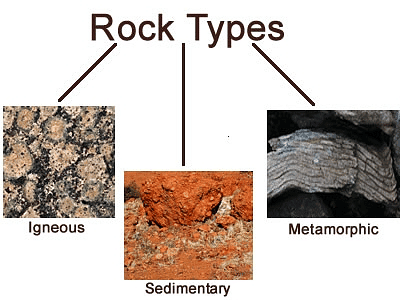
Class 5 Science - Rocks and Minerals - Question Answers
Q1: Name the three types of rocks with one example each.
Ans: The three types of rocks are:
- Igneous rock: Igneous rocks solidify from molten rock. Example: Pumice
- Sedimentary rock: Sedimentary rocks are layered. Example: Shale
- Metamorphic rock: Metamorphic rocks form when sedimentary, igneous, or pre-existing metamorphic rocks are changed by environmental factors. Example: Marble

Q2: What are metamorphic rocks? How are they formed?
Ans: Rocks that have changed their form over time are called metamorphic rocks. They are formed due to physical and chemical changes in igneous, sedimentary, or older metamorphic rocks themselves due to heat and pressure.
Q3: What are minerals? Give any three examples of minerals.
Ans: All rocks are made up of substances called minerals. Minerals are chemical substances that occur in nature. Eg: gold, silver and iron.
Q4: Name the different types of igneous rocks. Describe any two.
Ans: The different types of igneous rocks are:
- Granite
- Obsidian
- Pumice
Obsidian:
- It is smooth and glassy and is formed by quick cooling of lava.
- It is used in making jewellery and ornaments.
- It is usually black or dark coloured.
Pumice:
- It is porous, or full of holes is formed from lava that is frothy with a lot of air within it.
- It is the only rock that can float.
- It is used in making light weight materials like concrete blocks.
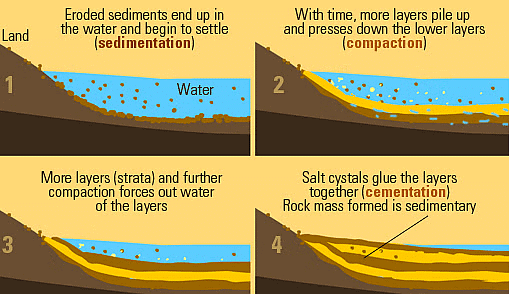
Q5: How are sedimentary rocks formed? Name the different types of sedimentary rocks. Describe any one.
Ans: Water, wind, rain, and snow break away big rocks. The rock particles so formed are carried away by wind and flowing water into rivers, lakes, and seas. These rock particles settle at the bottom of the water bodies and form layers. The layers are cemented together by minerals. Repeated deposition of layers presses down the lower layers and then turns them into rocks. Such rocks are called sedimentary rocks.
Types of Sedimentary Rocks
(i) Sandstone: It is a soft stone made from particles of sand that get cemented together. The most common mineral found in sandstone is quartz. This rock is used in construction. The Red Fort in Delhi and Agra Fort in Agra are made of red sandstone.
(ii) Dolomite:It is made up of limestone and magnesium. It resembles limestone.
(iii) Shale: It is made from clay particles cemented together. It is used to make bricks and tiles.
(iv) Limestone: It contains the mineral calcium and shells of sea creatures. It is used to make cement, lime, glass, and bricks. Chalk is a form of limestone.
Q6: What are the different types of metamorphic rocks? Describe any two.
Ans: The different types of metamorphic rocks are:
- Marble
- Slate
- Gneiss
- Quartzite
(i) Marble: It is formed from limestone, a sedimentary rock. It is used for making statues, floors, and slabs.
(ii) Slate:It is formed from shale, a sedimentary rock. Both shale and slate can split into thin layers. It is used for making blackboards and handheld writing boards (slates).
(iii) Gneiss: It is formed from granite. It has light and dark bands. It is used in construction.
(iv) Quartzite: It is formed from sandstone. It is a very hard rock and it is used for making glass and jewellery.
Q7: Describe the various uses of rocks and minerals.
Ans:
Uses of rocks are:
- Rocks are used as building material for making schools, houses, roads and bridges. Some rocks are used in their original form while some are used to make bricks, cement, tar and concrete. For eg: granite, limestone, sandstone and marble.
