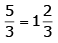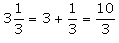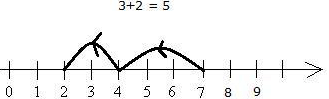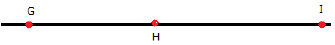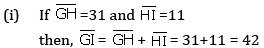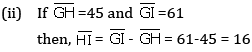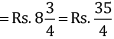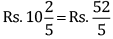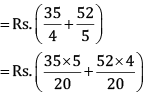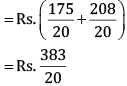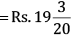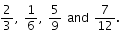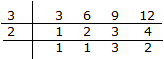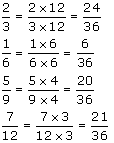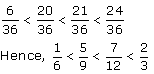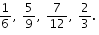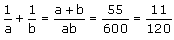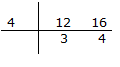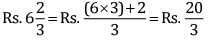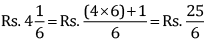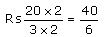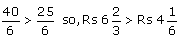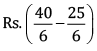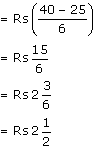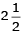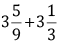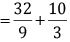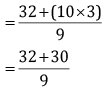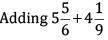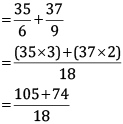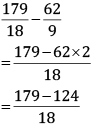Sample Paper 1 - Term 1 Mathematics, Class 6 | Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Section A
(Questions 1 to 12 carry 1 mark each)
Q 1. Which of the following statements is shown by the given number line?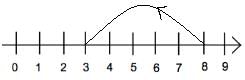 (a) 8 – 5 = 3
(a) 8 – 5 = 3
(b) 8 + 5 = 13
(c) 3 – 8 = –5
(d) 8 + 3 = 11
Correct Answer is Option (a)
On the given number line, from 8, five steps are moved towards the left.
Thus, the number line represents 8 - 5 = 3.
Q 2. 12 × (45 + 30) =
(a) (12 × 45) + (12 × 30)
(b) 12 × 65
(c) 12 × 45 × 30
(d) (12 × 45) × (12 × 30)
Correct Answer is Option (a)
According to distributive law of multiplication over addition, we have:
12 × (45 + 30) = (12 × 45) + (12 × 30)
Q 3. The sum of 267 + 132 to nearest ten is
(a) 500
(b) 400
(c) 300
(d) 200
Correct Answer is Option (b)
267 can be estimated as 270.
132 can be estimated as 130.
Thus the required estimated sum = 270 + 130 = 400
Q 4. The greatest number that will divide 10 and 18 is
(a) 4
(b) 2
(c) 5
(d) 3
Correct Answer is Option (b)
We have 10 = 2 × 5
18 = 2 × 3 × 3
HCF of 10 and 18 is 2.
Thus, 2 is the required number.
Q 5. Mixed fraction for 5/3 is
(a) 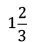
(b) 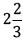
(c) 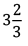
(d) 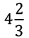
Correct Answer is Option (a)
To convert into mixed fraction first divide numerator by denominator. The quotient is taken as the whole number part of mixed fraction. Remainder obtained is taken as the numerator and divisor as the denominator of the fractional part of the mixed fraction.
Therefore,
Q 6. What does the shaded region in the following figure represent?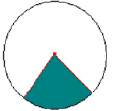 (a) Segment of a circle
(a) Segment of a circle
(b) Radius of a circle
(c) Chord of a circle
(d) Sector of a circle
Correct Answer is Option (d)
A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by an arc on one side and a pair of radii on the other two sides is called a sector of the circle.
Q 7. How many thousands make a crore?
(a) 10
(b) 100
(c) 1000
(d) 10000
Correct Answer is Option (d)
One crore can be written as 1,00,00,000.
One thousand can be written as 1000.
So, 10000 times one thousand would make one crore.
Q 8. How many whole numbers are there up to 1000?
(a) 1001
(b) 1000
(c) 100
(d) 999
Correct Answer is Option (a)
There are 1000 + 1 = 1001 whole numbers upto 1000.
i.e., 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, ........., 1000
Q 9. (–42) + (–35) =
(a) –7
(b) 7
(c) –77
(d) 41
Correct Answer is Option (c)
(–42) + (–35) = –42 – 35 = –77
Q 10. Which is the fifth multiple of 18?
(a) 80
(b) 90
(c) 72
(d) 180
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Fifth multiple of 18 = 18 × 5 = 90
Q 11. The improper fraction for 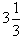 is________
is________
(a) 10/3
(b) 3/10
(c) 1/3
(d) 3/1
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Q 12. The English alphabet Z represents a/an ______ curve.
(a) Closed
(b) Open
(c) Polygon
(d) Triangle
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The English alphabet Z represents an open curve.
Section B
Q 13. Evaluate the difference between the place values of two 9's in the number 79520986.
