Sample Paper 1 with Solution - Chemistry, Class 11 | Sample Papers for Class 11 Medical and Non-Medical - JEE PDF Download
Section A
Ques 1: Explain why o- nitrophenol has a lower boiling point than p – nitrophenol? [1]
OR
Which of the two -O2NCH2CH2O- or CH3CH2O- is expected to be more stable and why?
Ans: This is because o – nitro phenol has intramolecular hydrogen bonding whereas p- nitro phenol has intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
OR
O2NCH2CH2O- will be more stable because -NO2 group has electron withdrawing inductive effect or – I effect.
Ques 2: Out of CO2 and BF3 , which one of them will have a larger bond angle and why? [1]
OR
Why N2 is more stable than O2? Explain on the basis of molecular orbital theory.
Ans: CO2 has a larger bond angle than BF3 . This is because CO2 has a linear shape and the bond angle is 180o, BF3 on the other hand has a trigonal planar geometry and hence the bond angle is 120o.
OR
Bond order of N2 is greater than that of O2. Higher is the bond order greater is the stability. Therefore N2 is more stable than O2.
Ques 3: Is the eclipsed conformation of propane has the same or different energy as the eclipsed conformation of ethane? [1]
Ans: The eclipsed conformation of propane is less stable and has more energy than the eclipsed conformation of ethane. This is because in propane there are additional interactions between C-H and C-C bond of methyl group.
Ques 4: Due to which compound, ozone depletion is caused in Antarctica? [1]
Ans: In Antarctica, ozone depletion is due to the formation of chlorine nitrate.
Ques 5: Why are alkali metals used in photoelectric cells? [1]
Ans: Alkali metals have low ionization energies. They can lose electrons when light falls on them, and hence are used in photo electric cells.
Section B
Ques 6: Which of the following statements related to the modern periodic table is incorrect and why? [2]
(a) Each block contains a number of columns equal to the number of electrons that can occupy that sub shell.
(b) The d - block has 8 columns, because a maximum 8 electrons can occupy all the orbitals in d - sub shell.
Ans: Statement ‘a’ is correct and b is incorrect.
Statement ‘b’ is incorrect because d sub shell can have a maximum of 10 electrons. Therefore it has 10 columns and not 8.
Ques 7: All transition metals are d-block elements but all d-block elements are not transition metals. Explain. [2]
Ans: Elements in which transition of electrons to higher energy d-orbital cannot take place are not transition elements. Thus, elements like Zn, Cd and Hg in which all the d-orbitals are completely filled are not transition elements although they have been grouped with d-block.
Ques 8: One of the spectral line of the caesium has a wavelength of 456 nm. Calculate the frequency of this line. [2]
Ans: Given:
λ = 456 nm
= 456 * 10-9 m
c = 3 * 108m/s
Wehave,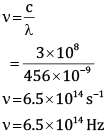
Frequency is 6.5×1014 Hz
Ques 9: PbO and PbO2 react with HCl according to the following reactions: [2]
2PbO + 4HCl → 2PbCl2 + 2H2O
PbO2 + 4HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Why do these compounds differ in their reactivity?
Ans: Oxidation number of Pb in PbO is +2 while in PbO2 it is +4. This causes the compounds to differ in their reactivity. While PbO reacts with HCl to give acid-base reaction, and PbO2 reacts with HCl to give redox reaction.
2PbO + 4HCl → 2PbCl2 + 2H2O (acid-base reaction)
PbO2 + 4HCl → PbCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O (redox reaction)
Ques 10: Consider the reaction of water with F2 and suggest, in terms of oxidation and reduction, which species are oxidized/ reduced. [2]
OR
Complete the following reactions: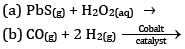
Ans: 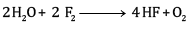
F2 is the oxidizing agent and H2O is reducing agent.
H2O is getting oxidized to O2 whereas F2 is getting reduced to F- ion.
