens (Group 16). These two groups of elements have highly negative electron gain enthalpies and readily add one or two electrons respectively to attain the stable noble gas configuration.
- The non-metallic character increases as we move from left to right across a period and metallic character increases as we go down the group.
d-Block ELEMENTS
These are the elements of Group 3 to 12
- These elements have the general outer electronic configuration (n-1)d1-10ns0-2 . They are all metals. They mostly form coloured ions, exhibit variable valence (oxidation states), paramagnetism & are used as catalyst.
- transition metals form a bridge between the chemically active metals of s-block elements and the less active elements of Groups 13 and 14 and thus take their name “Transition Elements”
f-Block ELEMENTS
The element of the periodic table in which the last electron gets filled up in the f-orbital, called f-block elements.
The f-block elements are from atomic number 58 to 71 and from 90 to 103.
The lanthanides occur in nature in low abundance and therefore, these are called rare earth elements.
There are 28 f-block elements in the periodic table.
The elements from atomic number 58 to 71 are called lanthanides because they come after lanthanum
(57). The elements from 90 to 103 are called actinides because they come after actinium (89).
All the actinide elements are radioactive.
All the elements after atomic number 92 (i.e. U92) are transuranic elements.
The general formula of these elements is (n–2) s2p6
d10 f(1-14) (n–1) s2 p6 d0-1 ns2
where n = 6 & 7.
|
22 videos|163 docs|17 tests
|