Place value of 9 at the Ten Lakhs place = 9000000
Place value of 9 at the hundreds place = 900
Difference = 9000000 – 900 = 8999100
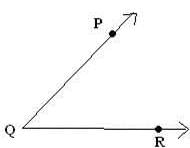
Q 14. Name all the radii drawn in the given figure.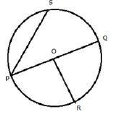
Radius of a circle is a line joining the center of circle to any point on the circle. So, the radii drawn in the given figure are OP, OQ and OR.
Q 15. How many vertices do the following shapes have?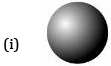
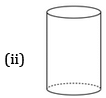
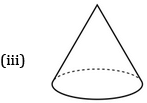
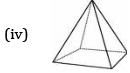
The number of vertices in the given shapes:
(i) Sphere: 0
(ii) Cylinder: 0
(iii) Cone: 1
(iv) Pyramid: 5
Q 16. Anna is standing on a rock that is 7 feet above sea level. She jumps off the rock and hits another rock 3 feet below and then walks 2 feet down. How many feet did she come down in all?
Anna is 7 feet above sea level.
She jumps 3 feet down and walks another 2 feet down. Total distance travelled downwards = 3 + 2 = 5 feet.
Q 17. Find the sum: (–13) + (–19) + (+15) + (–10).
(–13) + (–19) + (+15) + (–10)
= –13 – 19 + 15 – 10
= –13 – 19 – 10 + 15
= –42 + 15
= –27
Q 18. Write a 9 digit number in Indian system (in Numerals) and then write it in words according to International system.
A 9-digit numeral in Indian system = 94,50,27,983
In International system:
945,027,983: Nine hundred forty five million twenty seven thousand nine hundred eighty three.
Q 19. There is a line on which the points G, H and I lie such that H is in between G and I.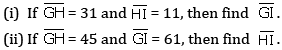
Q 20. Use divisibility test to determine whether the number 1258 is divisible by 6.
Given number is 1258.
Its unit digit is 8, which is divisible by 2. So, 1258 is divisible by 2.
Sum of its digits = 1 + 2 + 5 + 8 = 16, which is not divisible by 3.
So, 1258 is not divisible by 3.
Since, 1258 is divisible by 2 but not by 3, it is not divisible by 6.
Q 21. Subtract 3 from 8 using a number line.
Starting from zero, a jump of 8 units is made to the right to reach 8. Then, 3 jumps (each of 1 unit i.e. from 8 to 7, 7 to 6, 6 to 5) are taken to the left to reach 5.
So, we conclude that 8 – 3 = 5
Q 22. Fill in the blanks with appropriate symbols ‘>" or ‘<".
(i) –9 ___ -15
(ii) –10 ___ 10
(iii) 0 ___ 3
(iv) –28 ____ 17
(i) –9 > –15
(ii) –10 < 10
(iii) 0 < 3
(iv) –28 < 17
Q 23. In the following triangle, find the measure of ∠X.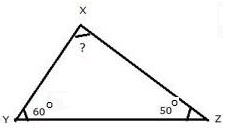
Since the sum of all three angles of a triangle is 180o.
We have, ∠X + ∠Y + ∠Z = 180o
Or, ∠X + 60o + 50o = 180o
Or, ∠X + 110o = 180o
Or, ∠X = 180o – 110o
Hence, ∠X = 70o
Q 24. Complete the following patterns by using the distributive property of multiplication over addition for whole numbers:
101 × 33 = 3333
101 × 333 = 33633
101 × 3333 = ?
101 × 33333 = ?
Using distributive property of multiplication over addition, we have:
101 × 33 = (100 + 1) × 33 = 3300 + 33 = 3333
101 × 333 = (100 + 1) × 333 = 33300 + 333 = 33633
101 × 3333 = (100 + 1) × 3333 = 333300 + 3333 = 336633
101 × 33333 = (100 + 1) × 33333 = 3333300 + 33333 = 3366633
Section C
(Questions 25 to 32 carry 3 marks each)
Q 25. Tanvi bought a notebook for Rs 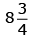 and a pen for Rs
and a pen for Rs 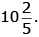 How much money should she pay to the shopkeeper?
How much money should she pay to the shopkeeper?
Cost of notebook
Cost of pen
LCM of 4 and 5 = (2 × 2 × 5) = 20
Total cost of both the items
Q 26. Arrange the fractions 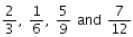 in ascending order.
in ascending order.
The given fractions are
LCM of 3, 6, 9, 12 = (3 x 2 x 3 x 2) = 36
So, we convert each one of given fractions into an equivalent fraction having 36 as denominator.
Now,
Clearly,
The given fractions in ascending order are
Q 27. The sum of two numbers is 55 and the H.C.F. and L.C.M. of these numbers are 5 and 120 respectively. Find the sum of the reciprocals of the numbers.
Let the numbers be a and b.
Then, a + b = 55 and ab = 5 × 120 = 600
Therefore, the required sum =
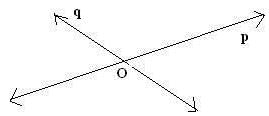
Q 28. Answer the following questions for the given figure.