OR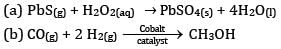
Ques 11: Why do magnesium and beryllium not impart colour to the flame in the flame test? [2]
Ans: The energy required to excite outer electrons in the atoms of Be and Mg does not lie in the visible range of radiation. Therefore, no absorption of radiation takes place and hence no colour is imparted to the flame in the flame test.
Ques 12: Calculate the mass percent of different elements in sodium sulphate,(Na2SO4) [2]
OR
How much copper can be obtained from 100 g of copper sulphate (CuSO4)? (Atomic mass of Cu – 63.5 amu)
Ans: Mass % of an element 
Molar mass of Na2So4= 2 (23) + 32 + 4(16)
= 142 g\mol
Mass % of Na = 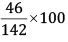
= 32.39%
Mass % of S = 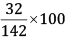
= 22.54%
Mass % of O = 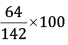
= 45.07%
OR
Given:
Weight of CuSO4 =100 g
Atomic mass of Cu – 63.5 amu
1 mole of CuSO4 contains 1 mole of Cu
Molar mass of CuSO4 = 63.5 + 32+ (4×16)
= 159.5 g/mol
So, Cu that can be obtained from 159.5 g of CuSO4 = 63.5 g
Therefore, Cu that can be obtained from 100 g of CuSO4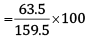
= 39.81g
Section C
Ques 13: (a) The 4f sub shell of an atom contains 12 electrons. What is the maximum number of electrons having the same spin in it?
(b) Explain the meaning of 4p6.
(c) Write the electronic configuration of the atom with atomic number 29
OR
(a) Calculate the total number of electrons present in one mole of methane.
(b) An atomic orbital has n = 3. What are the possible values of l and ml?
Ans: (a) The 4f sub shell of an atom contains 12 electrons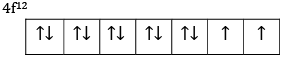
So maximum 7 electrons will have same spin.
(b) Six electrons are filled in three orbitals of 4p subshell.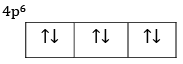
(c) Z =29
Electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 3d10 4s1
OR
(a) Number of electrons in 1 molecule of methane = 6 + 4 =10 electrons
Number of molecules in 1 mole of methane = 6.022 × 1023 molecules of methane
Number of electrons in 1 mole of methane
= 6.022×1023x10
= 6.022×1024 electrons
(b) n = 3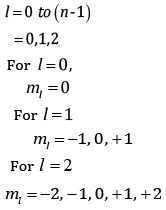
Ques 14: Explain the hybridisation of SF4 ? [3]
OR
(a) Although both CO2 and H2O are triatomic molecules, the shape of H2O molecule is bent while that of CO2 is linear. Explain on the basis of dipole moment.
(b) Write the significance of dipole moment.
Ans: The electronic configuration of S=1s22s22p63s23p4
Ground state 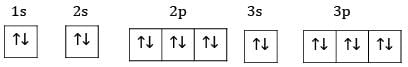
Excited State
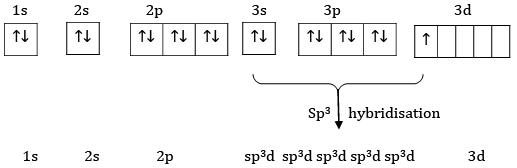
Hybridise State 
Sulphur undergoes sp3d hybridisation.
OR
(a) In CO2 there are two C=O bond. Each C=O bond is polar bond. The net dipole moment of CO2 molecule is zero. This is possible only if CO2 is a linear molecule (O=C=O). The bond dipoles of two C=O bond cancel with each other.
Whereas H2O molecule has a net dipole moment (1.84 D) H2O molecule has a bent structure because here the O-H bonds are oriented at an angle of 104.5° and do not cancel the bond moments of each other.
(b) Significance/applications of dipole moment-
i) In predicting the nature of the molecules: Molecules with specific dipole moments are polar in nature and those of zero dipole moments are non-polar in nature.
ii) In the determination of shapes of molecules.
iii) In calculating the percentage ionic character.