- Rocks give us useful metals for eg meals like iron, copper and aluminium are used for making utensils and precious metals like gold, platinum are used for making jewellery.
- Rocks give us fuel for eg: coal is used for producing electricity, heating and moving nuclear energy.
- Rocks are used as gemstones for eg: diamond, ruby, sapphire and emerald are used for making jewellery because when they are polished they appear shiny and beautiful.
Uses of minerals:
- Minerals like Sulphates and Nitrates are used as fertilizers because they help the plant to grow.
- Minerals are a very important part of our diet. For eg: minerals like calcium, sodium and iron are required for the healthy functioning of our body.
Q8: Continuous heating and cooling breaks even a hard rock into small pieces of sand. What should we learn from this process?
Ans: Continuous heating and cooling can break a hard rock into tiny pieces like sand. This teaches us that small changes over time can have big effects. Just like rocks, being patient and adaptable helps us handle challenges in life.
Q9: How does heat and pressure of earth contribute to the formation of metamorphic rocks?
Ans: Heat and pressure of the earth can change the physical or chemical composition of igneous or sedimentary rocks and leads to the formation of metamorphic rocks.
Q10: Can we find fossils in the granite or marble mines? Why?
Ans: We can find fossils in the granite or marble mines because it is formed from sedimentary rocks which can have fossils in them during their formation.
Q11: What is the difference between magma and lava.
Ans: The difference between magma and lava is:
- Magma: Molten rock inside the earth is called magma.
- Lava: Molten magma that flows out onto the surface of the earth is called lava.
Q12: Name the important minerals that are found in igneous rocks.
Ans: The important minerals that are found in igneous rocks are:
- Mica
- Feldspar
- Magnesium
Q13: What are minerals and how are they classified?
Ans: Minerals are natural substances found on Earth and are the basic components that make up rocks. They are classified into two types: metallic and non-metallic.
Q14: What are metallic minerals and where are they typically found?
Ans: Metallic minerals include metals like gold, iron, aluminium, and copper, referred to as ores. They are typically found in igneous rocks and are known for being hard with a natural shine.
Q15: Describe non-metallic minerals and give some examples.
Ans: Non-metallic minerals are usually found in sedimentary rocks and are typically soft without a shiny appearance. Examples include graphite, mica, asbestos, and precious stones like diamonds and rubies.
Q16: What are fossil fuels and why are they important?
Ans: Fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum, are valuable natural resources found underground. They serve as primary energy sources and are crucial due to the increasing energy demands since the country's development.
Q17: How is coal formed and where are major coal mines located in India?
Ans: Coal is formed from the remains of dead plants in swampy areas, transformed under high pressure and temperature over millions of years. Major coal mines in India are located in Suhagpur, Raniganj, Dhanbad, Neyveli, and Singareni.
Q18: What is petroleum and how is it extracted?
Ans: Petroleum is a thick, black liquid found beneath the Earth, formed from the remains of sea plants and animals. It is extracted by drilling holes into the Earth’s crust and pumping it out through pipes in oil wells.
Q19: Why is it important to conserve coal and petroleum?
Ans: Coal and petroleum are limited resources, and excessive use can lead to depletion. Additionally, their combustion releases harmful pollutants, which can cause health issues and environmental damage.
Q20: What is the difference between coal and petroleum in terms of their formation and uses?
Ans:Coal and petroleum are both fossil fuels, but they differ significantly in their formation and uses. Coal is a solid fossil fuel formed mainly from the remains of plants that accumulated on the forest floor and underwent compression over millions of years, primarily found in swampy areas. It is used for generating electricity, in the production of steel, and in various industrial processes.
Petroleum, on the other hand, is a liquid fossil fuel formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms. The transformation process involved heat and pressure beneath the Earth's surface over millions of years. Petroleum is extracted through drilling and is primarily used as fuel in the form of petrol, diesel, and kerosene. It is also a key raw material in the chemical industry, used to produce plastics, synthetic fibers, and a wide range of chemicals.
|
42 videos|202 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Class 5 Science - Rocks and Minerals - Question Answers
| 1. What are the main types of rocks? |  |
| 2. How are minerals different from rocks? |  |
| 3. What are some common uses of rocks and minerals? |  |
| 4. How do we identify different minerals? |  |
| 5. Why are rocks and minerals important to our environment? |  |