(a) What are lines p, q, and r called?
(b) What is the point at which they meet called? Label it on the figure.
(c) How many lines can pass through the labeled point?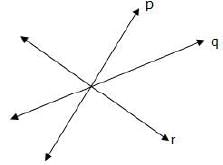
(a) Lines p, q and r are intersecting lines.
(b) Point at which the lines meet is called the point of intersection. The point O represents the point of intersection.(c) Infinite number of lines can pass through the point O (point of intersection).
Q 29. Compare the fractions 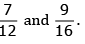
LCM of 12 and 16 = (4 × 3 × 4) = 48
So, we convert each one ofinto an equivalent fraction having 48 as denominator.
Q 30. Each corner of a cube is cut off, leaving a triangular face at each corner and an octagonal face in place of each face of the original cube. How many vertices and faces will the new polyhedron have?
Each of the 8 vertices of the cube has now been replaced by three vertices of a triangle. So, there are now 24 vertices. The cube had 6 square faces. Now those faces are still there but have become octagons. Additionally, there are now 8 new triangular faces. So, there is a total of 14 faces.
Q 31. Solve (–8 + 12 – 2) using number line.
To solve using number line start with -8, move 12 steps right and then back 2 steps as shown below:
So, we reach at 2, therefore (-8 + 12 - 2) = 2
Q 32. Shweta has made a chart on ‘Elementary Shapes’. She develops a pattern for the border using sticks as follows: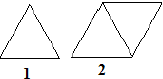
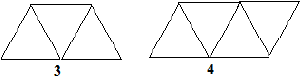 Find a rule that helps her find the number of sticks.
Find a rule that helps her find the number of sticks.
Let the number of triangles be n.
For 1 triangle: Number of sticks = 2 × 1 + 1 = 3 sticks
For 2 triangles: Number of sticks = 2 × 2 + 1 = 5 sticks
∴ Number of sticks used = 2 × n + 1
Section D
(Questions 33 to 37 carry 4 marks each)
Q 33. The cost of a pen is Rs. 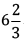 and that of a pencil is Rs.
and that of a pencil is Rs. 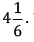 Which costs more and by how much?
Which costs more and by how much?
Cost of a pen =
Cost of a pencil =
Now, converting to like fractions
Clearly,
Hence, the cost of pen is more than the cost of pencil.
Difference between their cost =
Hence, the cost of pen is more than cost of pencil by Rs.
Q 34. Name the type of the triangle:
(i) ΔLMN with ∠L = 30°, ∠M = 70° and ∠N= 80°.
(ii) ΔDEF with ∠D= 90°.
(iii) ΔPQR such that PQ = QR = PR = 5 cm.
(iv) ΔXYZ with ∠Y= 90° and XY = YZ.
(i) Scalene triangle. Because none of the angles are equal, none of the sides will also be equal. Hence, it is a scalene triangle.
(ii) Right-angled triangle. Because the given angle is 90°, it is a right-angled triangle.
(iii) Equilateral triangle. Because all the sides of the given triangle are equal, it is an equilateral triangle.
(iv) Isosceles right-angled triangle. Since two sides are equal (XY = YZ) and one angle is 90°, it is an isosceles right-angled triangle.
Q 35. Simplify: 16 – [5 – 2 + {7 of 2 – (6 ÷ 3 × 2 – 1 + 3)}]
16 – [5 – 2 + {7 of 2 - (2 × 2 – 1 + 3)}]
= 16 – [5 – 2 + {7 of 2 - (4 – 1 + 3)}]
= 16 – [5 – 2 + {7 of 2 - 6}
= 16 – [5 – 2 + {8}]
= 16 – 11
= 5
Q 36. Draw a rough figure and label the following statements:
(a) Line l contains point A but not B
(b) Lines p and q intersect at point o
(c) Rays PQ and QR meet to form angle PQR
a. Line l contains point A but not B
b. Lines p and q intersect at point O
c. Rays PQ and QR meet to form angle PQR
Q 37. Subtract the sum of 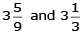 from the sum of
from the sum of 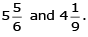
Adding
LCM of 3, 9 = 9
= 62/9
We also have
LCM of 6, 9 = (2 × 3 × 3) = 18
= 179/18
Thus,
= 55/18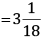
|
297 videos|1066 docs|204 tests
|
FAQs on Sample Paper 1 - Term 1 Mathematics, Class 6 - Class 6 All Subjects (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is the importance of Section A in the Term 1 Mathematics exam for Class 6? |  |
| 2. How many questions are usually included in Section B of the Term 1 Mathematics exam for Class 6? |  |
| 3. What kind of questions can be expected in Section C of the Term 1 Mathematics exam for Class 6? |  |
| 4. How can students prepare for Section D of the Term 1 Mathematics exam for Class 6? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific topics that students should pay extra attention to in the Term 1 Mathematics exam for Class 6? |  |