Ques 15: The drain cleaner contains small bits of aluminium which react with caustic soda to produce dihydrogen gas. What volume of dihydrogen at 20°C and one bar pressure will be released when 0.15 g of aluminium reacts. [3]
Ans: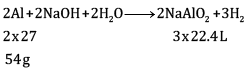
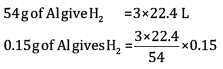
= 0.1867 L
=186.7ml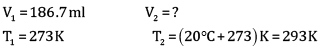
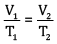
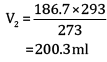
Volume of dihydrogen is 200.3 ml
Ques 16: (a) What is spontaneous process? [3]
(b) Predict in which of the following, entropy increases/decreases.
i) A liquid crystallises into a solid.
ii) Temperature of crystallise solid is raised from 0 K to 115 K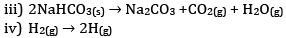
Ans: (a) A process is said to be spontaneous if it takes place by itself by own or under some condition.
(b) i) After freezing, the molecules attain an ordered state and therefore, entropy decreases.
ii) At 0 K the constituent particles are in static form therefore entropy is minimum. If the temperature is raised to 115 K particles begin to move and entropy increases.
iii) Reactant NaHCO3 is solid. Thus entropy is less in comparison to product which has high entropy.
Ques 17: (a) Write the expression for equilibrium constant for the reaction: [3]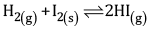
(b) Calculate the pH of a buffer solution containing 0.2 mole of NH4Cl and 0.1 mole of NH4OH per litre. (Given Kb for NH4OH = 1.85 X 10-5)
OR
Consider the reaction: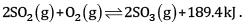
Indicate the direction in which the equilibrium with shift when:
(a) Temperature is increased
(b) Pressure is increased
(c) Concentration of SO2 is increase
Ans: (a)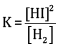
(b) According to Henderson’s equation,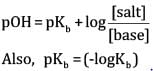
= ( - log1.85 x 10-5)
= 4.733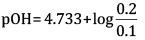
= 4.733 +0.3010
=5.034
pH =14- pOH
= 14 -5.034
=8.966
OR
(a) The equilibrium will shift the backward direction as the increase in temperature will be compensated by absorbing heat. It is an exothermic reaction.
(b) The equilibrium will shift in the forward direction since the reaction will shift to the direction of lesser number of moles.
(c) The equilibrium will shift in the forward direction so that additional SO2 is used up.
Ques 18: Balance P + HNO3 → H3 PO4 + NO2 + H2O by oxidation number method. [3]
OR
Write the half reactions for each of the following redox reactions: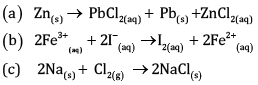
Ans:
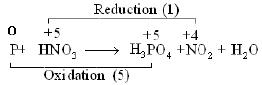
Oxygen and Hydrogen atoms are balanced.
OR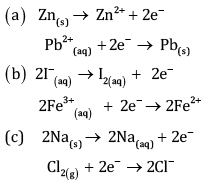
Ques 19: What do you understand by the term ‘non-stoichiometric hydrides? Do you expect this this type of hydrides to be formed by alkali metals? Justify. [3]
Ans: Those hydrides which do not have fix composition are called non-stoichiometric hydride, and the composition varies with temperature and pressure.
This type of hydrides are formed by d and f block elements. They cannot be formed by alkali metals because alkali metal hydrides form ionic hydrides.
Ques 20:
(A) 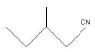
(B) 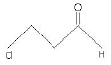
(C) 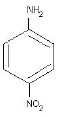
Ans: (a) 3 – Methylpentanenitrile
(b) 3-Chloropropanal
(c) 4- Nitroaniline
Ques 21: (a) Arrange the following carbanions in the increasing order of their stability (3)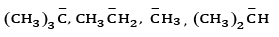
(b) What is the hybridisation of the negatively charged carbon atom in a carbanion?
Ans: (a) Order of stability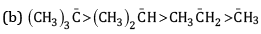
This is because -CH3 group has electron releasing inductive effect or +I effect. Due to this, electron density increases on the negatively charged carbon and hence makes it more unstable. As the number of methyl groups increases the instability increases.
(c) The negatively charged carbon atom in a carbanion is sp3 hybridized.
Ques 22: Explain.[3]
(a) Alkali metals are prepared by electrolysis of their fused chlorides.
(b) Why are lithium salts commonly hydrated and those of other alkali metal ions usually anhydrous?
Ans: (a) Because the discharge potential of alkali metals is much higher than that of hydrogen, therefore when aqueous solution of any alkali metal chloride is subjected to electrolysis H2 instead of alkali metal is produced at cathode. Therefore alkali metals are prepared by electrolysis of their fused chlorides.
(b) Due to smallest size of Li2+ can polarise water molecules easily than the other alkali metal ions.
Ques 23: Calculate the molarity of a solution of ethanol in water in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.040. [3]
Ans: Given:
Mole fraction of C2H5OH = 0.040
We know,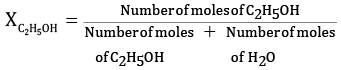
Let the molesof C2H5OH=x
Density of water is 1
Weight of 1000 ml of water = volume*density
= 1000 x 1 ml
Molar massof water = 18g/mol
No.of moles of water = 1000/18
= 55.55 mol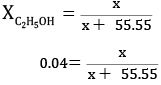
x = 0.04x + 2.22
x = 2.31 mol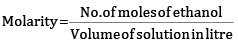
Molarity = 2.31 M
Molarity of solution is 2.31 M
Ques 24: Complete the following chemical equations: [3]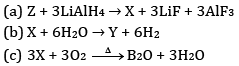
Ans: 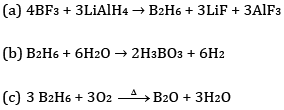
Section D
Ques 25: For the reaction (5)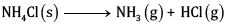
At 25°C, enthalpy change, Δ H = + 177 kJ mol-1
Entropy change ΔS=+285J K-1 mol-1 .
Calculate free energy change ΔG at 25oC and predict whether the reaction is spontaneous or not.
OR
Calculate the enthalpy of formation of benzene, using the following data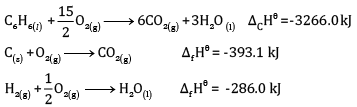
Ans: 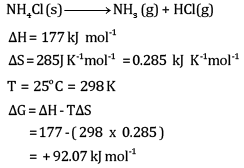
The reaction will be non-spontaneous.
This is because the value of ΔG is positive.
OR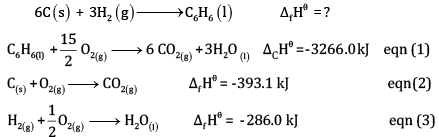
Multiplying equation (2) by 6 and (3) by 3, and adding,
(1 x 3)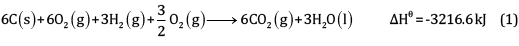
Subtracting eqn (4) – eqn (1)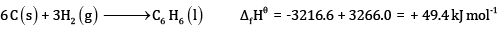
Ques 26: Explain giving reasons for the following: [5]
(a) Boron does not form B3+ ions.
(b) Molten aluminium bromide is a poor conductor of electricity.
(c) BCl3 is more stable than TlCl3.
(d) B-Cl bond has a dipole moment but BCl3 has zero dipole moment.
(e) Al is used to make transmission cables.
OR
Explain the following reactions:
(a) Silicon is heated with methyl chloride at high temperature in the presence of copper powder
(b) CO is heated with ZnO
(c) Reaction of boron trifluoride with LiAlH4 in diethyl ether
(d) Reaction of boron trifluoride with sodium hydride at 450 K
(e) Reaction of diborane and water
Ans: (a) Boron has a very small size and has a very high sum of three ionisation enthalpies (IE1+ IE2+ IE3). Therefore, it cannot lose its three electrons to form B3+ ions.
(b) AlBr3 is predominantly a covalent compound. Even in molten state it does not have ions which can conduct electricity.
(c) B exhibits +3 oxidation state and can form stable BCl3. Thallium shows +3 oxidation state as well as +1 oxidation state but +1 oxidation state is more predominant than +3 oxidation state because of inert pair effect. Therefore, TiCl3 is not stable. It can form stable TiCl.
(d) BCl3 molecule has a symmetrical trigonal planar structure in which three B-Cl bonds are oriented at an angle of 120° to one another. The three bonds lie in one plane and the dipole moments of these bonds cancel one another giving net dipole moment zero.
(e) Electrical conductivity of aluminium is twice as that of copper. On mass to mass basis, Al conducts electricity twice as Cu. Therefore, it is used in transmission cables.
OR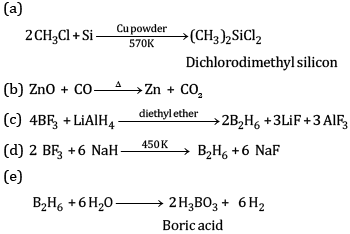
Ques 27: (a) Compound ‘A’ with the molecular formula C6H8 reacts with hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar’s catalyst to form a compound B with the molecular formula C5H10. A on reacting with sodium in liquid ammonia forms a compound ‘C’ with the same molecular formula as that of B. Identify ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’. Give the chemical reactions involved.
(b) Write the chemical reaction involved in Kolbe’s electrolytic process.
What are the products formed at cathode and anode?
or
(a) Complete the reactions and identify A, B and C. 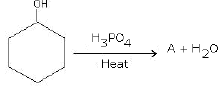
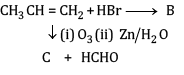
(b)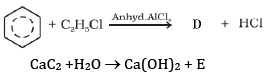
Ans: (a) Compound A is H3 C - C ≡ C - C2H5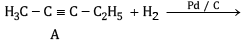
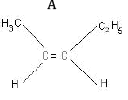
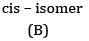
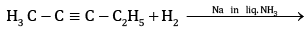
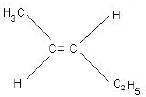
(b) Kolbe’s electrolytic method –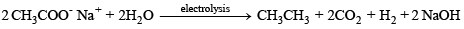
Mechanism: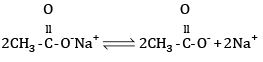
At anode: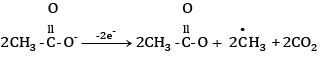
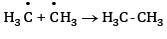
At cathode: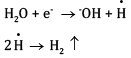
At cathode hydrogen is liberated. At anode ethane is formed.
OR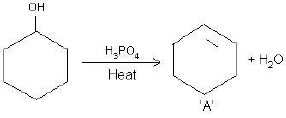
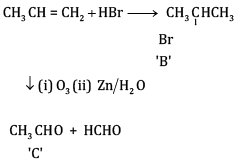
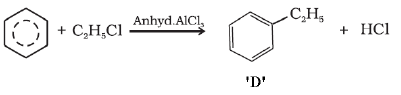
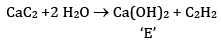
FAQs on Sample Paper 1 with Solution - Chemistry, Class 11 - Sample Papers for Class 11 Medical and Non-Medical - JEE
| 1. What is the importance of Chemistry in Class 11? |  |
| 2. What are the topics covered in Class 11 Chemistry? |  |
| 3. How can I improve my understanding of Chemistry in Class 11? |  |
| 4. What are the practical aspects of studying Chemistry in Class 11? |  |
| 5. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 11 Chemistry exam? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















